Melanocortins induce interleukin 6 gene expression and secretion through melanocortin receptors 2 and 5 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 20089716
- PMCID: PMC3058511
- DOI: 10.1677/JME-09-0161
Melanocortins induce interleukin 6 gene expression and secretion through melanocortin receptors 2 and 5 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
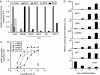
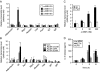
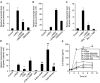
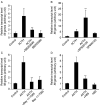
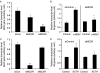
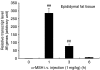
Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a pleiotropic cytokine that not only affects the immune system, but also plays an active role in many physiological events in various organs. Notably, 35% of systemic IL6 originates from adipose tissues under noninflammatory conditions. Here, we describe a previously unknown function of melanocortins in regulating Il6 gene expression and production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through membrane receptors which are called melanocortin receptors (MCRs). Of the five MCRs that have been cloned, MC2R and MC5R are expressed during adipocyte differentiation. alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) or ACTH treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes induces Il6 gene expression and production in a time- and concentration-dependent manner via various signaling pathways including the protein kinase A, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, cJun N-terminal kinase, and IkappaB kinase pathways. Specific inhibition of MC2R and MC5R expression with short interfering Mc2r and Mc5r RNAs significantly attenuated the alpha-MSH-induced increase of intracellular cAMP and both the level of Il6 mRNA and secretion of IL6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Finally, when injected into mouse tail vein, alpha-MSH dramatically increased the Il6 transcript levels in epididymal fat pads. These results suggest that alpha-MSH in addition to ACTH may function as a regulator of inflammation by regulating cytokine production.
Figures

References
-
- Ajuwon KM, Spurlock ME. Palmitate activates the NF-κB transcription factor and induces IL-6 and TNFalpha expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Journal of Nutrition. 2005;135:1841–1846. - PubMed
-
- An J, Sun Y, Sun R, Rettig MB. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoded vFLIP induces cellular IL-6 expression: the role of the NF-κB and JNK/AP1 pathways. Oncogene. 2003;22:3371–3385. - PubMed
-
- An JJ, Rhee Y, Kim SH, Kim DM, Han DH, Hwang JH, Jin YJ, Cha BS, Baik JH, Lee WT, et al. Peripheral effect of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;282:2862–2870. - PubMed
-
- Antunes TT, Gagnon A, Chen B, Pacini F, Smith TJ, Sorisky A. Interleukin-6 release from human abdominal adipose cells is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone: effect of adipocyte differentiation and anatomic depot. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2006;290:E1140–E1144. - PubMed
-
- Antunes TT, Gagnon A, Langille ML, Sorisky A. Thyroid-stimulating hormone induces interleukin-6 release from human adipocytes through activation of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Endocrinology. 2008;149:3062–3066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

