In vivo biodistribution and clearance studies using multimodal organically modified silica nanoparticles
- PMID: 20088598
- PMCID: PMC2827663
- DOI: 10.1021/nn901146y
In vivo biodistribution and clearance studies using multimodal organically modified silica nanoparticles
Abstract
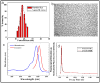
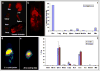
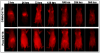
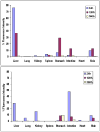
Successful translation of the use of nanoparticles from laboratories to clinics requires exhaustive and elaborate studies involving the biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility of nanoparticles for in vivo biomedical applications. We report here the use of multimodal organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) nanoparticles for in vivo bioimaging, biodistribution, clearance, and toxicity studies. We have synthesized ORMOSIL nanoparticles with diameters of 20-25 nm, conjugated with near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores and radiolabeled them with (124)I, for optical and PET imaging in vivo. The biodistribution of the nontargeted nanoparticles was studied in nontumored nude mice by optical fluorescence imaging, as well by measuring the radioactivity from harvested organs. Biodistribution studies showed a greater accumulation of nanoparticles in liver, spleen, and stomach than in kidney, heart, and lungs. The clearance studies carried out over a period of 15 days indicated hepatobiliary excretion of the nanoparticles. Selected tissues were analyzed for any potential toxicity by histological analysis, which confirmed the absence of any adverse effect or any other abnormalities in the tissues. The results demonstrate that these multimodal nanoparticles have potentially ideal attributes for use as biocompatible probes for in vivo imaging.
Figures
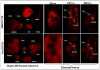
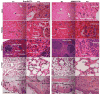


Comment in
-
Multimodal imaging for cancer detection.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2010 Jul;5(5):687-91. doi: 10.2217/nnm.10.47. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20662640 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer mediated large Stokes shifting near-infrared fluorescent silica nanoparticles for in vivo small-animal imaging.Anal Chem. 2012 Nov 6;84(21):9056-64. doi: 10.1021/ac301461s. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 23017033
-
Biomedical In Vivo Studies with ORMOSIL Nanoparticles Containing Active Agents.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2118:121-138. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0319-2_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32152975
-
Multifunctional organically modified silica nanoparticles for chemotherapy, adjuvant hyperthermia and near infrared imaging.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Nov 1;147:492-500. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.07.048. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27614237 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeling Silica-Based Nanoparticles via Coordination Chemistry: Basic Principles, Strategies, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):778-788. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00635. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29489335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent nanoparticles based on AIE fluorogens for bioimaging.Nanoscale. 2016 Feb 7;8(5):2471-87. doi: 10.1039/c5nr05051k. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 26478255 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles in the brain: a potential therapeutic system targeted to an early defect observed in many neurodegenerative diseases.Pharm Res. 2013 Oct;30(10):2459-74. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1037-0. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23625095 Review.
-
A Heparan Sulfate-Binding Cell Penetrating Peptide for Tumor Targeting and Migration Inhibition.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:237969. doi: 10.1155/2015/237969. Epub 2015 May 3. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26064887 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting drug delivery efficiency into tumor tissues through molecular simulation of transport in complex vascular networks.J Control Release. 2018 Dec 28;292:221-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 8. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30415016 Free PMC article.
-
In-vivo time course of organ uptake and blood-brain-barrier permeation of poly(L-lactide) and poly(perfluorodecyl acrylate) nanoparticles with different surface properties in unharmed and brain-traumatized rats.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 6;14:994877. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.994877. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36814997 Free PMC article.
-
Design and pharmacokinetical aspects for the use of inorganic nanoparticles in radiomedicine.Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1057):20150210. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150210. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Br J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26495872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kobyashi H, Brechbiel M. Nano-Sized Mri Contrast Agents With Dendrimer Cores. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2005;57:2271–2286. - PubMed
-
- Prasad PN. Introduction To Biophotonics. Wiley-Interscience; New York: 2004.
-
- Sevick-Muraca E, Houston J, Gurfinkel M. Fluorescence-enhanced, Near Infrared Diagnostic Imaging With Contrast Agent. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6:642–650. - PubMed
-
- Frangioni JV. In Vivo Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:626–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

