The metal-responsive transcription factor-1 protein is elevated in human tumors
- PMID: 20087061
- PMCID: PMC3039317
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.9.6.10979
The metal-responsive transcription factor-1 protein is elevated in human tumors
Abstract
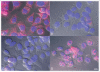
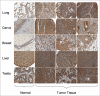
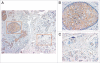
We previously identified metal-responsive transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) as a positive contributor to mouse fibrosarcoma growth through effects on cell survival, proliferation, tumor angiogenesis and extracellular matrix remodeling. In the present study, we investigated MTF-1 protein expression in human tissues by specific immunostaining of both normal and tumor tissue samples. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of a human tissue microarray (TMA), using a unique anti-human MTF-1 antibody, indicated constitutive MTF-1 expression in most normal tissues, with liver and testis displaying comparatively high levels of expression. Nevertheless, MTF-1 protein levels were found to be significantly elevated in diverse human tumor types, including breast, lung and cervical carcinomas. IHC analysis of a separate panel of full-size tissue sections of human breast cancers, including tumor and normal adjacent, surrounding tissue, confirmed and extended the results of the TMA analysis. Taken with our previous findings, this new study suggests a role for MTF-1 in human tumor development, growth or spread. Moreover, the study suggests that MTF-1 could be a novel therapeutic target that offers the opportunity to manipulate metal or redox homeostasis in tumor cells.
Figures


References
-
- Lichtlen P, Schaffner W. Putting its fingers on stressful situations: the heavy metal-regulatory transcription factor MTF-1. Bioessays. 2001;23:1010–7. - PubMed
-
- Laity JH, Andrews GK. Understanding the mechanisms of zinc-sensing by metal-response element binding transcription factor-1 (MTF-1). Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;463:201–10. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Wimmer U, Lichtlen P, Inderbitzin D, Stieger B, Meier PJ, et al. Metal-responsive transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) is essential for embryonic liver development and heavy metal detoxification in the adult liver. Faseb J. 2004;18:1071–9. - PubMed
-
- Adilakshmi T, Laine RO. Ribosomal protein S25 mRNA partners with MTF-1 and La to provide a p53-mediated mechanism for survival or death. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4147–51. - PubMed
-
- Bellingham SA, Coleman LA, Masters CL, Camakaris J, Hill AF. Regulation of prion gene expression by transcription factors SP1 and metal transcription factor-1. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:1291–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
