Cross-reactivity of autoantibodies from patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with murine collagen VII
- PMID: 20084423
- PMCID: PMC11115820
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0256-3
Cross-reactivity of autoantibodies from patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with murine collagen VII
Abstract
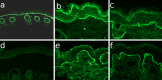
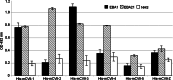
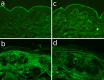
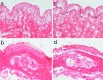
The pathomechanism of antibody-mediated tissue damage in autoimmune diseases can be best studied in experimental models by passively transferring specific autoantibodies into animals. The reproduction of the disease in animals depends on several factors, including the cross-reactivity of patient autoantibodies with the animal tissue. Here, we show that autoantibodies from patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA), a subepidermal autoimmune blistering disease, recognize multiple epitopes on murine collagen VII. Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that EBA patients' IgG cross-reacts with mouse skin. Overlapping, recombinant fragments of murine collagen VII were used to characterize the reactivity of EBA sera and to map the epitopes on the murine antigen by ELISA and immunoblotting. The patients' autoantibody binding to murine collagen VII triggered pathogenic events as demonstrated by a complement fixing and an ex vivo granulocyte-dependent dermal-epidermal separation assay. These findings should greatly facilitate the development of improved disease models and novel therapeutic strategies.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Z, Diaz LA, Troy JL, Taylor AF, Emery DJ, Fairley JA, Giudice GJ. A passive transfer model of the organ-specific autoimmune disease, bullous pemphigoid, using antibodies generated against the hemidesmosomal antigen, BP180. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:2480–2488. doi: 10.1172/JCI116856. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

