Haemodiafiltration-optimal efficiency and safety
- PMID: 20090878
- PMCID: PMC2808132
- DOI: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfp149
Haemodiafiltration-optimal efficiency and safety
Abstract
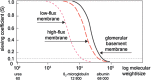
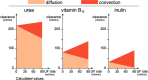
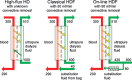
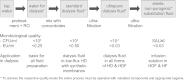
Haemodiafiltration (HDF) is the blood purification therapy of choice for those who want significant removal of uraemic solutes beyond the traditional range of small molecules. Combining diffusive and convective solute transport, a HDF treatment comprises the largest number of variables among blood purification therapies, and it is important to understand how they interact in order to optimize the therapy. This review discusses the parameters that determine the efficiency of HDF and how they can be controlled in the different forms of HDF and 'HDF-like' therapies practised today. The key to safe and effective HDF therapy is to have access to large volumes of high-quality fluids. Starting with ultrapure dialysis fluid, on-line preparation of a sterile, non-pyrogenic substitution solution can be made an integral part of the treatment, and we describe the necessary conditions for this. On-line HDF can provide the largest removal of the widest range of solutes among available dialysis therapies, and the potential clinical benefits of this are within practical reach for the increasing number of patients dialysed with high-flux membranes and ultrapure dialysis fluid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Change from conventional haemodiafiltration to on-line haemodiafiltration.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999 May;14(5):1202-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/14.5.1202. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10344362
-
On-line haemodiafiltration versus low-flux haemodialysis. A prospective randomized study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000;15 Suppl 1:43-8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a027963. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000. PMID: 10737166 Clinical Trial.
-
On-line haemodiafiltration: state of the art.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998;13 Suppl 5:3-11. doi: 10.1093/ndt/13.suppl_5.3. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998. PMID: 9623523 Review.
-
Removal of water-soluble and protein-bound solutes with reversed mid-dilution versus post-dilution haemodiafiltration.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Aug;27(8):3278-83. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs060. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22492823
-
The early years of on-line HDF: how did it all start? How did we get here?Contrib Nephrol. 2011;175:93-109. doi: 10.1159/000333627. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 22188692 Review.
Cited by
-
Confronting Practical Problems for Initiation of On-line Hemodiafiltration Therapy.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2016 Jun;14(1):1-4. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2016.14.1.1. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2016. PMID: 27453712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High convection volume in online post-dilution haemodiafiltration: relevance, safety and costs.Clin Kidney J. 2015 Aug;8(4):368-73. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv040. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Clin Kidney J. 2015. PMID: 26251701 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of haemodiafiltration vs conventional haemodialysis on growth and cardiovascular outcomes in children - the HDF, heart and height (3H) study.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Aug 10;19(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0998-y. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30097064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hemodiafiltration for children with stage 5 chronic kidney disease: technical aspects and outcomes.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Sep;39(9):2611-2626. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06285-w. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38347283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Middle molecule elimination in expanded haemodialysis: only convective transport?Clin Kidney J. 2018 Dec 15;12(3):447-455. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfy097. eCollection 2019 Jun. Clin Kidney J. 2018. PMID: 31198548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eknoyan G, Beck GJ, Cheung AK, et al. Effect of dose and membrane flux in maintenance hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:2010–2019. - PubMed
-
- Cheung AK, Levin NW, Greene T, et al. Effects of high-flux hemodialysis on clinical outcomes: results of the HEMO study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:3251–3263. - PubMed
-
- Delmez JA, Yan B, Bailey J, et al. Cerebrovascular disease in maintenance hemodialysis patients: results of the HEMO study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:131–138. - PubMed
-
- Meert N, Eloot S, Waterloos M-A, et al. Effective removal of protein-bound uraemic solutes by different convective strategies: a prospective trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:562–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
