Respiratory function and pulmonary lesions in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
- PMID: 20089425
- PMCID: PMC7128265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2009.12.022
Respiratory function and pulmonary lesions in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
Abstract
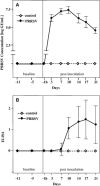
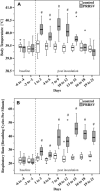
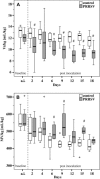
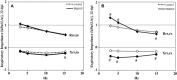
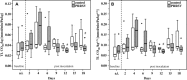
Pulmonary dysfunction was evaluated in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV, isolate VR-2332) and compared to clinical and pathological findings. Infected pigs developed fever, reduced appetite, respiratory distress and dullness at 9 days post-inoculation (dpi). Non-invasive pulmonary function tests using impulse oscillometry and rebreathing of test gases (He, CO) revealed peripheral airway obstruction, reduced lung compliance and reduced lung CO-transfer factor. PRRSV-induced pulmonary dysfunction was most marked at 9-18 dpi and was accompanied by a significantly increased respiratory rate and decreased tidal volume. Expiration was affected more than inspiration. On histopathological examination, multifocal areas of interstitial pneumonia (more severe and extensive at 10 dpi than 21 dpi) were identified as a possible structural basis for reduced lung compliance and gas exchange disturbances.
Copyright © 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Experimental reproduction of severe disease in CD/CD pigs concurrently infected with type 2 porcine circovirus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Vet Pathol. 2001 Sep;38(5):528-39. doi: 10.1354/vp.38-5-528. Vet Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11572560
-
Effects of low (modified-live virus vaccine) and high (VR-2385)-virulence strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on pulmonary clearance of copper particles in pigs.Vet Pathol. 1998 Sep;35(5):398-406. doi: 10.1177/030098589803500509. Vet Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9754545
-
Pathogenesis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-induced increase in susceptibility to Streptococcus suis infection.Vet Pathol. 2000 Mar;37(2):143-52. doi: 10.1354/vp.37-2-143. Vet Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10714643
-
[Review: diagnostic methods for the detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infections].Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 2006 Aug 15;131(16):566-72. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 2006. PMID: 17007245 Review. Dutch.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) with special reference to clinical aspects and diagnosis. A review.Vet Q. 2002 Jun;24(2):95-100. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2002.9695128. Vet Q. 2002. PMID: 12095084 Review.
Cited by
-
Global Challenges and Advancements in the Management of Pivotal Porcine/Swine Viral Diseases.In Vivo. 2025 Jul-Aug;39(4):1810-1832. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13982. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 40578970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid hormone suppression in feeder pigs following polymicrobial or porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-2 challenge.J Anim Sci. 2021 Nov 1;99(11):skab325. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab325. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34734242 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome developments: An in-depth review of recent findings.Open Vet J. 2024 Sep;14(9):2138-2152. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i9.3. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39553781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Lung Disease in Finishing Pigs at Slaughter: Pulmonary Lesions and Implications on Productivity Parameters.Animals (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;11(12):3604. doi: 10.3390/ani11123604. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944380 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Lessons Learned from a Field Trial on the Understanding of the Porcine Respiratory Disease Complex.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;13(7):740. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13070740. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Botner A., Nielsen J., Bille-Hansen V. Isolation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus in a Danish swine herd and experimental infection of pregnant gilts with the virus. Veterinary Microbiology. 1994;40:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Brockmeier S.L., Palmer M.V., Bolin S.R. Effects of intranasal inoculation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, Bordetella bronchiseptica, or a combination of both organisms in pigs. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 2000;61:892–899. - PubMed
-
- Christianson W.T., Collins J.E., Benfield D.A., Harris L., Gorcya D.E., Chladek D.W., Morrison R.B., Joo H.S. Experimental reproduction of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome in pregnant sows. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 1992;53:485–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

