Calcium as a crucial cofactor for low density lipoprotein receptor folding in the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 20089850
- PMCID: PMC2838288
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105718
Calcium as a crucial cofactor for low density lipoprotein receptor folding in the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
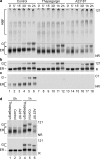
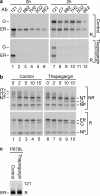
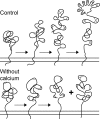
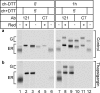
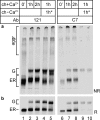
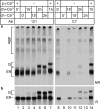
The family of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors mediate uptake of a plethora of ligands from the circulation and couple this to signaling, thereby performing a crucial role in physiological processes including embryonic development, cancer development, homeostasis of lipoproteins, viral infection, and neuronal plasticity. Structural integrity of individual ectodomain modules in these receptors depends on calcium, and we showed before that the LDL receptor folds its modules late after synthesis via intermediates with abundant non-native disulfide bonds and structure. Using a radioactive pulse-chase approach, we here show that for proper LDL receptor folding, calcium had to be present from the very early start of folding, which suggests at least some native, essential coordination of calcium ions at the still largely non-native folding phase. As long as the protein was in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), its folding was reversible, which changed only upon both proper incorporation of calcium and exit from the ER. Coevolution of protein folding with the high calcium concentration in the ER may be the basis for the need for this cation throughout the folding process even though calcium is only stably integrated in native repeats at a later stage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Observing the nonvectorial yet cotranslational folding of a multidomain protein, LDL receptor, in the ER of mammalian cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 14;117(28):16401-16408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004606117. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32601215 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated nonvectorial folding in a newly synthesized multidomain protein.Science. 2002 Dec 20;298(5602):2401-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1078376. Science. 2002. PMID: 12493918
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor structure and folding.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Oct;61(19-20):2461-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4090-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15526154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folding, calcium binding, and structural characterization of a concatemer of the first and second ligand-binding modules of the low-density lipoprotein receptor.Biochemistry. 1998 Aug 4;37(31):10994-1002. doi: 10.1021/bi980452c. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9692993
-
The many functions of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and folding enzymes.IUBMB Life. 2014 May;66(5):318-26. doi: 10.1002/iub.1272. Epub 2014 May 19. IUBMB Life. 2014. PMID: 24839203 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox-Mediated Regulatory Mechanisms of Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 May 1;11(5):a033910. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033910. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30396882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein secretion and the endoplasmic reticulum.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Aug 1;4(8):a012872. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012872. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22700933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERdj5 is the ER reductase that catalyzes the removal of non-native disulfides and correct folding of the LDL receptor.Mol Cell. 2013 Jun 27;50(6):793-804. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.014. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23769672 Free PMC article.
-
Observing the nonvectorial yet cotranslational folding of a multidomain protein, LDL receptor, in the ER of mammalian cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 14;117(28):16401-16408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004606117. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32601215 Free PMC article.
-
Divalent cations regulate the folding and activation status of integrins during their intracellular trafficking.J Cell Sci. 2011 May 15;124(Pt 10):1672-80. doi: 10.1242/jcs.084483. Epub 2011 Apr 21. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21511727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeon H., Blacklow S. C. (2005) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 535–562 - PubMed
-
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. (1974) Science 185, 61–63 - PubMed
-
- Willnow T. E., Nykjaer A., Herz J. (1999) Nat. Cell Biol. 1, E157–162 - PubMed
-
- May P., Bock H. H., Herz J. (2003) Sci. STKE 2003, PE12. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. (1984) Cell 39, 27–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

