17-AAG induces cytoplasmic alpha-synuclein aggregate clearance by induction of autophagy
- PMID: 20090920
- PMCID: PMC2807466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008753
17-AAG induces cytoplasmic alpha-synuclein aggregate clearance by induction of autophagy
Abstract
Background: The accumulation and aggregation of alpha-synuclein in nerve cells and glia are characteristic features of a number of neurodegenerative diseases termed synucleinopathies. alpha-Synuclein is a highly soluble protein which in a nucleation dependent process is capable of self-aggregation. The causes underlying aggregate formation are not yet understood, impairment of the proteolytic degradation systems might be involved.
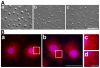
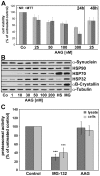
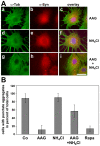
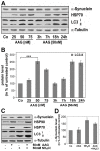
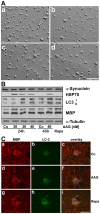
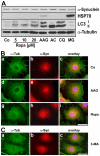
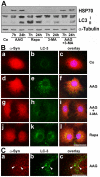
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study the possible aggregate clearing effects of the geldanamycin analogue 17-AAG (17-(Allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin) was investigated. Towards this, an oligodendroglial cell line (OLN-93 cells), stably expressing human alpha-synuclein (A53T mutation) was used. In these cells small punctate aggregates, not staining with thioflavine S, representing prefibrillary aggregates, occur characteristically. Our data demonstrate that 17-AAG attenuated the formation of alpha-synuclein aggregates by stimulating macroautophagy. By blocking the lysosomal compartment with NH(4)Cl the aggregate clearing effects of 17-AAG were abolished and alpha-synuclein deposits were enlarged. Analysis of LC3-II immunoreactivity, which is an indicator of autophagosome formation, further revealed that 17-AAG led to the recruitment of LC3-II and to the formation of LC3 positive puncta. This effect was also observed in cultured oligodendrocytes derived from the brains of newborn rats. Inhibition of macroautophagy by 3-methyladenine prevented 17-AAG induced occurrence of LC3 positive puncta as well as the removal of alpha-synuclein aggregates in OLN-A53T cells.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate for the first time that 17-AAG not only causes the upregulation of heat shock proteins, but also is an effective inducer of the autophagic pathway by which alpha-synuclein can be removed. Hence geldanamycin derivatives may provide a means to modulate autophagy in neural cells, thereby ameliorating pathogenic aggregate formation and protecting the cells during disease and aging.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of HDAC6 modifies tau inclusion body formation and impairs autophagic clearance.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Apr;55(4):1031-46. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0460-y. Epub 2014 Dec 2. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25434725
-
Mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress compromise autophagosomal degradation of α-synuclein in oligodendroglial cells.J Neurochem. 2015 Oct;135(1):194-205. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13256. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26212128
-
A Novel Hsp90 Inhibitor Activates Compensatory Heat Shock Protein Responses and Autophagy and Alleviates Mutant A53T α-Synuclein Toxicity.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;88(6):1045-54. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.101451. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26405178 Free PMC article.
-
Rab7 induces clearance of α-synuclein aggregates.J Neurochem. 2016 Sep;138(5):758-74. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13712. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27333324
-
Modulation of Hsp90 function in neurodegenerative disorders: a molecular-targeted therapy against disease-causing protein.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Aug;84(8):635-46. doi: 10.1007/s00109-006-0066-0. Epub 2006 Jun 2. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16741751 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Protein Aggregation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress as a Targeted Therapy for α-Synucleinopathy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 30;15(8):2051. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082051. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular chaperones and protein folding as therapeutic targets in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013 Dec 5;1(1):79. doi: 10.1186/2051-5960-1-79. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013. PMID: 24314025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock protein 90-mediated inactivation of nuclear factor-κB switches autophagy to apoptosis through becn1 transcriptional inhibition in selenite-induced NB4 cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Apr 15;22(8):1167-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-10-0860. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21346199 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic treatment with 17-DMAG improves balance and coordination in a new mouse model of Machado-Joseph disease.Neurotherapeutics. 2014 Apr;11(2):433-49. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0255-9. Neurotherapeutics. 2014. PMID: 24477711 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Hyaluronan Signaling and Autophagy Dysfunction by VPS35 D620N.Neuroscience. 2020 Aug 10;441:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.06.009. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Neuroscience. 2020. PMID: 32540366 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

