Gq-coupled purinergic receptors inhibit insulin-like growth factor-I/phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway-dependent keratinocyte migration
- PMID: 20089844
- PMCID: PMC2836975
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0497
Gq-coupled purinergic receptors inhibit insulin-like growth factor-I/phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway-dependent keratinocyte migration
Abstract
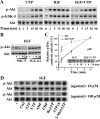
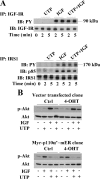
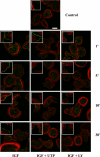
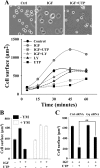
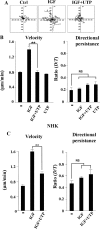
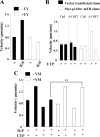
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) activation of phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is an essential pathway for keratinocyte migration that is required for epidermis wound healing. We have previously reported that activation of Galpha((q/11))-coupled-P2Y(2) purinergic receptors by extracellular nucleotides delays keratinocyte wound closure. Here, we report that activation of P2Y(2) receptors by extracellular UTP inhibits the IGF-I-induced p110alpha-PI3K activation. Using siRNA and pharmacological inhibitors, we demonstrate that the UTP antagonistic effects on PI3K pathway are mediated by Galpha((q/11))-and not G((i/o))-independently of phospholipase Cbeta. Purinergic signaling does not affect the formation of the IGF-I receptor/insulin receptor substrate-I/p85 complex, but blocks the activity of a membrane-targeted active p110alpha mutant, indicating that UTP acts downstream of PI3K membrane recruitment. UTP was also found to efficiently attenuate, within few minutes, the IGF-I-induced PI3K-controlled translocation of the actin-nucleating protein cortactin to the plasma membrane. This supports the UTP ability to alter later migratory events. Indeed, UTP inhibits keratinocyte spreading and migration promoted by either IGF-I or a membrane-targeted active p110alpha mutant, in a Galpha(q/11)-dependent manner both. These findings provide new insight into the signaling cross-talk between receptor tyrosine kinase and Galpha((q/11))-coupled receptors, which mediate opposite effects on p110alpha-PI3K activity and keratinocyte migration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
G alpha(q/11)-coupled P2Y2 nucleotide receptor inhibits human keratinocyte spreading and migration.FASEB J. 2007 Dec;21(14):4047-58. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7476com. Epub 2007 Jul 3. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17609252
-
P2Y2 receptor-Gq/11 signaling at lipid rafts is required for UTP-induced cell migration in NG 108-15 cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Sep 1;334(3):809-19. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.167528. Epub 2010 May 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20511347
-
A novel Galphaq/11-selective inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):47438-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408846200. Epub 2004 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15339913
-
Gαq signalling: the new and the old.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24440667 Review.
-
P2Y2 nucleotide receptor-mediated responses in brain cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;41(2-3):356-66. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8115-7. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20387013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential roles of CXCL2 and CXCL3 and their receptors in regulating normal and asthmatic airway smooth muscle cell migration.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 1;191(5):2731-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203421. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23904157 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y4 receptor-mediated pinocytosis contributes to amyloid beta-induced self-uptake by microglia.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;33(21):4282-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00544-13. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24001770 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal loss of Gαq confers a migratory and differentiation defect in keratinocytes.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0173692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173692. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28301547 Free PMC article.
-
PKD1 mediates negative feedback of PI3K/Akt activation in response to G protein-coupled receptors.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e73149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073149. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039875 Free PMC article.
-
Gαq Is the Specific Mediator of PAR-1 Transactivation of Kinase Receptors in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 20;23(22):14425. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214425. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert P. R., Robillard L. G protein specificity: traffic direction required. Cell Signal. 2002;14:407–418. - PubMed
-
- Ando Y., Jensen P. J. Epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I enhance keratinocyte migration. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1993;100:633–639. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson P. J., Young K. W., Ennion S. J., Kew J. N., Nahorski S. R., Challiss R. A. Altered expression of G(q/11alpha) protein shapes mGlu1 and mGlu5 receptor-mediated single cell inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and Ca(2+) signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006;69:174–184. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi S., Liao Z., Gonzalez F. A., Chorna N. E., Seye C. I., Weisman G. A., Erb L. The P2Y2 nucleotide receptor interacts with alphav integrins to activate Go and induce cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:39050–39057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

