Biological and structural basis for Aha1 regulation of Hsp90 ATPase activity in maintaining proteostasis in the human disease cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 20089831
- PMCID: PMC2836968
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-12-1017
Biological and structural basis for Aha1 regulation of Hsp90 ATPase activity in maintaining proteostasis in the human disease cystic fibrosis
Abstract
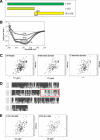
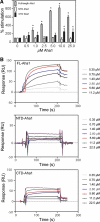
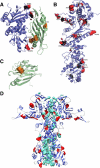
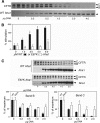
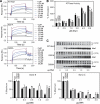
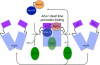
The activator of Hsp90 ATPase 1, Aha1, has been shown to participate in the Hsp90 chaperone cycle by stimulating the low intrinsic ATPase activity of Hsp90. To elucidate the structural basis for ATPase stimulation of human Hsp90 by human Aha1, we have developed novel mass spectrometry approaches that demonstrate that the N- and C-terminal domains of Aha1 cooperatively bind across the dimer interface of Hsp90 to modulate the ATP hydrolysis cycle and client activity in vivo. Mutations in both the N- and C-terminal domains of Aha1 impair its ability to bind Hsp90 and stimulate its ATPase activity in vitro and impair in vivo the ability of the Hsp90 system to modulate the folding and trafficking of wild-type and variant (DeltaF508) cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) responsible for the inherited disease cystic fibrosis (CF). We now propose a general model for the role of Aha1 in the Hsp90 ATPase cycle in proteostasis whereby Aha1 regulates the dwell time of Hsp90 with client. We suggest that Aha1 activity integrates chaperone function with client folding energetics by modulating ATPase sensitive N-terminal dimer structural transitions, thereby protecting transient folding intermediates in vivo that could contribute to protein misfolding systems disorders such as CF when destabilized.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hsp90 cochaperone Aha1 downregulation rescues misfolding of CFTR in cystic fibrosis.Cell. 2006 Nov 17;127(4):803-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.043. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17110338
-
Ordered ATP hydrolysis in the Hsp90 chaperone is regulated by Aha1 and a conserved post-translational modification.Protein Sci. 2025 Jan;34(1):e5255. doi: 10.1002/pro.5255. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39665290 Free PMC article.
-
Co-chaperone regulation of conformational switching in the Hsp90 ATPase cycle.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 10;279(50):51989-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410562200. Epub 2004 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15466438
-
p23 and Aha1: Distinct Functions Promote Client Maturation.Subcell Biochem. 2023;101:159-187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14740-1_6. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36520307 Review.
-
p23 and Aha1.Subcell Biochem. 2015;78:113-31. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-11731-7_6. Subcell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25487019 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp90 co-chaperones, FKBP52 and Aha1, promote tau pathogenesis in aged wild-type mice.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Apr 8;9(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01159-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 33832539 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SNPs in the cystic fibrosis interactome influencing pulmonary progression in cystic fibrosis.Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Apr;21(4):397-403. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.181. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 22892532 Free PMC article.
-
Aha1 Exhibits Distinctive Dynamics Behavior and Chaperone-Like Activity.Molecules. 2021 Mar 30;26(7):1943. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071943. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33808352 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Hsp90 ATPase Stimulation by Aha1.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 12;6:33179. doi: 10.1038/srep33179. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27615124 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydropyridines Allosterically Modulate Hsp90 Providing a Novel Mechanism for Heat Shock Protein Co-induction and Neuroprotection.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jun 7;5:51. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00051. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29930942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aridor M., Bannykh S. I., Rowe T., Balch W. E. Cargo can modulate COPII vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:4389–4399. - PubMed
-
- Balch W. E., Morimoto R. I., Dillin A., Kelly J. W. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Fuller W., Cuthbert A. W. Post-translational disruption of the delta F508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)-molecular chaperone complex with geldanamycin stabilizes delta F508 CFTR in the rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:37462–37468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

