Vesicular calcium regulates coat retention, fusogenicity, and size of pre-Golgi intermediates
- PMID: 20089833
- PMCID: PMC2836956
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-10-0914
Vesicular calcium regulates coat retention, fusogenicity, and size of pre-Golgi intermediates
Abstract
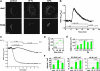
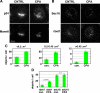
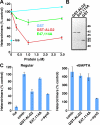
The significance and extent of Ca(2+) regulation of the biosynthetic secretory pathway have been difficult to establish, and our knowledge of regulatory relationships integrating Ca(2+) with vesicle coats and function is rudimentary. Here, we investigated potential roles and mechanisms of luminal Ca(2+) in the early secretory pathway. Specific depletion of luminal Ca(2+) in living normal rat kidney cells using cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) resulted in the extreme expansion of vesicular tubular cluster (VTC) elements. Consistent with this, a suppressive role for vesicle-associated Ca(2+) in COPII vesicle homotypic fusion was demonstrated in vitro using Ca(2+) chelators. The EF-hand-containing protein apoptosis-linked gene 2 (ALG-2), previously implicated in the stabilization of sec31 at endoplasmic reticulum exit sites, inhibited COPII vesicle fusion in a Ca(2+)-requiring manner, suggesting that ALG-2 may be a sensor for the effects of vesicular Ca(2+) on homotypic fusion. Immunoisolation established that Ca(2+) chelation inhibits and ALG-2 specifically favors residual retention of the COPII outer shell protein sec31 on pre-Golgi fusion intermediates. We conclude that vesicle-associated Ca(2+), acting through ALG-2, favors the retention of residual coat molecules that seem to suppress membrane fusion. We propose that in cells, these Ca(2+)-dependent mechanisms temporally regulate COPII vesicle interactions, VTC biogenesis, cargo sorting, and VTC maturation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ALG-2 attenuates COPII budding in vitro and stabilizes the Sec23/Sec31A complex.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 19;8(9):e75309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075309. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069399 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of COPII vesicle fusion to generate a pre-Golgi intermediate compartment.J Cell Biol. 2004 Dec 20;167(6):997-1003. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200408135. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15611329 Free PMC article.
-
Steady-state regulation of COPII-dependent secretory cargo sorting by inositol trisphosphate receptors, calcium, and penta EF hand proteins.J Biol Chem. 2023 Dec;299(12):105471. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105471. Epub 2023 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37979918 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the golgi.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013367. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013367. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptor functions of the Ca2+-binding protein ALG-2 in protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019 Jan;83(1):20-32. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2018.1525274. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30259798 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural characterization of carbohydrate binding by LMAN1 protein provides new insight into the endoplasmic reticulum export of factors V (FV) and VIII (FVIII).J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20499-509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.461434. Epub 2013 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23709226 Free PMC article.
-
Annexins as Overlooked Regulators of Membrane Trafficking in Plant Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 19;18(4):863. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040863. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28422051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a dihydropyridine scaffold that blocks ryanodine receptors.iScience. 2021 Dec 27;25(1):103706. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103706. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35059610 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Nitric Oxide (NO•) Probes, the geNOps, for Real-time Imaging of NO• Signals in Single Cells.J Vis Exp. 2017 Mar 16;(121):55486. doi: 10.3791/55486. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28362417 Free PMC article.
-
Coat/Tether Interactions-Exception or Rule?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 May 17;4:44. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00044. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27243008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahluwalia J. P., Topp J. D., Weirather K., Zimmerman M., Stamnes M. A role for calcium in stabilizing transport vesicle coats. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:34148–34155. - PubMed
-
- Allan B. B., Moyer B. D., Balch W. E. Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science. 2000;289:444–448. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez C., Garcia-Mata R., Hauri H. P., Sztul E. The p115-interactive proteins GM130 and giantin participate in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi traffic. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:2693–2700. - PubMed
-
- Amodio G., Renna M., Paladino S., Venturi C., Tacchetti C., Moltedo O., Franceschelli S., Mallardo M., Bonatti S., Remondelli P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress reduces the export from the ER and alters the architecture of post-ER compartments. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009;41:2511–2521. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C., Roche A. C., Nufer O., Hauri H. P. pH-induced conversion of the transport lectin ERGIC-53 triggers glycoprotein release. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:12943–12950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

