Global conformational change associated with the two-step reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli lipoate-protein ligase A
- PMID: 20089862
- PMCID: PMC2843243
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.078717
Global conformational change associated with the two-step reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli lipoate-protein ligase A
Abstract
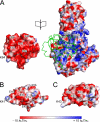
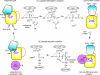
Lipoate-protein ligase A (LplA) catalyzes the attachment of lipoic acid to lipoate-dependent enzymes by a two-step reaction: first the lipoate adenylation reaction and, second, the lipoate transfer reaction. We previously determined the crystal structure of Escherichia coli LplA in its unliganded form and a binary complex with lipoic acid (Fujiwara, K., Toma, S., Okamura-Ikeda, K., Motokawa, Y., Nakagawa, A., and Taniguchi, H. (2005) J Biol. Chem. 280, 33645-33651). Here, we report two new LplA structures, LplA.lipoyl-5'-AMP and LplA.octyl-5'-AMP.apoH-protein complexes, which represent the post-lipoate adenylation intermediate state and the pre-lipoate transfer intermediate state, respectively. These structures demonstrate three large scale conformational changes upon completion of the lipoate adenylation reaction: movements of the adenylate-binding and lipoate-binding loops to maintain the lipoyl-5'-AMP reaction intermediate and rotation of the C-terminal domain by about 180 degrees . These changes are prerequisites for LplA to accommodate apoprotein for the second reaction. The Lys(133) residue plays essential roles in both lipoate adenylation and lipoate transfer reactions. Based on structural and kinetic data, we propose a reaction mechanism driven by conformational changes.
Figures
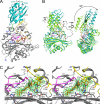

Similar articles
-
Lipoic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: the lplA and lipB genes define redundant pathways for ligation of lipoyl groups to apoprotein.J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):1-10. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.1-10.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 8002607 Free PMC article.
-
The Thermoplasma acidophilum LplA-LplB complex defines a new class of bipartite lipoate-protein ligases.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 7;284(32):21317-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.015016. Epub 2009 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19520844 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the gene encoding lipoate-protein ligase A of Escherichia coli. Molecular cloning and characterization of the lplA gene and gene product.J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16091-100. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8206909
-
Structure of a putative lipoate protein ligase from Thermoplasma acidophilum and the mechanism of target selection for post-translational modification.J Mol Biol. 2006 Feb 24;356(3):625-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.057. Epub 2005 Dec 5. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16384580 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid attachment to proteins: stimulating new developments.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0000524. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00005-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38624243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Apr 13;80(2):429-50. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00073-15. Print 2016 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27074917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational design of conformation-biasing mutations to alter protein functions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 2:2025.05.03.652001. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.03.652001. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501788 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Structural basis for catalysis by human lipoyl synthase.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 10;16(1):6355. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61393-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40640146 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae lipoate protein ligase homologue, Lip3, in lipoic acid synthesis.Yeast. 2013 Oct;30(10):415-27. doi: 10.1002/yea.2979. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Yeast. 2013. PMID: 23960015 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of a red fluorophore ligase for site-specific protein labeling in living cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 28;111(43):E4551-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404736111. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25313043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reed L. J., Hackert M. L. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 8971–8974 - PubMed
-
- Perham R. N. (1991) Biochemistry 30, 8501–8512 - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara K., Okamura-Ikeda K., Motokawa Y. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8836–8841 - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara K., Okamura-Ikeda K., Motokawa Y. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 20011–20016 - PubMed
-
- Morris T. W., Reed K. E., Cronan J. E., Jr. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 16091–16100 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

