In vivo parasitological measures of artemisinin susceptibility
- PMID: 20085495
- PMCID: PMC4291277
- DOI: 10.1086/650301
In vivo parasitological measures of artemisinin susceptibility
Abstract
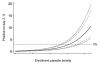
Parasite clearance data from 18,699 patients with falciparum malaria treated with an artemisinin derivative in areas of low (n=14,539), moderate (n=2077), and high (n=2083) levels of malaria transmission across the world were analyzed to determine the factors that affect clearance rates and identify a simple in vivo screening measure for artemisinin resistance. The main factor affecting parasite clearance time was parasite density on admission. Clearance rates were faster in high-transmission settings and with more effective partner drugs in artemisinin-based combination treatments (ACTs). The result of the malaria blood smear on day 3 (72 h) was a good predictor of subsequent treatment failure and provides a simple screening measure for artemisinin resistance. Artemisinin resistance is highly unlikely if the proportion of patients with parasite densities of <100,000 parasites/microL given the currently recommended 3-day ACT who have a positive smear result on day 3 is <3%; that is, for n patients the observed number with a positive smear result on day 3 does not exceed (n + 60)/24.
Figures
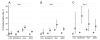

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO guidelines for the treatment of malaria. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2006.
-
- White NJ. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): the price of success. Science. 2008;320:330–334. - PubMed
-
- Verdrager J. Epidemiology of the emergence and spread of drug-resistant falciparum malaria in South-east Asia and Australasia. J Trop Med Hyg. 1986;89:277–289. - PubMed
-
- Roper C, Pearce R, Nair S, Sharp B, Nosten F, Anderson T. Intercontinental spread of pyrimethamine-resistant malaria. Science. 2004;305:1124. - PubMed
-
- Harinasuta T, Suntharasamai P, Viravan C. Chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Lancet. 1965;2:657–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

