Mast cells as early responders in the regulation of acute blood-brain barrier changes after cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage
- PMID: 20087366
- PMCID: PMC2949160
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.282
Mast cells as early responders in the regulation of acute blood-brain barrier changes after cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage
Abstract
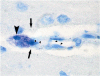
The inflammatory response triggered by stroke has been viewed as harmful, focusing on the influx and migration of blood-borne leukocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages. This review hypothesizes that the brain and meninges have their own resident cells that are capable of fast host response, which are well known to mediate immediate reactions such as anaphylaxis, known as mast cells (MCs). We discuss novel research suggesting that by acting rapidly on the cerebral vessels, this cell type has a potentially deleterious role in the very early phase of acute cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage. Mast cells should be recognized as a potent inflammatory cell that, already at the outset of ischemia, is resident within the cerebral microvasculature. By releasing their cytoplasmic granules, which contain a host of vasoactive mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, histamine, heparin, and proteases, MCs act on the basal membrane, thus promoting blood-brain barrier (BBB) damage, brain edema, prolonged extravasation, and hemorrhage. This makes them a candidate for a new pharmacological target in attempts to even out the inflammatory responses of the neurovascular unit, and to stabilize the BBB after acute stroke.
Figures



References
-
- Andriopoulou P, Navarro P, Zanetti A, Lampugnani MG, Dejana E. Histamine induces tyrosine phosphorylation of endothelial cell-to-cell adherens junctions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:2286–2297. - PubMed
-
- Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ, Fini ME, Lo EH. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1681–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

