Alpha2-adrenoceptor blockade accelerates the neurogenic, neurotrophic, and behavioral effects of chronic antidepressant treatment
- PMID: 20089918
- PMCID: PMC2880491
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2309-09.2010
Alpha2-adrenoceptor blockade accelerates the neurogenic, neurotrophic, and behavioral effects of chronic antidepressant treatment
Abstract
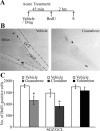
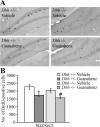
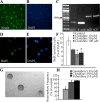
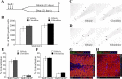
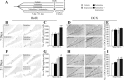
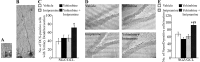
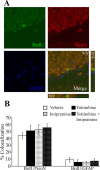
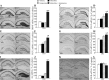
Slow-onset adaptive changes that arise from sustained antidepressant treatment, such as enhanced adult hippocampal neurogenesis and increased trophic factor expression, play a key role in the behavioral effects of antidepressants. alpha(2)-Adrenoceptors contribute to the modulation of mood and are potential targets for the development of faster acting antidepressants. We investigated the influence of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Our results indicate that alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists, clonidine and guanabenz, decrease adult hippocampal neurogenesis through a selective effect on the proliferation, but not the survival or differentiation, of progenitors. These effects persist in dopamine beta-hydroxylase knock-out (Dbh(-/-)) mice lacking norepinephrine, supporting a role for alpha(2)-heteroceptors on progenitor cells, rather than alpha(2)-autoreceptors on noradrenergic neurons that inhibit norepinephrine release. Adult hippocampal progenitors in vitro express all the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor subtypes, and decreased neurosphere frequency and BrdU incorporation indicate direct effects of alpha(2)-adrenoceptor stimulation on progenitors. Furthermore, coadministration of the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine with the antidepressant imipramine significantly accelerates effects on hippocampal progenitor proliferation, the morphological maturation of newborn neurons, and the increase in expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor and vascular endothelial growth factor implicated in the neurogenic and behavioral effects of antidepressants. Finally, short-duration (7 d) yohimbine and imipramine treatment results in robust behavioral responses in the novelty suppressed feeding test, which normally requires 3 weeks of treatment with classical antidepressants. Our results demonstrate that alpha(2)-adrenoceptors, expressed by progenitor cells, decrease adult hippocampal neurogenesis, while their blockade speeds up antidepressant action, highlighting their importance as targets for faster acting antidepressants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippocampal transcriptional and neurogenic changes evoked by combination yohimbine and imipramine treatment.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Aug 3;61:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25784603
-
Enhanced sensitivity of the MRL/MpJ mouse to the neuroplastic and behavioral effects of chronic antidepressant treatments.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jun;34(7):1764-73. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.234. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19177066 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenoceptor mechanisms underlying imipramine-induced memory deficits in rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2003 Mar;17(1):83-8. doi: 10.1177/0269881103017001709. J Psychopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12680743
-
Hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation by stress and antidepressants.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Jun 15;59(12):1136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.082. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16797263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidepressants and Cdk inhibitors: releasing the brake on neurogenesis?Cell Cycle. 2008 Aug;7(15):2321-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.6446. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18682686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic loss of norepinephrine does not alter adult hippocampal neurogenesis in dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficient mice.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Oct 27;13:420-425. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.10.010. eCollection 2022 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36386600 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicity of prenatal alcohol exposure on medullary pre-Bötzinger complex neurons in neonatal rats.Neural Regen Res. 2015 Jul;10(7):1095-100. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.160101. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 26330832 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Monoamines and Antidepressants on Astrocyte Physiology: Implications for Monoamine Hypothesis of Depression.J Exp Neurosci. 2018 Jul 23;12:1179069518789149. doi: 10.1177/1179069518789149. eCollection 2018. J Exp Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30046253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal Noradrenaline Is a Positive Regulator of Spatial Working Memory and Neurogenesis in the Rat.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15;24(6):5613. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065613. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982688 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine directly activates adult hippocampal precursors via beta3-adrenergic receptors.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 17;30(7):2795-806. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3780-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20164362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airan RD, Meltzer LA, Roy M, Gong Y, Chen H, Deisseroth K. High-speed imaging reveals neurophysiological links to behavior in an animal model of depression. Science. 2007;317:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Altman JD, Trendelenburg AU, MacMillan L, Bernstein D, Limbird L, Starke K, Kobilka BK, Hein L. Abnormal regulation of the sympathetic nervous system in alpha2A-adrenergic receptor knockout mice. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:154–161. - PubMed
-
- Andrade C, Sudha S. Electroconvulsive therapy and the alpha-2 noradrenergic receptor: implications of treatment schedule effects. J ECT. 2000;16:268–278. - PubMed
-
- Blier P. The pharmacology of putative early-onset antidepressant strategies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003;13:57–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
