Potent anti-tumor effects of a dual specific oncolytic adenovirus expressing apoptin in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 20085660
- PMCID: PMC2818692
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-10
Potent anti-tumor effects of a dual specific oncolytic adenovirus expressing apoptin in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
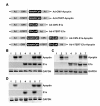
Background: Oncolytic virotherapy is an attractive drug platform of cancer gene therapy, but efficacy and specificity are important prerequisites for success of such strategies. Previous studies determined that Apoptin is a p53 independent, bcl-2 insensitive apoptotic protein with the ability to specifically induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Here, we generated a conditional replication-competent adenovirus (CRCA), designated Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, and investigated the effectiveness of the CRCA a gene therapy agent for further clinical trials.
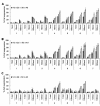
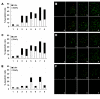
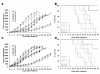
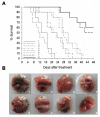
Results: The observation that infection with Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin significantly inhibited growth of the melanoma cells, protecting normal human epidermal melanocytes from growth inhibition confirmed cancer cell selective adenoviral replication, growth inhibition, and apoptosis induction of this therapeutic approach. The in vivo assays performed by using C57BL/6 mice containing established primary or metastatic tumors expanded the in vitro studies. When treated with Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, the subcutaneous primary tumor volume reduction was not only observed in intratumoral injection group but in systemic delivery mice. In the lung metastasis model, Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin effectively suppressed pulmonary metastatic lesions. Furthermore, treatment of primary and metastatic models with Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin increased mice survival.
Conclusions: These data further reinforce the previously research showing that an adenovirus expressing Apoptin is more effective and advocate the potential applications of Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin in the treatment of neoplastic diseases in future clinical trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic efficacy of an hTERT promoter-driven oncolytic adenovirus that expresses apoptin in gastric carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Oct;30(4):747-54. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1077. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22842823
-
Preclinical pharmacology and toxicology study of Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, a novel dual cancer-specific oncolytic adenovirus.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 15;280(2):362-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25151223
-
Potent growth-inhibitory effect of a dual cancer-specific oncolytic adenovirus expressing apoptin on prostate carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2013 Mar;42(3):1052-60. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1783. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23338489
-
Apoptin: specific killer of tumor cells?Apoptosis. 2005 Aug;10(4):717-24. doi: 10.1007/s10495-005-0930-3. Apoptosis. 2005. PMID: 16133863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidisciplinary oncolytic virotherapy for gastrointestinal cancer.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019 Jul 5;3(4):396-404. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12270. eCollection 2019 Jul. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019. PMID: 31346579 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptin mediates mitophagy and endogenous apoptosis by regulating the level of ROS in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Sep 1;20(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00940-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36050738 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumor Synergistic Effect of a Dual Cancer-Specific Recombinant Adenovirus and Paclitaxel on Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 25;10:244. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00244. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32269962 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Specific Promoters in Colorectal Cancer.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:390161. doi: 10.1155/2015/390161. Epub 2015 Nov 15. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 26648599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomerase downregulation induces proapoptotic genes expression and initializes breast cancer cells apoptosis followed by DNA fragmentation in a cell type dependent manner.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Aug;40(8):4995-5004. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2600-9. Epub 2013 May 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23677713 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic and autophagic cell death induced in cervical cancer cells by a dual specific oncolytic adenovirus.Anticancer Drugs. 2023 Mar 1;34(3):361-372. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001452. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Anticancer Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36730009 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

