Involvement of microRNAs in the cytotoxic effects exerted by proinflammatory cytokines on pancreatic beta-cells
- PMID: 20086228
- PMCID: PMC2844845
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0881
Involvement of microRNAs in the cytotoxic effects exerted by proinflammatory cytokines on pancreatic beta-cells
Abstract
Objective: Pancreatic beta-cells exposed to proinflammatory cytokines display alterations in gene expression resulting in defective insulin secretion and apoptosis. MicroRNAs are small noncoding RNAs emerging as key regulators of gene expression. Here, we evaluated the contribution of microRNAs to cytokine-mediated beta-cell cytotoxicity.
Research design and methods: We used global microarray profiling and real-time PCR analysis to detect changes in microRNA expression in beta-cells exposed to cytokines and in islets of pre-diabetic NOD mice. We assessed the involvement of the microRNAs affected in cytokine-mediated beta-cell failure by modifying their expression in insulin-secreting MIN6 cells.
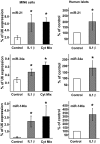
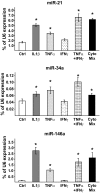
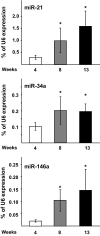
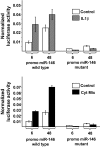
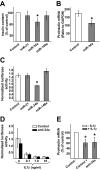
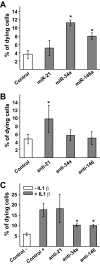
Results: We found that IL-1beta and TNF-alpha induce the expression of miR-21, miR-34a, and miR-146a both in MIN6 cells and human pancreatic islets. We further show an increase of these microRNAs in islets of NOD mice during development of pre-diabetic insulitis. Blocking miR-21, miR-34a, or miR-146a function using antisense molecules did not restore insulin-promoter activity but prevented the reduction in glucose-induced insulin secretion observed upon IL-1beta exposure. Moreover, anti-miR-34a and anti-miR-146a treatment protected MIN6 cells from cytokine-triggered cell death.
Conclusions: Our data identify miR-21, miR-34a, and miR-146a as novel players in beta-cell failure elicited in vitro and in vivo by proinflammatory cytokines, notably during the development of peri-insulitis that precedes overt diabetes in NOD mice.
Figures


References
-
- Eizirik DL, Colli ML, Ortis F: The role of inflammation in insulitis and beta-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009; 5: 219– 226 - PubMed
-
- Prentki M, Vischer S, Glennon MC, Regazzi R, Deeney JT, Corkey BE: Malonyl-CoA and long chain acyl-CoA esters as metabolic coupling factors in nutrient-induced insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 5802– 5810 - PubMed
-
- Donath MY, Storling J, Berchtold LA, Billestrup N, Mandrup-Poulsen T: Cytokines and beta-cell biology: from concept to clinical translation. Endocr Rev 2008; 29: 334– 350 - PubMed
-
- McDaniel ML, Kwon G, Hill JR, Marshall CA, Corbett JA: Cytokines and nitric oxide in islet inflammation and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1996; 211: 24– 32 - PubMed
-
- Pipeleers D, Hoorens A, Marichal-Pipeleers M, Van de Casteele M, Bouwens L, Ling Z: Role of pancreatic β-cells in the process of β-cell death. Diabetes 2001; 50( Suppl. 1): S52– S57 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

