Behavior problems in children adopted from psychosocially depriving institutions
- PMID: 20084451
- PMCID: PMC2892211
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-009-9383-4
Behavior problems in children adopted from psychosocially depriving institutions
Abstract
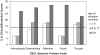
Behavior problems were investigated in 342 6- to 18-year-old children adopted from psychosocially depriving Russian institutions that provided adequate physical resources but not consistent, responsive caregiving. Results indicated that attention and externalizing problems were the most prevalent types of behavior problems in the sample as a whole. Behavior problem rates increased with age at adoption, such that children adopted at 18 months or older had higher rates than never-institutionalized children but younger-adopted children did not. There was a stronger association between age at adoption and behavior problems during adolescence than at younger ages at assessment. Children adopted from psychosocially depriving institutions had lower behavior problem rates than children adopted from severely depriving Romanian institutions in the 1990s. The implications of these results are that early psychosocial deprivation is associated with behavior problems, children exposed to prolonged early deprivation may be especially vulnerable to the developmental stresses of adolescence, and severe institutional deprivation is associated with a higher percentage of behavior problems after a shorter duration of exposure.
Figures

References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991.
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families; 2001.
-
- Ainsworth MDM, Blehar MC, Waters E, Wall S. Patterns of attachment. Hillsdale: Erlbaum; 1978.
-
- Berlin L, Bohlin G, Rydell A. Relations between inhibition, executive functioning, and ADHD symptoms: a longitudinal study from age 5 to 8 1/2 years. Child Neuropsychology. 2003;9:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein MH, Tamis-LeMonda CS. Maternal responsiveness and cognitive development in children. In: Bornstein MH, editor. Maternal responsiveness: Characteristics and consequences. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1989. pp. 49–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

