Differential insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) expression: A potential role for breast cancer survival disparity
- PMID: 20089431
- PMCID: PMC2885869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2009.12.002
Differential insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) expression: A potential role for breast cancer survival disparity
Abstract
Objective: Increased risk of cancer and other adult diseases have been associated with perinatal exposure to adverse conditions such as stress and famine. Recently, Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) was identified as the first gene associated with altered expression caused by fetal exposure to poor nutrition. IGF-II regulates fetal development and breast cancer cell survival, in part, by regulating anti-apoptotic proteins through activation of the IGF-I and insulin receptors. African-American (AA) women have a lower overall breast cancer (BC) incidence, however, they present with advanced disease at diagnosis, poorer prognosis and lower survival than Caucasian (CA) women. The reasons for the BC survival disparity are not well understood. We hypothesize that IGF-II plays a role in the survival disparity observed among AA breast cancer patients by stimulating rapid tumor growth, inhibiting apoptosis, and promoting metastasis.
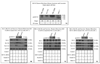
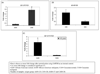
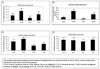
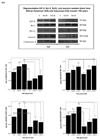
Design: This study examines IGF-II expression and regulation of the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and survivin in Hs578t (ER-), CRL 2335 (ER-), and CRL 2329 (ER+) breast cancer cells and compares with the expression of these proteins in paired breast tissue samples from AA and CA women by qRT-PCR and Western blotting.
Results: IGF-II expression was significantly higher in AA cell lines and tissue samples when compared to Caucasians. IGF-II siRNA treatment decreased anti-apoptotic protein levels in all cell lines (regardless of ER status). These effects were blocked by the addition of recombinant IGF-II. Of significance, IGF-II expression and regulation of Bcl-X(L) and survivin in cell lines correlated with their expression in paired breast tissues.
Conclusions: IGF-II and the anti-apoptotic proteins differential expression among AA and CA patients may contribute to the breast cancer survival disparities observed between these ethnic groups.
Copyright (c) 2009. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factors I and II receptors in the breast cancer survival disparity among African-American women.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010 Jun;20(3):245-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2010.03.001. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010. PMID: 20347606 Free PMC article.
-
Precursor IGF-II (proIGF-II) and mature IGF-II (mIGF-II) induce Bcl-2 And Bcl-X L expression through different signaling pathways in breast cancer cells.Growth Factors. 2008 Apr;26(2):92-103. doi: 10.1080/08977190802057258. Growth Factors. 2008. PMID: 18428028 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effect of proIGF-II and IGF-II on resveratrol induced cell death by regulating survivin cellular localization and mitochondrial depolarization in breast cancer cells.Growth Factors. 2007 Dec;25(6):363-72. doi: 10.1080/08977190801886905. Growth Factors. 2007. PMID: 18365867 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1991 May;18 Suppl 1:S55-62. doi: 10.1007/BF02633529. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1991. PMID: 1651793 Review.
-
IGF-I and IGF-II expression in human breast cancer xenografts: relationship to hormone independence.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22(1):39-45. doi: 10.1007/BF01833332. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992. PMID: 1421423 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Intratumoral IGF-II Is Regulated by the Gene Imprinting Status in Triple Negative Breast Cancer from Vietnamese Patients.Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:401851. doi: 10.1155/2015/401851. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Int J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26448747 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of insulin and IGF signaling in breast cancer: Implications for therapy.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 May 1;527:111213. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111213. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33607269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 29;12(12):1992. doi: 10.3390/life12121992. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF2 knockdown in two colorectal cancer cell lines decreases survival, adhesion and modulates survival-associated genes.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12485-12495. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5115-x. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27337954
-
Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR Verifying Gene Expression Profile of Cavitations Within Human Jaw Bone.Biomedicines. 2025 May 8;13(5):1144. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051144. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program (SEER) SEER Stat Database: Mortality-All COD, Public-Use with State, Total U.S. for Expanded Races/Hispanics (1991–2001) National Cancer Institute, DC-CPS, Surveillance Research Program, Cancer Statistics Branch; 2004. Apr, Released http://www.seer.cancer.gov.
-
- Sciacca L, Constantino A, Pandini G, Mineo R, Frasca F, Scalia P, Sbraccia P, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Insulin receptor activation by IGF-II in breast cancers: evidence for a new autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Oncogene. 1999;18:2471–2479. - PubMed
-
- Pravtcheva DD, Wise TL. Metastazing mammary carcinomas in H19 enhancers-Igf2 transgenic mice. The Journal of Experimental Zoology. 1998;281:43–57. - PubMed
-
- Perdue JF, LeBon TR, Kato J, Hampton B, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Binding specificities and transducing function of the different molecular weight forms of IGF-II on IGF-IR. Endocrinology. 1991;129:3101–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

