The RhoA activator GEF-H1/Lfc is a transforming growth factor-beta target gene and effector that regulates alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and cell migration
- PMID: 20089843
- PMCID: PMC2836967
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0567
The RhoA activator GEF-H1/Lfc is a transforming growth factor-beta target gene and effector that regulates alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and cell migration
Abstract
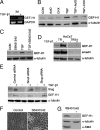
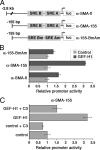
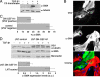
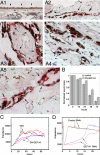
Maintenance of the epithelial phenotype is crucial for tissue homeostasis. In the retina, dedifferentiation and loss of integrity of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) leads to retinal dysfunction and fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta critically contributes to RPE dedifferentiation and induces various responses, including increased Rho signaling, up-regulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA), and cell migration and dedifferentiation. Cellular TGF-beta responses are stimulated by different signal transduction pathways: some are Smad dependent and others Smad independent. Alterations in Rho signaling are crucial to both types of TGF-beta signaling, but how TGF-beta-stimulates Rho signaling is poorly understood. Here, we show that primary RPE cells up-regulated GEF-H1 in response to TGF-beta. GEF-H1 was the only detectable Rho exchange factor increased by TGF-beta1 in a genome-wide expression analysis. GEF-H1 induction was Smad4-dependant and led to Rho activation. GEF-H1 inhibition counteracted alpha-SMA up-regulation and cell migration. In patients with retinal detachments and fibrosis, migratory RPE cells exhibited increased GEF-H1 expression, indicating that induction occurs in diseased RPE in vivo. Our data indicate that GEF-H1 is a target and functional effector of TGF-beta by orchestrating Rho signaling to regulate gene expression and cell migration, suggesting that it represents a new marker and possible therapeutic target for degenerative and fibrotic diseases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 regulates cell migration via localized activation of RhoA at the leading edge.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(18):4070-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0041. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19625450 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity-regulating kinase partitioning-defective 1b (PAR1b) phosphorylates guanine nucleotide exchange factor H1 (GEF-H1) to regulate RhoA-dependent actin cytoskeletal reorganization.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 30;286(52):44576-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.267021. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22072711 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the RhoA exchange factor GEF-H1 by profibrotic stimuli through a positive feedback loop involving RhoA, MRTF, and Sp1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Aug 1;327(2):C387-C402. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00088.2024. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38912734
-
Cellular functions of GEF-H1, a microtubule-regulated Rho-GEF: is altered GEF-H1 activity a crucial determinant of disease pathogenesis?Trends Cell Biol. 2008 May;18(5):210-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.02.006. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18394899 Review.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
GEF-H1 is necessary for neutrophil shear stress-induced migration during inflammation.J Cell Biol. 2016 Oct 10;215(1):107-119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201603109. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27738004 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory microenvironment contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 7;22(29):6619-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6619. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27547005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational activation of BRAF confers sensitivity to transforming growth factor beta inhibitors in human cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):81995-82012. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13226. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835901 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual Role of TGFβ in Human Cancer: From Tumor Suppression to Cancer Metastasis.ISRN Mol Biol. 2012 Dec 24;2012:381428. doi: 10.5402/2012/381428. eCollection 2012. ISRN Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 27340590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal control of actomyosin contractility by MRCKβ signaling drives phagocytosis.J Cell Biol. 2022 Nov 7;221(11):e202012042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202012042. Epub 2022 Sep 19. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36121394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aijaz S., D'Atri F., Citi S., Balda M. S., Matter K. Binding of GEF-H1 to the tight junction-associated adaptor cingulin results in inhibition of Rho signaling and G1/S phase transition. Dev. Cell. 2005;8:777–786. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge J. W., Stephens C., Parsley K., Demaison C., Halfyard A., Thrasher A. J., Ali R. R. In vivo gene transfer to the mouse eye using an HIV-based lentiviral vector; efficient long-term transduction of corneal endothelium and retinal pigment epithelium. Gene Ther. 2001;8:1665–1668. - PubMed
-
- Bakin A. V., Rinehart C., Tomlinson A. K., Arteaga C. L. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFbeta-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:3193–3206. - PubMed
-
- Benais-Pont G., Punn A., Flores-Maldonado C., Eckert J., Raposo G., Fleming T. P., Cereijido M., Balda M. S., Matter K. Identification of a tight junction-associated guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates Rho and regulates paracellular permeability. J. Cell Biol. 2003;160:729–740. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

