Behavioral and genetic characteristics of a new species of Nasonia
- PMID: 20087394
- PMCID: PMC3533498
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2009.147
Behavioral and genetic characteristics of a new species of Nasonia
Abstract
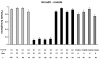
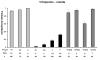
Nasonia (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) is a genus of parasitoid wasps, which is fast emerging as a model system for evolutionary, genetic, developmental and host-endosymbiont interaction studies. In this study, we report a new species, Nasonia oneida, distinguish its behavioral, genetic and morphological features, and characterize its pre-mating and post-mating isolation with the other Nasonia species. Phylogenetic analyses indicate that N. oneida is the sister species to Nasonia giraulti with its own uniquely distinct cuticular hydrocarbon profiles, behavioral characteristics and subtle morphological differences. An important characteristic of N. oneida is the strong mate discrimination shown by the females against all the other Nasonia species. A genetic analysis of this phenotype by interspecies hybridization indicates that this strong discriminating phenotype is recessive. A formal species description of N. oneida Raychoudhury & Desjardins is also provided.
Figures





References
-
- Ayasse M, Paxton RJ, Tengo J. Mating behavior and chemical communication in the order hymenoptera. Annual Review of Entomology. 2001;46:31–78. - PubMed
-
- Beukeboom L, van den Assem J. Courtship and mating behaviour of interspecific Nasonia hybrids (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae): a grandfather effect. Behav Genet. 2002;31:167–177. - PubMed
-
- Bordenstein SR, O’Hara FP, Werren JH. Wolbachia-induced incompatibility precedes other hybrid incompatibilities in Nasonia. Nature. 2001;409(6821):707–710. - PubMed
-
- Breeuwer JA, Stouthamer R, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Weisburg WG, Werren JH. Phylogeny of cytoplasmic incompatibility micro-organisms in the parasitoid wasp genus Nasonia (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) based on 16S ribosomal DNA sequences. Insect Mol Biol. 1992;1(1):25–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

