The RAD23 family provides an essential connection between the 26S proteasome and ubiquitylated proteins in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 20086187
- PMCID: PMC2828702
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.072660
The RAD23 family provides an essential connection between the 26S proteasome and ubiquitylated proteins in Arabidopsis
Abstract
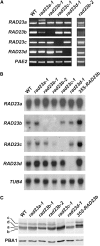
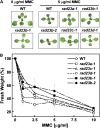
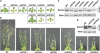
The ubiquitin (Ub)/26S proteasome system (UPS) directs the turnover of numerous regulatory proteins, thereby exerting control over many aspects of plant growth, development, and survival. The UPS is directed in part by a group of Ub-like/Ub-associated (UBL/UBA) proteins that help shuttle ubiquitylated proteins to the 26S proteasome for breakdown. Here, we describe the collection of UBL/UBA proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana, including four isoforms that comprise the RADIATION SENSITIVE23 (RAD23) family. The nuclear-enriched RAD23 proteins bind Ub conjugates, especially those linked internally through Lys-48, via their UBA domains, and associate with the 26S proteasome Ub receptor RPN10 via their N-terminal UBL domains. Whereas homozygous mutants individually affecting the four RAD23 genes are without phenotypic consequences (rad23a, rad23c, and rad23d) or induce mild phyllotaxy and sterility defects (rad23b), higher-order mutant combinations generate severely dwarfed plants, with the quadruple mutant displaying reproductive lethality. Both the synergistic effects of a rad23b-1 rpn10-1 combination and the response of rad23b plants to mitomycin C suggest that RAD23b regulates cell division. Taken together, RAD23 proteins appear to play an essential role in the cell cycle, morphology, and fertility of plants through their delivery of UPS substrates to the 26S proteasome.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The defective proteasome but not substrate recognition function is responsible for the null phenotypes of the Arabidopsis proteasome subunit RPN10.Plant Cell. 2011 Jul;23(7):2754-73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.086702. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21764993 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis RAD23B regulates pollen development by mediating degradation of KRP1.J Exp Bot. 2020 Jul 6;71(14):4010-4019. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa167. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32242227
-
Rad23 promotes the targeting of proteolytic substrates to the proteasome.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4902-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4902-4913.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052895 Free PMC article.
-
The moonlighting of RAD23 in DNA repair and protein degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023 Jun;1866(2):194925. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194925. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023. PMID: 36863450 Review.
-
Proteasome regulation, plant growth and stress tolerance.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Oct;4(10):924-7. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.10.9469. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19826220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Ubiquitin-Binding Protein OsDSK2a Mediates Seedling Growth and Salt Responses by Regulating Gibberellin Metabolism in Rice.Plant Cell. 2020 Feb;32(2):414-428. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00593. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 31826965 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase Interaction Partners-Insight from Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 29;23(1):368. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010368. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008793 Free PMC article.
-
The defective proteasome but not substrate recognition function is responsible for the null phenotypes of the Arabidopsis proteasome subunit RPN10.Plant Cell. 2011 Jul;23(7):2754-73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.086702. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21764993 Free PMC article.
-
More Than Just Cleaning: Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteolysis in Fungal Pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 10;11:774613. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.774613. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34858882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-like 3 as a new protein-sorting factor for small extracellular vesicles.Cell Struct Funct. 2022;47(1):1-18. doi: 10.1247/csf.21078. Cell Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35197392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Bertolaet B.L., Clarke D.J., Wolff M., Watson M.H., Henze M., Divita G., Reed S.I. (2001). UBA domains mediate protein-protein interactions between two DNA damage-inducible proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 313: 955–963 - PubMed
-
- Cui X., Brenneman M., Meyne J., Oshimura M., Goodwin E.H., Chen D.J. (1999). The XRCC2 and XRCC3 repair genes are required for chromosome stability in mammalian cells. Mutat. Res. 434: 75–88 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

