Ro60-associated single-stranded RNA links inflammation with fetal cardiac fibrosis via ligation of TLRs: a novel pathway to autoimmune-associated heart block
- PMID: 20089705
- PMCID: PMC3551297
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902248
Ro60-associated single-stranded RNA links inflammation with fetal cardiac fibrosis via ligation of TLRs: a novel pathway to autoimmune-associated heart block
Abstract
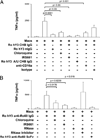
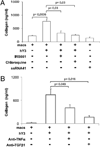
Activation of TLR by ssRNA after FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis of immune complexes (IC) may be relevant in autoimmune-associated congenital heart block (CHB) where the obligate factor is a maternal anti-SSA/Ro Ab and the fetal factors, protein/RNA on an apoptotic cardiocyte and infiltrating macrophages. This study addressed the hypothesis that Ro60-associated ssRNAs link macrophage activation to fibrosis via TLR engagement. Both macrophage transfection with noncoding ssRNA that bind Ro60 and an IC generated by incubation of Ro60-ssRNA with an IgG fraction from a CHB mother or affinity purified anti-Ro60 significantly increased TNF-alpha secretion, an effect not observed using control RNAs or normal IgG. Dependence on TLR was supported by the significant inhibition of TNF-alpha release by IRS661 and chloroquine. The requirement for FcgammaRIIIa-mediated delivery was provided by inhibition with an anti-CD16a Ab. Fibrosis markers were noticeably increased in fetal cardiac fibroblasts after incubation with supernatants generated from macrophages transfected with ssRNA or incubated with the IC. Supernatants generated from macrophages with ssRNA in the presence of IRS661 or chloroquine did not cause fibrosis. In a CHB heart, but not a healthy heart, TLR7 immunostaining was localized to a region near the atrioventricular groove at a site enriched in mononuclear cells and fibrosis. These data support a novel injury model in CHB, whereby endogenous ligand, Ro60-associated ssRNA, forges a nexus between TLR ligation and fibrosis instigated by binding of anti-Ro Abs to the target protein likely accessible via apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Brucato A, Frassi M, Franceschini F, Cimaz R, Faden D, Pisoni MP, Muscarà M, Vignati G, Stramba-Badiale M, Catelli L, et al. Risk of congenital complete heart block in newborns of mothers with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies detected by counterimmunoelectrophoresis: a prospective study of 100 women. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1832–1835. - PubMed
-
- Buyon JP, Clancy RM. Neonatal lupus. In: Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, editors. Dubois’ Lupus Erythematosus. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. pp. 1058–1080.
-
- Nield LE, Silverman ED, Smallhorn JF, Taylor GP, Mullen JB, Benson LN, Hornberger LK. Endocardial fibroelastosis associated with maternal anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies in the absence of atrioventricular block. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002;40:796–802. - PubMed
-
- Clancy RM, Backer CB, Yin X, Kapur RP, Molad Y, Buyon JP. Cytokine polymorphisms and histologic expression in autopsy studies: contribution of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta 1 to the pathogenesis of autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. J. Immunol. 2003;171:3253–3261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

