Elevated levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in the plasma of HIV-1-infected patients and in HIV-1-infected cell cultures: a relevant role on viral replication
- PMID: 20085845
- PMCID: PMC3140709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.12.018
Elevated levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in the plasma of HIV-1-infected patients and in HIV-1-infected cell cultures: a relevant role on viral replication
Abstract
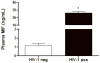
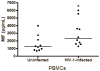
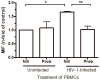
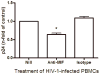
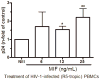
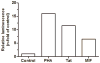
The cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and infectious diseases, however its role in HIV-1 infection is unknown. Here we show that HIV-1-infected patients present elevated plasma levels of MIF, that HIV-1-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) release a greater amount of MIF, and that the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 induces MIF secretion from uninfected PBMCs. The HIV-1 replication in PBMCs declines when these cells are treated with anti-MIF antibodies, and exposure of HIV-1-infected cells to the ABC-transporter inhibitor probenecid results in inhibition of MIF secretion. The addition of recombinant MIF (rhMIF) to HIV-1-infected PBMCs enhances viral replication of CCR5- or CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 isolates. Using a T CD4(+) cell lineage containing an HIV long terminal repeats (LTR)-Luciferase construct, we detected that rhMIF promotes transcription from HIV-1 LTR. Our results show that HIV-1 induces MIF secretion and suggest that MIF influences the HIV-1 biology through activation of HIV-1 LTR.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Increased macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) plasma levels in acute HIV-1 infection.Cytokine. 2012 Nov;60(2):338-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.07.027. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22898393
-
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Promotes Increased Proportions of the Highly Permissive Th17-like Cell Profile during HIV Infection.Viruses. 2022 Oct 9;14(10):2218. doi: 10.3390/v14102218. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298774 Free PMC article.
-
Increased macrophage migration inhibitory factor is associated with inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Apr;44(4):1475-1484. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07361-8. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39953337
-
Regulated secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is mediated by a non-classical pathway involving an ABC transporter.FEBS Lett. 2003 Sep 11;551(1-3):78-86. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00900-1. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12965208
-
Macrophage signaling in HIV-1 infection.Retrovirology. 2010 Apr 9;7:34. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-34. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20380698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of protein expression profiles in the thymus of chickens infected with Marek's disease virus.Virol J. 2012 Nov 1;9:256. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-256. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23116199 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-27 Promotes Divergent Effects on HIV-1 Infection in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells through BST-2/Tetherin.J Virol. 2023 Jan 31;97(1):e0175222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01752-22. Epub 2023 Jan 5. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36602368 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during dengue virus infection.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:547094. doi: 10.1155/2015/547094. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25821355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Encephalitis : CSF Biomarkers of SIV Encephalitis.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;11(2):332-47. doi: 10.1007/s11481-016-9666-9. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059917 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences in innate responses and gene expression profiles in memory CD4 T cells are apparent very early during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 6;14(9):e0221159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221159. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31490965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar-Cordova E, Chinen J, Donehower L, Lewis DE, Belmont JW. A sensitive reporter cell line for HIV-1 tat activity, HIV-1 inhibitors, and T cell activation effects. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10(3):295–301. - PubMed
-
- Alfano M, Crotti A, Vicenzi E, Poli G. New players in cytokine control of HIV infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2008;5(1):27–32. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Nishihira J, Miki I. Blockade of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) prevents the antigen-induced response in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Inflamm Res. 2007;56(1):24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

