Identifying cochlear implant channels with poor electrode-neuron interface: partial tripolar, single-channel thresholds and psychophysical tuning curves
- PMID: 20090533
- PMCID: PMC2836401
- DOI: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181c7daf4
Identifying cochlear implant channels with poor electrode-neuron interface: partial tripolar, single-channel thresholds and psychophysical tuning curves
Erratum in
- Ear Hear. 2011 Sep-Oct;32(5):633
Abstract
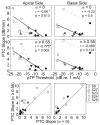
Objective: The goal of this study was to evaluate the ability of a threshold measure, made with a restricted electrode configuration, to identify channels exhibiting relatively poor spatial selectivity. With a restricted electrode configuration, channel-to-channel variability in threshold may reflect variations in the interface between the electrodes and auditory neurons (i.e., nerve survival, electrode placement, and tissue impedance). These variations in the electrode-neuron interface should also be reflected in psychophysical tuning curve (PTC) measurements. Specifically, it is hypothesized that high single-channel thresholds obtained with the spatially focused partial tripolar (pTP) electrode configuration are predictive of wide or tip-shifted PTCs.
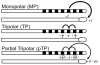
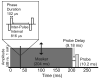
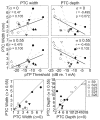
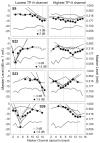
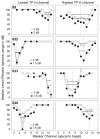
Design: Data were collected from five cochlear implant listeners implanted with the HiRes90k cochlear implant (Advanced Bionics Corp., Sylmar, CA). Single-channel thresholds and most comfortable listening levels were obtained for stimuli that varied in presumed electrical field size by using the pTP configuration for which a fraction of current (sigma) from a center-active electrode returns through two neighboring electrodes and the remainder through a distant indifferent electrode. Forward-masked PTCs were obtained for channels with the highest, lowest, and median tripolar (sigma = 1 or 0.9) thresholds. The probe channel and level were fixed and presented with either the monopolar (sigma = 0) or a more focused pTP (sigma > or = 0.55) configuration. The masker channel and level were varied, whereas the configuration was fixed to sigma = 0.5. A standard, three-interval, two-alternative forced choice procedure was used for thresholds and masked levels.
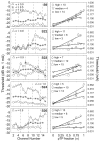
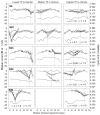
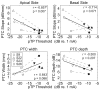
Results: Single-channel threshold and variability in threshold across channels systematically increased as the compensating current, sigma, increased and the presumed electrical field became more focused. Across subjects, channels with the highest single-channel thresholds, when measured with a narrow, pTP stimulus, had significantly broader PTCs than the lowest threshold channels. In two subjects, the tips of the tuning curves were shifted away from the probe channel. Tuning curves were also wider for the monopolar probes than with pTP probes for both the highest and lowest threshold channels.
Conclusions: These results suggest that single-channel thresholds measured with a restricted stimulus can be used to identify cochlear implant channels with poor spatial selectivity. Channels having wide or tip-shifted tuning characteristics would likely not deliver the appropriate spectral information to the intended auditory neurons, leading to suboptimal perception. As a clinical tool, quick identification of impaired channels could lead to patient-specific mapping strategies and result in improved speech and music perception.
Figures

References
-
- Berenstein CK, Mens LH, Mulder JJ, et al. Current steering and current focusing in cochlear implants: Comparison of monopolar, tripolar, and virtual channel electrode configurations. Ear Hear. 2008;29(2):250–260. - PubMed
-
- Bierer JA. Threshold and channel interaction in cochlear implant users: Evaluation of the tripolar electrode configuration. J Acoust Soc Am. 2007;121(3):1642–1653. - PubMed
-
- Bierer JA, Middlebrooks JC. Auditory cortical images of cochlear-implant stimuli: Dependence on electrode configuration. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87(1):478–492. - PubMed
-
- Boex C, Kos MI, Pelizonne M. Forward masking in different cochlear implant systems. J Acoust Soc Am. 2003;114(4 Pt 1):2058–2065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

