Non-coding changes cause sex-specific wing size differences between closely related species of Nasonia
- PMID: 20090834
- PMCID: PMC2799512
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000821
Non-coding changes cause sex-specific wing size differences between closely related species of Nasonia
Abstract
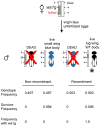
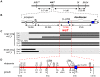
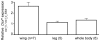
The genetic basis of morphological differences among species is still poorly understood. We investigated the genetic basis of sex-specific differences in wing size between two closely related species of Nasonia by positional cloning a major male-specific locus, wing-size1 (ws1). Male wing size increases by 45% through cell size and cell number changes when the ws1 allele from N. giraulti is backcrossed into a N. vitripennis genetic background. A positional cloning approach was used to fine-scale map the ws1 locus to a 13.5 kilobase region. This region falls between prospero (a transcription factor involved in neurogenesis) and the master sex-determining gene doublesex. It contains the 5'-UTR and cis-regulatory domain of doublesex, and no coding sequence. Wing size reduction correlates with an increase in doublesex expression level that is specific to developing male wings. Our results indicate that non-coding changes are responsible for recent divergence in sex-specific morphology between two closely related species. We have not yet resolved whether wing size evolution at the ws1 locus is caused by regulatory alterations of dsx or prospero, or by another mechanism. This study demonstrates the feasibility of efficient positional cloning of quantitative trait loci (QTL) involved in a broad array of phenotypic differences among Nasonia species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Nasonia tools up.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Mar;11(3):170. doi: 10.1038/nrg2759. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21485429 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kopp A, True JR. Evolution of male sexual characters in the Oriental Drosophila melanogaster species group. Evol Dev. 2002;4:278–291. - PubMed
-
- Kopp A, Duncan I, Carroll SB. Genetic control and evolution of sexually dimorphic characters in Drosophila. Nature. 2000;408:553–559. - PubMed
-
- Stern DL. Perspective: Evolutionary Developmental Biology and the Problem of Variation. Evolution. 2000;54:1079–1091. - PubMed
-
- Carroll SB. Evolution at Two Levels: On Genes and Form. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

