Vinculin regulates cell-surface E-cadherin expression by binding to beta-catenin
- PMID: 20086044
- PMCID: PMC2818194
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.056432
Vinculin regulates cell-surface E-cadherin expression by binding to beta-catenin
Abstract
Vinculin was identified as a component of adherens junctions 30 years ago, yet its function there remains elusive. Deletion studies are consistent with the idea that vinculin is important for the organization of cell-cell junctions. However, this approach removes vinculin from both cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesions, making it impossible to distinguish its contribution at each site. To define the role of vinculin in cell-cell junctions, we established a powerful short hairpin-RNA-based knockdown/substitution model system that perturbs vinculin preferentially at sites of cell-cell adhesion. When this system was applied to epithelial cells, cell morphology was altered, and cadherin-dependent adhesion was reduced. These defects resulted from impaired E-cadherin cell-surface expression. We have investigated the mechanism for the effects of vinculin and found that the reduced surface E-cadherin expression could be rescued by introduction of vinculin, but not of a vinculin A50I substitution mutant that is defective for beta-catenin binding. These findings suggest that an interaction between beta-catenin and vinculin is crucial for stabilizing E-cadherin at the cell surface. This was confirmed by analyzing a beta-catenin mutant that fails to bind vinculin. Thus, our study identifies vinculin as a novel regulator of E-cadherin function and provides important new insight into the dynamic regulation of adherens junctions.
Figures

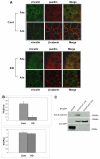
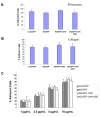
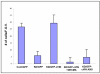
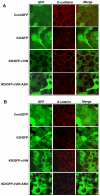
References
-
- Bakolitsa C., Cohen D. M., Bankston L. A., Bobkov A. A., Cadwell G. W., Jennings L., Critchley D. R., Craig S. W., Liddington R. C. (2004). Structural basis for vinculin activation at sites of cell adhesion. Nature 430, 583-586 - PubMed
-
- Barth A. I., Nathke I. S., Nelson W. J. (1997). Cadherins, catenins and APC protein: interplay between cytoskeletal complexes and signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 683-690 - PubMed
-
- Bryant D. M., Stow J. L. (2004). The ins and outs of E-cadherin trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 427-434 - PubMed
-
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. (1980). Microinjection and localization of a 130K protein in living fibroblasts: a relationship to actin and fibronectin. Cell 19, 587-595 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

