In vivo diffusion tensor imaging and histopathology of the fimbria-fornix in temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 20089908
- PMCID: PMC6633109
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1619-09.2010
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging and histopathology of the fimbria-fornix in temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
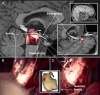
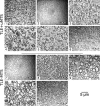
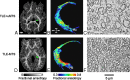
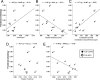
While diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been extensively used to infer micro-structural characteristics of cerebral white matter in human conditions, correlations between human in vivo DTI and histology have not been performed. Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) patients with mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS) have abnormal DTI parameters of the fimbria-fornix (relative to TLE patients without MTS) which are presumed to represent differences in axonal/myelin integrity. Medically intractable TLE patients who undergo temporal lobe resection including the fimbria-fornix provide a unique opportunity to study the anatomical correlates of water diffusion abnormalities in freshly excised tissue. Eleven patients with medically intractable TLE were recruited (six with and five without MTS) for presurgical DTI followed by surgical excision of a small specimen of the fimbria-fornix which was processed for electron microscopy. Blinded quantitative analysis of the microphotographs included axonal diameter, density and area, cumulative axon membrane circumference, and myelin thickness and area. As predicted by DTI the fimbria-fornix of TLE patients with MTS had increased extra-axonal fraction, and reduced cumulative axonal membrane circumference and myelin area. Consistent with the animal literature, water diffusion anisotropy over the crus of the fimbria-fornix was strongly correlated with axonal membranes (cumulative membrane circumference) within the surgical specimen (approximately 15% of what was analyzed with DTI). The demonstration of a correlation between histology and human in vivo DTI, in combination with the observation that in vivo DTI accurately predicted white matter abnormalities in a human disease condition, provides strong validation of the application of DTI as a noninvasive marker of white matter pathology.
Figures

References
-
- Arfanakis K, Hermann BP, Rogers BP, Carew JD, Seidenberg M, Meyerand ME. Diffusion tensor MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy. Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;20:511–519. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system-a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002;15:435–455. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu C, Allen PS. Determinants of anisotropic water diffusion in nerves. Magn Reson Med. 1994a;31:394–400. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu C, Allen PS. Water diffusion in the giant axon of the squid: implications for diffusion-weighted MRI of the nervous system. Magn Reson Med. 1994b;32:579–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
