Partial reduction of BACE1 improves synaptic plasticity, recent and remote memories in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
- PMID: 20089133
- PMCID: PMC2921968
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06608.x
Partial reduction of BACE1 improves synaptic plasticity, recent and remote memories in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
Abstract
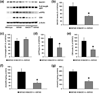
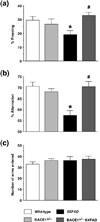
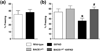
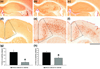
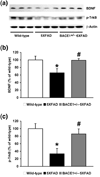
beta-Site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) initiates amyloid-beta (Abeta) generation that is central to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Therefore, lowering Abeta levels by BACE1 manipulations represents a key therapeutic strategy, but it remains unclear whether partial inhibition of BACE1, as expected for AD treatments, can improve memory deficits. In this study, we used heterozygous BACE1 gene knockout (BACE1+/-) mice to evaluate the effects of partial BACE1 suppression on different types of synaptic and cognitive dysfunctions in Alzheimer's transgenic mice (5XFAD model). We found that approximately 50% BACE1 reductions rescued deficits of 5XFAD mice not only in hippocampus-dependent memories as tested by contextual fear conditioning and spontaneous alternation Y-maze paradigms but also in cortex-dependent remote memory stabilization during 30 days after contextual conditioning. Furthermore, 5XFAD-associated impairments in long-term potentiation (a synaptic model of learning and memory) and declines in synaptic plasticity/learning-related brain-derived neurotrophic factor-tyrosine kinase B signaling pathways were prevented in BACE1+/-.5XFAD mice. Finally, these improvements were related with reduced levels of beta-secretase-cleaved C-terminal fragment (C99), Abeta peptides and plaque burden in relevant brain regions of BACE1+/-.5XFAD mice. Therefore, our findings provide compelling evidence for beneficial effects of partially BACE1-inhibiting approaches on multiple forms of functional defects associated with AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic reductions of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and amyloid-beta ameliorate impairment of conditioned taste aversion memory in 5XFAD Alzheimer's disease model mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Jan;31(1):110-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.07031.x. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20092558 Free PMC article.
-
7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule TrkB agonist, reverses memory deficits and BACE1 elevation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jan;37(2):434-44. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.191. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21900882 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of BACE1 haploinsufficiency on APP processing and Aβ concentrations in male and female 5XFAD Alzheimer mice at different disease stages.Neuroscience. 2015 Oct 29;307:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.037. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26314636 Free PMC article.
-
BACE1: the beta-secretase enzyme in Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(1-2):105-14. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:1-2:105. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15126696 Review.
-
The beta-secretase, BACE: a prime drug target for Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2001 Oct;17(2):157-70. doi: 10.1385/JMN:17:2:157. J Mol Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11816789 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampus-based contextual memory alters the morphological characteristics of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus.Mol Brain. 2016 Jul 26;9(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0253-z. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27460927 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ agonist pioglitazone reverses memory impairment and biochemical changes in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Aug;18(8):659-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00341.x. Epub 2012 May 24. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22620268 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference-mediated silencing of BACE and APP attenuates the isoflurane-induced caspase activation.Med Gas Res. 2011 Apr 28;1(1):5. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-1-5. Med Gas Res. 2011. PMID: 22146340 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia treatment alleviates memory impairment in the 6-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 mice and reduces amyloid beta accumulation and inflammation in the brain.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Nov 29;13(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00935-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34844651 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid beta dimers/trimers potently induce cofilin-actin rods that are inhibited by maintaining cofilin-phosphorylation.Mol Neurodegener. 2011 Jan 24;6:10. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-10. Mol Neurodegener. 2011. PMID: 21261978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aisen PS. The development of anti-amyloid therapy for Alzheimer's disease: from secretase modulators to polymerisation inhibitors. CNS Drugs. 2005;19:989–996. - PubMed
-
- Arancibia S, Silhol M, Mouliere F, Meffre J, Hollinger I, Maurice T, Tapia-Arancibia L. Protective effect of BDNF against beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;31:316–326. - PubMed
-
- Ashe KH. Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer's disease. Learn Mem. 2001;8:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia F, Wang HY, Ghilardi MF, Gashi E, Quartarone A, Friedman E, Nixon RA. Cortical plasticity in Alzheimer's disease in humans and rodents. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62:1405–1412. - PubMed
-
- Berger-Sweeney J, McPhie DL, Arters JA, Greenan J, Oster-Granite ML, Neve RL. Impairments in learning and memory accompanied by neurodegeneration in mice transgenic for the carboxyl-terminus of the amyloid precursor protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;66:150–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

