The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer
- PMID: 20085938
- PMCID: PMC2834432
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.3641
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer
Abstract
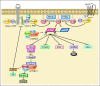
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling axis impacts on cancer cell growth, survival, motility, and metabolism. This pathway is activated by several different mechanisms in cancers, including somatic mutation and amplification of genes encoding key components. In addition, PI3K signaling may serve integral functions for noncancerous cells in the tumor microenvironment. Consequently, therapeutics targeting the PI3K pathway are being developed at a rapid pace, and preclinical and early clinical studies are beginning to suggest specific strategies to effectively use them. However, the central role of PI3K signaling in a large array of diverse biologic processes raises concerns about its use in therapeutics and increases the need to develop sophisticated strategies for its use. In this review, we will discuss how PI3K signaling affects the growth and survival of tumor cells. From this vantage, we will consider how inhibitors of the PI3K signaling cascade, either alone or in combination with other therapeutics, can most effectively be used for the treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan DR, Whitman M, Schaffhausen B, et al. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987;50:1021–1029. - PubMed
-
- Whitman M, Kaplan DR, Schaffhausen B, et al. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985;315:239–242. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

