How synchronization protects from noise
- PMID: 20090826
- PMCID: PMC2797083
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000637
How synchronization protects from noise
Abstract
THE FUNCTIONAL ROLE OF SYNCHRONIZATION HAS ATTRACTED MUCH INTEREST AND DEBATE: in particular, synchronization may allow distant sites in the brain to communicate and cooperate with each other, and therefore may play a role in temporal binding, in attention or in sensory-motor integration mechanisms. In this article, we study another role for synchronization: the so-called "collective enhancement of precision". We argue, in a full nonlinear dynamical context, that synchronization may help protect interconnected neurons from the influence of random perturbations-intrinsic neuronal noise-which affect all neurons in the nervous system. More precisely, our main contribution is a mathematical proof that, under specific, quantified conditions, the impact of noise on individual interconnected systems and on their spatial mean can essentially be cancelled through synchronization. This property then allows reliable computations to be carried out even in the presence of significant noise (as experimentally found e.g., in retinal ganglion cells in primates). This in turn is key to obtaining meaningful downstream signals, whether in terms of precisely-timed interaction (temporal coding), population coding, or frequency coding. Similar concepts may be applicable to questions of noise and variability in systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
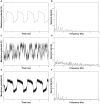
 ,
,  ,
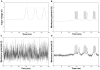
,  . (A) shows the trajectory of the “membrane potential” of a noise-free oscillator and (B) depicts the frequency spectrum of this trajectory computed by Fast Fourier Transformation. (C) and (D) present the trajectory (respectively the frequency spectrum) of a noisy uncoupled oscillator (
. (A) shows the trajectory of the “membrane potential” of a noise-free oscillator and (B) depicts the frequency spectrum of this trajectory computed by Fast Fourier Transformation. (C) and (D) present the trajectory (respectively the frequency spectrum) of a noisy uncoupled oscillator ( ). (E) and (F) show the trajectory (respectively the frequency spectrum) of a noisy synchronized oscillator within an all-to-all network (
). (E) and (F) show the trajectory (respectively the frequency spectrum) of a noisy synchronized oscillator within an all-to-all network ( ,
,  ,
,  ). Note the temporal and frequential similarities between a noise-free oscillator and a noisy synchronized one. For instance, the main frequency and the first harmonics are very similar in the two frequency spectra. In contrast, the frequency spectrum of a noisy uncoupled oscillator shows no clear harmonics.
). Note the temporal and frequential similarities between a noise-free oscillator and a noisy synchronized one. For instance, the main frequency and the first harmonics are very similar in the two frequency spectra. In contrast, the frequency spectrum of a noisy uncoupled oscillator shows no clear harmonics.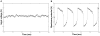
 noisy uncoupled oscillators (
noisy uncoupled oscillators ( ). (B) shows the average “membrane potential” computed over
). (B) shows the average “membrane potential” computed over  noisy synchronized oscillators within an all-to-all network (
noisy synchronized oscillators within an all-to-all network ( ,
,  ). Observe that, in the first plot, the average trajectory of uncoupled oscillators carries essentially no information, while in the second plot, the average trajectory of synchronized oscillators is very similar to a noise-free one.
). Observe that, in the first plot, the average trajectory of uncoupled oscillators carries essentially no information, while in the second plot, the average trajectory of synchronized oscillators is very similar to a noise-free one.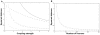
 's and
's and  (given by
(given by  ) as a function of the coupling strength
) as a function of the coupling strength  (
( ). Theoretical bound
). Theoretical bound  (cf equations (7) and (4)) for
(cf equations (7) and (4)) for  (bold line), for
(bold line), for  (plain line), for
(plain line), for  (dashed line); simulation results for
(dashed line); simulation results for  (squares), for
(squares), for  (triangles), for
(triangles), for  (crosses). (B) Expected squared distance between a noisy synchronized oscillator and its observer (given by
(crosses). (B) Expected squared distance between a noisy synchronized oscillator and its observer (given by  ) as a function of
) as a function of  (
( ,
,  ). The bound
). The bound  was plotted in plain line and the simulation results were represented by crosses.
was plotted in plain line and the simulation results were represented by crosses.
 ,
,  ,
,  ).
).Similar articles
-
Detecting and characterizing phase synchronization in nonstationary dynamical systems.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2006 Feb;73(2 Pt 2):026214. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.73.026214. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2006. PMID: 16605436
-
Impact of spatially correlated noise on neuronal firing.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2004 Jan;69(1 Pt 1):011909. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.69.011909. Epub 2004 Jan 29. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2004. PMID: 14995649
-
The relationship between synchronization among neuronal populations and their mean activity levels.Neural Comput. 1999 Aug 15;11(6):1389-411. doi: 10.1162/089976699300016287. Neural Comput. 1999. PMID: 10423500
-
Nonlinear multivariate analysis of neurophysiological signals.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):1-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.10.003. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16289760 Review.
-
Neuronal coherence during selective attentional processing and sensory-motor integration.J Physiol Paris. 2006 Oct;100(4):182-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2007.01.005. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Physiol Paris. 2006. PMID: 17317118 Review.
Cited by
-
Achieving stable dynamics in neural circuits.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Aug 7;16(8):e1007659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007659. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32764745 Free PMC article.
-
Entrainment to periodic initiation and transition rates in a computational model for gene translation.PLoS One. 2014 May 6;9(5):e96039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096039. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24800863 Free PMC article.
-
Interregional neural synchrony has similar dynamics during spontaneous and stimulus-driven states.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1481. doi: 10.1038/srep01481. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23512004 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biology: advancing the design of diverse genetic systems.Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2013;4:69-102. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-061312-103351. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2013. PMID: 23413816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Information transmission in microbial and fungal communication: from classical to quantum.J Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Jun;12(2):491-502. doi: 10.1007/s12079-018-0462-6. Epub 2018 Feb 23. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29476316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer W. Synchronization of cortical activity and its putative role in information processing and learning. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:349–74. - PubMed
-
- Buzsaki G. Rhythms of the Brain. Oxford University Press; 2006.
-
- Hestrin S, Galarreta M. Electrical synapses define networks of neocortical gabaergic neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:304–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

