Down-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 gene expression by short interfering RNA attenuates bone cancer pain in a rat model
- PMID: 20089147
- PMCID: PMC2819998
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-2
Down-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 gene expression by short interfering RNA attenuates bone cancer pain in a rat model
Abstract
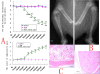
Background: This study demonstrates a critical role in CNS innate immunity of the microglial Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the induction and maintenance of behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of bone cancer pain with the technique of RNA interference (RNAi). We hypothesized that after intramedullary injection of Walker 256 cells (a breast cancer cell line) into the tibia, CNS neuroimmune activation and subsequent cytokine expression are triggered by the stimulation of microglial membrane-bound TLR4.
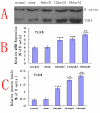
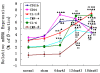
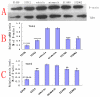
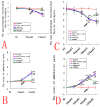
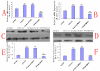
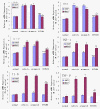
Results: We assessed tactile allodynia and spontaneous pain in female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats after intramedullary injection of Walker 256 cells into the tibia. In a complementary study, TLR4 small interfering RNA(siRNA) was administered intrathecally to bone cancer pain rats to reduce the expression of spinal TLR4. The bone cancer pain rats treated with TLR4 siRNA displayed significantly attenuated behavioral hypersensitivity and decreased expression of spinal microglial markers and proinflammatory cytokines compared with controls. Only intrathecal injection of TRL4 siRNA at post-inoculation day 4 could prevent initial development of bone cancer pain; intrathecal injection of TRL4 siRNA at post-inoculation day 9 could attenuate, but not completely block, well-established bone cancer pain.
Conclusions: TLR4 might be the main mediator in the induction of bone cancer pain. Further study of this early, specific, and innate CNS/microglial response, and how it leads to sustained glial/neuronal hypersensitivity, might lead to new therapies for the prevention and treatment of bone cancer pain syndromes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tibia tumor-induced cancer pain involves spinal p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation via TLR4-dependent mechanisms.Brain Res. 2010 Jul 30;1346:213-23. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.014. Epub 2010 May 15. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20478276
-
P2X4 receptor in the dorsal horn partially contributes to brain-derived neurotrophic factor oversecretion and toll-like receptor-4 receptor activation associated with bone cancer pain.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Dec;92(12):1690-702. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23443. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 24984884
-
The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 19;102(16):5856-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501634102. Epub 2005 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15809417 Free PMC article.
-
Robust spinal neuroinflammation mediates mechanical allodynia in Walker 256 induced bone cancer rats.Mol Brain. 2012 May 20;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-5-16. Mol Brain. 2012. PMID: 22607655 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible Lentivirus-Mediated siRNA against TLR4 Reduces Nociception in a Rat Model of Bone Cancer Pain.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:523896. doi: 10.1155/2015/523896. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26556957 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Investigation of Correlation between Resistance to Diazepam and Expression of Inflammatory Markers in The Peripheral Blood of Patients with Status Epilepticus.Acta Med Acad. 2023 Dec;52(3):169-181. doi: 10.5644/ama2006-124.423. Acta Med Acad. 2023. PMID: 38407083 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-induced bone pain sequentially activates the ERK/MAPK pathway in different cell types in the rat spinal cord.Mol Pain. 2011 Jul 1;7:48. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-48. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21722369 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of Toll-like receptors in the control of pain and itch.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):131-44. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1219-5. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small non-coding RNAs-based bone regulation and targeting therapeutic strategies.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Nov 15;456:16-35. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.11.018. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27888003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the neuroimmunopharmacology of opioids: an integrative review of mechanisms of central immune signaling and their implications for opioid analgesia.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Sep;63(3):772-810. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.004135. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21752874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yao M, Yang JP, Wang LN, Cheng H, Zhang YB, Xu QN, Wu YW. Feasibility of establishment of rat model of bone cancer pain by using Walker 256 cells cultured in vitro or in vivo. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;88(13):880–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

