Impulsivity characterization in the Roman high- and low-avoidance rat strains: behavioral and neurochemical differences
- PMID: 20090672
- PMCID: PMC3055403
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.224
Impulsivity characterization in the Roman high- and low-avoidance rat strains: behavioral and neurochemical differences
Abstract
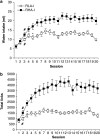
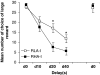
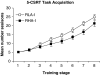
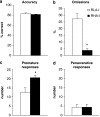
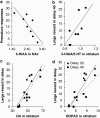
The selective breeding of Roman high- (RHA) and low-avoidance (RLA) rats for rapid vs extremely poor acquisition of active avoidance behavior in a shuttle-box has generated two phenotypes with different emotional and motivational profiles. The phenotypic traits of the Roman rat lines/strains (outbred or inbred, respectively) include differences in sensation/novelty seeking, anxiety/fearfulness, stress responsivity, and susceptibility to addictive substances. We designed this study to characterize differences between the inbred RHA-I and RLA-I strains in the impulsivity trait by evaluating different aspects of the multifaceted nature of impulsive behaviors using two different models of impulsivity, the delay-discounting task and five-choice serial reaction time (5-CSRT) task. Previously, rats were evaluated on a schedule-induced polydipsia (SIP) task that has been suggested as a model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. RHA-I rats showed an increased acquisition of the SIP task, higher choice impulsivity in the delay-discounting task, and poor inhibitory control as shown by increased premature responses in the 5-CSRT task. Therefore, RHA-I rats manifested an increased impulsivity phenotype compared with RLA-I rats. Moreover, these differences in impulsivity were associated with basal neurochemical differences in striatum and nucleus accumbens monoamines found between the two strains. These findings characterize the Roman rat strains as a valid model for studying the different aspects of impulsive behavior and for analyzing the mechanisms involved in individual predisposition to impulsivity and its related psychopathologies.
Figures
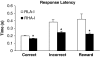
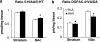
References
-
- Aguilar R, Gil L, Gray JA, Driscoll P, Flint J, Dawson GR, et al. Fearfulness and sex in F2 Roman rats: males display more fear though both sexes share the same fearfulness traits. Physiol Behav. 2003;78:723–732. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association 2000Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders4th edn, text revision.American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC
-
- Annetrude JG, de Mooij-van Malsen A, Berend Olivier AB, Martien JHK. Behavioural genetics in mood and anxiety: a next step in finding novel pharmacological targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;585:436–440. - PubMed
-
- Aubry JM, Bartanusz V, Driscoll P, Schulz P, Steimer T, Kiss Jz. Corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin mRNA levels in Roman high- and low-avoidance rats: response to open-field exposure. Neuroendocrinology. 1995;61:89–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

