Clinical course of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients experiencing hypertension during treatment with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel on ECOG 4599
- PMID: 20085937
- PMCID: PMC2834434
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4482
Clinical course of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients experiencing hypertension during treatment with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel on ECOG 4599
Abstract
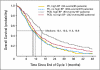
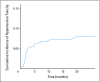
PURPOSE Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with demonstrated efficacy in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel (PCB) for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Administration of bevacizumab is postulated to decrease nitric oxide synthesis and lead to hypertension, which may be a physiological sign that the VEGF pathway is more actively being blocked and could result in improved outcomes. PATIENTS AND METHODS Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 4599 randomly assigned patients with nonsquamous NSCLC to carboplatin and paclitaxel (PC) versus PCB. Hypertensive patients were compared with nonhypertensive patients with respect to overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) using blood pressure data and adverse event data separately. High blood pressure (HBP) by the end of cycle 1 was defined as blood pressure > 150/100 at any previous time or at least a 20-mmHg increase in diastolic blood pressure from baseline. Results In a multivariable Cox model adjusting for HBP as a time-varying covariate, comparing those on PCB with HBP with those on PC gave an OS hazard ratio (HR) of 0.60 (95% CI, 0.43 to 0.81; P = .001); comparing those on PCB without HBP with those on PC alone, the OS HR was 0.86 (95% CI, 0.74 to 1.00; P = .05). Comparing the PCB HBP group with PC gave an adjusted PFS HR of 0.54 (95% CI, 0.41 to 0.73; P < .0001) and comparing those on PCB without HBP to those on PC, the HR was 0.72 (95% CI, 0.62 to 0.84; P < .0001). The 6-month cumulative incidence of hypertension was 6.2% (95% CI, 3.9% to 8.6%). CONCLUSION Data from ECOG 4599 suggest that onset of HBP during treatment with PCB may be associated with improved outcomes, and additional studies of the downstream effects of VEGF suppression and hypertension are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcomes for elderly, advanced-stage non small-cell lung cancer patients treated with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel: analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial 4599.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jan 1;26(1):60-5. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.1144. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18165641 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment outcomes by tumor histology in Eastern Cooperative Group Study E4599 of bevacizumab with paclitaxel/carboplatin for advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2010 Sep;5(9):1416-23. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181da36f4. J Thorac Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20686429 Clinical Trial.
-
FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) plus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as first-line treatment of advanced/metastatic recurrent nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer.Oncologist. 2007 Jun;12(6):713-8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-6-713. Oncologist. 2007. PMID: 17602060
-
Bevacizumab in non-small cell lung cancer.Drugs. 2008;68(6):737-46. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200868060-00002. Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18416583 Review.
-
Antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Jun;3(6 Suppl 2):S113-8. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318174e993. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18520292 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer-an integrative view by PPPM.EPMA J. 2013 Jan 28;4(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1878-5085-4-3. EPMA J. 2013. PMID: 23356214 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Toxicity and Risk Mitigation with Lung Cancer Treatment.Curr Oncol Rep. 2023 May;25(5):433-444. doi: 10.1007/s11912-023-01387-4. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36811807 Review.
-
VEGF Receptor Inhibitor-Induced Hypertension: Emerging Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Curr Oncol Rep. 2022 Apr;24(4):463-474. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01224-0. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35179707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a phase III trial.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Oct 20;31(30):3791-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.4940. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24019545 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toxicity as a biomarker of efficacy of molecular targeted therapies: focus on EGFR and VEGF inhibiting anticancer drugs.Oncologist. 2011;16(12):1729-40. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0163. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 22135123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995;1:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1011–1027. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Hainsworth JD, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin: An active regimen for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3502–3508. - PubMed
-
- Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3200. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1539–1544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

