Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 deletion impairs glucose tolerance and exacerbates hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetic mice
- PMID: 20086057
- PMCID: PMC2846027
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.162271
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 deletion impairs glucose tolerance and exacerbates hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetic mice
Abstract
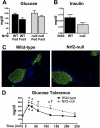
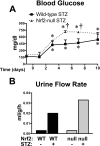
The transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) induces a battery of cytoprotective genes after oxidative stress. Nrf2 aids in liver regeneration by altering insulin signaling; however, whether Nrf2 participates in hepatic glucose homeostasis is unknown. Compared with wild-type mice, mice lacking Nrf2 (Nrf2-null) have lower basal serum insulin and prolonged hyperglycemia in response to an intraperitoneal glucose challenge. In the present study, blood glucose, serum insulin, urine flow rate, and hepatic expression of glucose-related genes were quantified in male diabetic wild-type and Nrf2-null mice. Type 1 diabetes was induced with a single intraperitoneal dose (200 mg/kg) of streptozotocin (STZ). Histopathology and serum insulin levels confirmed depleted pancreatic beta-cells in STZ-treated mice of both genotypes. Five days after STZ, Nrf2-null mice had higher blood glucose levels than wild-type mice. Nine days after STZ, polyuria occurred in both genotypes with more urine output from Nrf2-null mice (11-fold) than wild-type mice (7-fold). Moreover, STZ-treated Nrf2-null mice had higher levels of serum beta-hydroxybutyrate, triglycerides, and fatty acids 10 days after STZ compared with wild-type mice. STZ reduced hepatic glycogen in both genotypes, with less observed in Nrf2-null mice. Increased urine output and blood glucose in STZ-treated Nrf2-null mice corresponded with enhanced gluconeogenesis (glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase)- and reduced glycolysis (pyruvate kinase)-related mRNA expression in their livers. Furthermore, the Nrf2 activator oltipraz lowered blood glucose in wild-type but not Nrf2-null mice administered STZ. Collectively, these data indicate that the absence of Nrf2 worsens hyperglycemia in type I diabetic mice and Nrf2 may represent a therapeutic target for reducing circulating glucose levels.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effects of Oltipraz on the Glycolipid Metabolism and the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 5;18:5685-5700. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S485729. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39654602 Free PMC article.
-
The orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner negatively regulates pancreatic beta cell survival and hyperglycemia in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic mice.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;45(8):1538-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 May 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23680671
-
Nrf2 deficiency improves glucose tolerance in mice fed a high-fat diet.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 1;264(3):305-14. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.09.014. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23017736 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2-and p53-inducible REDD2/DDiT4L/Rtp801L confers pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, leading to glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110271. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110271. Epub 2025 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40409543 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Nrf2 signaling by natural products-can it alleviate diabetes?Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Nov 1;36(6):1738-1767. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 29289692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids Activation of the Transcription Factor Nrf2 as a Hypothesis Approach for the Prevention and Modulation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Severity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 24;9(8):659. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080659. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722164 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Nrf2 in the liver is associated with stress resistance mediated by suppression of the growth hormone-regulated STAT5b transcription factor.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 16;13(8):e0200004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200004. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30114225 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 represses FGF21 during long-term high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice.Diabetes. 2011 Oct;60(10):2465-73. doi: 10.2337/db11-0112. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21852674 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the protective effect of rosiglitazone against electronic cigarette/tobacco smoke-induced blood-brain barrier impairment.BMC Neurosci. 2019 Apr 4;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12868-019-0497-5. BMC Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30947684 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activators in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes. 2011 Nov;60(11):3055-66. doi: 10.2337/db11-0807. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 22025779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE. (2007) Emerging role of Nrf2 in protecting against hepatic and gastrointestinal disease. Toxicol Pathol 35:459–473 - PubMed
-
- Bae EJ, Yang YM, Kim JW, Kim SG. (2007) Identification of a novel class of dithiolethiones that prevent hepatic insulin resistance via the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-p70 ribosomal S6 kinase-1 pathway. Hepatology 46:730–739 - PubMed
-
- da Silva Xavier G, Rutter GA, Diraison F, Andreolas C, Leclerc I. (2006) ChREBP binding to fatty acid synthase and L-type pyruvate kinase genes is stimulated by glucose in pancreatic beta-cells. J Lipid Res 47:2482–2491 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR021940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES009716/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007079/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES013714/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES009649/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES007079/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES009649/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES013714/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES009716/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK080774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

