Blockade of endogenous tissue kallikrein aggravates renal injury by enhancing oxidative stress and inhibiting matrix degradation
- PMID: 20089675
- PMCID: PMC2853308
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00518.2009
Blockade of endogenous tissue kallikrein aggravates renal injury by enhancing oxidative stress and inhibiting matrix degradation
Abstract
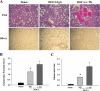
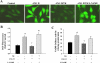
Levels of tissue kallikrein (TK) are significantly lower in the urine of patients with kidney failure, and TK expression is specifically diminished in rat kidney after recovery from ischemia-reperfusion injury. In this study, we investigated the functional consequence of blocking endogenous TK activity in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Inhibition of endogenous TK levels for 10 days by neutralizing TK antibody injection in DOCA-salt rats caused a significant increase in blood urea nitrogen and urinary protein levels, and a decrease in creatinine clearance. Kidney sections from anti-TK antibody-treated rats displayed a marked rise in tubular dilation and protein cast accumulation as well as glomerular sclerosis and size. TK blockade also increased inflammatory cell infiltration, myofibroblast and collagen accumulation, and collagen fraction volume. Elevated renal inflammation and fibrosis by anti-TK antibody were associated with increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). Moreover, the detrimental effect of TK blockade resulted in reduced nitric oxide (NO) levels as well as increased serum lipid peroxidation, renal NADH oxidase activity, and superoxide formation. In cultured proximal tubular cells, TK inhibited angiotensin II-induced superoxide production and NADH oxidase activity via NO formation. In addition, TK markedly increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity with a parallel reduction of TIMP-2 and PAI-1 synthesis. These findings indicate that endogenous TK has the propensity to preserve kidney structure and function in rats with chronic renal disease by inhibiting oxidative stress and activating matrix degradation pathways.
Figures


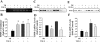
Similar articles
-
Depletion of endogenous kallistatin exacerbates renal and cardiovascular oxidative stress, inflammation, and organ remodeling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):F1230-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00257.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22811485 Free PMC article.
-
Kallikrein-modified mesenchymal stem cell implantation provides enhanced protection against acute ischemic kidney injury by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation.Hum Gene Ther. 2008 Aug;19(8):807-19. doi: 10.1089/hum.2008.016. Hum Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18554097 Free PMC article.
-
Salutary effect of kallistatin in salt-induced renal injury, inflammation, and fibrosis via antioxidative stress.Hypertension. 2008 May;51(5):1358-65. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.108514. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Hypertension. 2008. PMID: 18391098
-
[Molecular mechanisms of nephro-protective action of enalapril in experimental chronic renal failure].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999;Suppl 52:1-93. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999. PMID: 10589103 Review. Polish.
-
Kallikrein-kinin in stroke, cardiovascular and renal disease.Exp Physiol. 2005 May;90(3):291-8. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2004.028464. Epub 2005 Jan 14. Exp Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15653716 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue kallikrein activation of the epithelial Na channel.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;303(4):F540-50. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00133.2012. Epub 2012 May 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22622459 Free PMC article.
-
The attenuation of Moutan Cortex on oxidative stress for renal injury in AGEs-induced mesangial cell dysfunction and streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:463815. doi: 10.1155/2014/463815. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24876912 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically‑modified stem cells in treatment of human diseases: Tissue kallikrein (KLK1)‑based targeted therapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2018 Mar;41(3):1177-1186. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3361. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29328364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin protects cardiomyocytes from cell death during hypoxia/reperfusion injury through activation of survival signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 19;9(9):e107453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107453. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25237819 Free PMC article.
-
Kallikrein-kinin in stem cell therapy.World J Stem Cells. 2014 Sep 26;6(4):448-57. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i4.448. World J Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 25258666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azizi M, Emanueli C, Peyrard S, Maddedu P, Alhenc-Gelas F, Campbell DJ. Genetic and dietary control of plasma tissue kallikrein secretion and urinary kinins exretion in man. J Hypertens 26: 714–720, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Basile DP, Fredrich K, Alausa M, Vio CP, Liang M, Rieder MR, Greene AS, Cowley AW., Jr Identification of persistently altered gene expression in the kidney after functional recovery from ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F953–F963, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bledsoe G, Crickman S, Mao J, Xia CF, Murakami H, Chao L, Chao J. Kallikrein/kinin protects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 624–633, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bledsoe G, Shen B, Yao Y, Zhang JJ, Chao L, Chao J. Reversal of renal fibrosis, inflammation, and glomerular hypertrophy by kallikrein gene delivery. Hum Gene Ther 17: 545–555, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Catania JM, Chen G, Parrish AR. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in renal pathophysiologies. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292: F905–F911, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

