Emi2 inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome absolutely requires Emi2 binding via the C-terminal RL tail
- PMID: 20089832
- PMCID: PMC2836971
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-11-0974
Emi2 inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome absolutely requires Emi2 binding via the C-terminal RL tail
Abstract
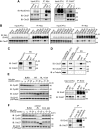
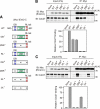
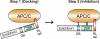
Emi2 (also called Erp1) inhibits the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and thereby causes metaphase II arrest in unfertilized vertebrate eggs. Both the D-box and the zinc-binding region (ZBR) of Emi2 have been implicated in APC/C inhibition. However, it is not well known how Emi2 interacts with and hence inhibits the APC/C. Here we show that Emi2 binds the APC/C via the C-terminal tail, termed here the RL tail. When expressed in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts, Emi2 lacking the RL tail fails to interact with and inhibit the APC/C. The RL tail itself can directly bind to the APC/C, and, when added to egg extracts, either an excess of RL tail peptides or anti-RL tail peptide antibody can dissociate endogenous Emi2 from the APC/C, thus allowing APC/C activation. Furthermore, and importantly, the RL tail-mediated binding apparently promotes the inhibitory interactions of the D-box and the ZBR (of Emi2) with the APC/C. Finally, Emi1, a somatic paralog of Emi2, also has a functionally similar RL tail. We propose that the RL tail of Emi1/Emi2 serves as a docking site for the APC/C, thereby promoting the interaction and inhibition of the APC/C by the D-box and the ZBR.
Figures

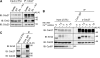

Similar articles
-
A role for the anaphase-promoting complex inhibitor Emi2/XErp1, a homolog of early mitotic inhibitor 1, in cytostatic factor arrest of Xenopus eggs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 22;102(12):4318-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501108102. Epub 2005 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15753281 Free PMC article.
-
Emi2-mediated inhibition of E2-substrate ubiquitin transfer by the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome through a D-box-independent mechanism.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Aug 1;21(15):2589-97. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-08-0708. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20534816 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Erp1 by p90rsk is required for cytostatic factor arrest in Xenopus laevis eggs.Nature. 2007 Apr 26;446(7139):1096-9. doi: 10.1038/nature05696. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17410129
-
Cytostatic factor: an activity that puts the cell cycle on hold.J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 1;119(Pt 7):1213-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02919. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16554437 Review.
-
Across the meiotic divide - CSF activity in the post-Emi2/XErp1 era.J Cell Sci. 2008 Nov 1;121(Pt 21):3509-14. doi: 10.1242/jcs.036855. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18946022 Review.
Cited by
-
TDM1 Regulation Determines the Number of Meiotic Divisions.PLoS Genet. 2016 Feb 12;12(2):e1005856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005856. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26871453 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Emi2 as a distinctive regulatory hub in second meiotic metaphase.Development. 2010 Oct;137(19):3281-91. doi: 10.1242/dev.052480. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Development. 2010. PMID: 20724447 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis ULTRAVIOLET-B-INSENSITIVE4 maintains cell division activity by temporal inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome.Plant Cell. 2011 Dec;23(12):4394-410. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.091793. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 22167059 Free PMC article.
-
State of the APC/C: organization, function, and structure.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;46(2):118-36. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.541420. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21261459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electron microscopy structure of human APC/C(CDH1)-EMI1 reveals multimodal mechanism of E3 ligase shutdown.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;20(7):827-35. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2593. Epub 2013 May 26. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23708605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castro A., Bernis C., Vigneron S., Labbe J. C., Lorca T. The anaphase-promoting complex: a key factor in the regulation of cell cycle. Oncogene. 2005;24:314–325. - PubMed
-
- Ellman G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959;82:70–77. - PubMed
-
- Gross S. D., Schwab M. S., Taieb F. E., Lewellyn A. L., Qian Y. W., Maller J. L. The critical role of the MAP kinase pathway in meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes is mediated by p90Rsk. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:430–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

