Complex environment experience rescues impaired neurogenesis, enhances synaptic plasticity, and attenuates neuropathology in familial Alzheimer's disease-linked APPswe/PS1DeltaE9 mice
- PMID: 20086049
- PMCID: PMC4050966
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-136945
Complex environment experience rescues impaired neurogenesis, enhances synaptic plasticity, and attenuates neuropathology in familial Alzheimer's disease-linked APPswe/PS1DeltaE9 mice
Abstract
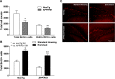
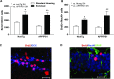
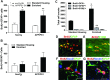
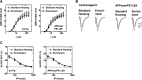
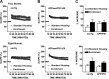
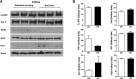
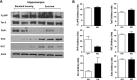
Experience in complex environments induces numerous forms of brain plasticity, improving structure and function. It has been long debated whether brain plasticity can be induced under neuropathological conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), to an extent that would reduce neuropathology, rescue brain structure, and restore its function. Here we show that experience in a complex environment rescues a significant impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis in transgenic mice harboring familial AD-linked mutant APPswe/PS1DeltaE9. Proliferation of hippocampal cells is enhanced significantly after enrichment, and these proliferating cells mature to become new neurons and glia. Enhanced neurogenesis was accompanied by a significant reduction in levels of hyperphosphorylated tau and oligomeric Abeta, the precursors of AD hallmarks, in the hippocampus and cortex of enriched mice. Interestingly, enhanced expression of the neuronal anterograde motor kinesin-1 was observed, suggesting enhanced axonal transport in hippocampal and cortical neurons after enrichment. Examination of synaptic physiology revealed that environmental experience significantly enhanced hippocampal long-term potentiation, without notable alterations in basal synaptic transmission. This study suggests that environmental modulation can rescue the impaired phenotype of the Alzheimer's brain and that induction of brain plasticity may represent therapeutic and preventive avenues in AD.
Figures
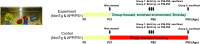

References
-
- Rosen W. G., Mohs R. C., Davis K. L. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psych. 1984;141:1356–1364. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe D. J. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741–766. - PubMed
-
- Cleary J. P., Walsh D. M., Hofmeister J. J., Shankar G. M., Kuskowski M. A., Selkoe D. J., Ashe K. H. Natural oligomers of the amyloid-beta protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Shankar G. M., Li S., Mehta T. H., Garcia-Munoz A., Shepardson N. E., Smith I., Brett F. M., Farrell M. A., Rowan M. J., Lemere C. A., Regan C. M., Walsh D. M., Sabatini B. L., Selkoe D. J. Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med. 2008;14:837–842. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

