Rad54, the motor of homologous recombination
- PMID: 20089461
- PMCID: PMC2827677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.12.006
Rad54, the motor of homologous recombination
Abstract
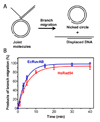
Homologous recombination (HR) performs crucial functions including DNA repair, segregation of homologous chromosomes, propagation of genetic diversity, and maintenance of telomeres. HR is responsible for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks and DNA interstrand cross-links. The process of HR is initiated at the site of DNA breaks and gaps and involves a search for homologous sequences promoted by Rad51 and auxiliary proteins followed by the subsequent invasion of broken DNA ends into the homologous duplex DNA that then serves as a template for repair. The invasion produces a cross-stranded structure, known as the Holliday junction. Here, we describe the properties of Rad54, an important and versatile HR protein that is evolutionarily conserved in eukaryotes. Rad54 is a motor protein that translocates along dsDNA and performs several important functions in HR. The current review focuses on the recently identified Rad54 activities which contribute to the late phase of HR, especially the branch migration of Holliday junctions.
(c) 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures









References
-
- Krogh BO, Symington LS. Recombination proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:233–271. - PubMed
-
- San Filippo J, Sung P, Klein H. Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:229–257. - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK. Multiple mechanisms of meiotic recombination. Cell. 2006;127:1095–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

