PhenomiR: a knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes
- PMID: 20089154
- PMCID: PMC2847718
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-1-r6
PhenomiR: a knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes
Abstract
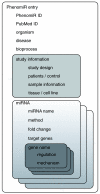
In recent years, microRNAs have been shown to play important roles in physiological as well as malignant processes. The PhenomiR database http://mips.helmholtz-muenchen.de/phenomir provides data from 542 studies that investigate deregulation of microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes as a systematic, manually curated resource. Using the PhenomiR dataset, we could demonstrate that, depending on disease type, independent information from cell culture studies contrasts with conclusions drawn from patient studies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PhenomiR: microRNAs in human diseases and biological processes.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;822:249-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-427-8_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22144204
-
MIPS: curated databases and comprehensive secondary data resources in 2010.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D220-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1157. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21109531 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of microRNA function in heart development.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2010 Sep;42(9):662-70. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmq072. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2010. PMID: 20716610
-
Similarity computation strategies in the microRNA-disease network: a survey.Brief Funct Genomics. 2016 Jan;15(1):55-64. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv024. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26134276 Review.
-
Got target? Computational methods for microRNA target prediction and their extension.Exp Mol Med. 2010 Apr 30;42(4):233-44. doi: 10.3858/emm.2010.42.4.032. Exp Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20177143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep sequencing identifies circulating mouse miRNAs that are functionally implicated in manifestations of aging and responsive to calorie restriction.Aging (Albany NY). 2013 Feb;5(2):130-41. doi: 10.18632/aging.100540. Aging (Albany NY). 2013. PMID: 23470454 Free PMC article.
-
Combined embedding model for MiRNA-disease association prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Mar 25;22(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04092-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33765909 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Prediction of Small Molecule-miRNA Associations Based on the HeteSim Algorithm.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Mar 1;14:274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 30654189 Free PMC article.
-
miRModuleNet: Detecting miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Modules.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 12;13:767455. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.767455. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495139 Free PMC article.
-
Stability indicators in network reconstruction.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e89815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089815. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M, Lin C, Socci ND, Hermida L, Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Foa R, Schliwka J, Fuchs U, Novosel A, Muller RU, Schermer B, Bissels U, Inman J, Phan Q, Chien M, Weir DB, Choksi R, De VG, Frezzetti D, Trompeter HI. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007;129:1401–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

