Interferon-inducible factor 16 is a novel modulator of glucocorticoid action
- PMID: 20086048
- PMCID: PMC3000051
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-139998
Interferon-inducible factor 16 is a novel modulator of glucocorticoid action
Abstract
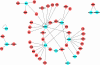
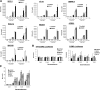
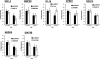
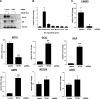
Previously, we used cDNA expression profiling to identify genes associated with glucocorticoid (Gc) sensitivity. We now identify which of these directly influence Gc action. Interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16), bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II (BMPRII), and regulator of G-protein signaling 14 (RGS14) increased Gc transactivation, whereas sialyltransferase 4B (SIAT4B) had a negative effect. Amyloid beta (A4) precursor-protein binding, family B, member 1 (APBB1/Fe65) and neural cell expressed developmentally down-regulated 9 (NEDD9) were without effect. Only IFI16 potentiated Gc repression of NF-kappaB. In addition, IFI16 affected basal expression, and Gc induction of endogenous target genes. IFI16 did not affect glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression, ligand-dependent repression of GR expression, or the ligand-dependent induction of GR phosphorylation on Ser-211 or Ser-203. Coimmunoprecipitation revealed an interaction, suggesting that IFI16 modulation of GR function is mediated by protein crosstalk. Transfection analysis with GR mutants showed that the ligand-binding domain of GR binds IFI16 and is the target domain for IFI16 regulation. Analysis of human lung sections identified colocalization of GR and IFI16, suggesting a physiologically relevant interaction. We demonstrate that IFI16 is a novel modulator of GR function and show the importance of analyzing variation in Gc sensitivity in humans, using appropriate technology, to drive discovery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CBP (CREB binding protein) integrates NF-kappaB (nuclear factor-kappaB) and glucocorticoid receptor physical interactions and antagonism.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Aug;14(8):1222-34. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.8.0506. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10935546
-
Negative cross-talk between RelA and the glucocorticoid receptor: a possible mechanism for the antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids.Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Apr;9(4):401-12. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.4.7659084. Mol Endocrinol. 1995. PMID: 7659084
-
Glucocorticoid/glucocorticoid receptor inhibition of surfactant protein-A (SP-A) gene expression in lung type II cells is mediated by repressive changes in histone modification at the SP-A promoter.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Mar;22(3):585-96. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0412. Epub 2007 Dec 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18079322 Free PMC article.
-
How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: a scope beyond tethering.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.12.014. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23267834 Review.
-
New insights into the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of glucocorticoids: an emerging role for glucocorticoid-receptor-mediated transactivation.Endocrinology. 2013 Mar;154(3):993-1007. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2045. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23384835 Review.
Cited by
-
IFI16 Expression Is Related to Selected Transcription Factors during B-Cell Differentiation.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:747645. doi: 10.1155/2015/747645. Epub 2015 Jun 22. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26185770 Free PMC article.
-
Betacoronavirus-specific alternate splicing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jul 2:2021.07.02.450920. doi: 10.1101/2021.07.02.450920. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Genomics. 2022 Mar;114(2):110270. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110270. PMID: 34230929 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Interferon-inducible p200-family protein IFI16, an innate immune sensor for cytosolic and nuclear double-stranded DNA: regulation of subcellular localization.Mol Immunol. 2012 Jan;49(4):567-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22137500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immune landscape in tuberculosis reveals populations linked to disease and latency.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Feb 10;29(2):165-178.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.013. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 33340449 Free PMC article.
-
The methyltransferase WBSCR22/Merm1 enhances glucocorticoid receptor function and is regulated in lung inflammation and cancer.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):8931-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.540906. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24488492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kino T, Chrousos G P. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid resistance/hypersensitivity syndromes. J Endocrinol. 2001;169:437–445. - PubMed
-
- Franchimont D, Louis E, Dupont P, Vrindts-Gevaert Y, Dewe W, Chrousos G, Geenen V, Belaiche J. Decreased corticosensitivity in quiescent Crohn’s disease: an ex vivo study using whole blood cell cultures. Dig Dis Sci. 1999;44:1208–1215. - PubMed
-
- Van Rossum E F, Lamberts S W. Polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor gene and their associations with metabolic parameters and body composition. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:333–357. - PubMed
-
- Szatmary Z, Garabedian M J, Vilcek J. Inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcriptional activation by p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:43708–43715. - PubMed
-
- Waters C E, Stevens A, White A, Ray D W. Analysis of co-factor function in a glucocorticoid-resistant small cell carcinoma cell line. J Endocrinol. 2004;183:375–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

