Irradiation-induced Deinococcus radiodurans genome fragmentation triggers transposition of a single resident insertion sequence
- PMID: 20090938
- PMCID: PMC2806898
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000799
Irradiation-induced Deinococcus radiodurans genome fragmentation triggers transposition of a single resident insertion sequence
Abstract
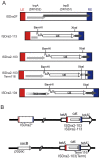
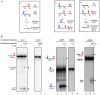
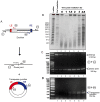
Stress-induced transposition is an attractive notion since it is potentially important in creating diversity to facilitate adaptation of the host to severe environmental conditions. One common major stress is radiation-induced DNA damage. Deinococcus radiodurans has an exceptional ability to withstand the lethal effects of DNA-damaging agents (ionizing radiation, UV light, and desiccation). High radiation levels result in genome fragmentation and reassembly in a process which generates significant amounts of single-stranded DNA. This capacity of D. radiodurans to withstand irradiation raises important questions concerning its response to radiation-induced mutagenic lesions. A recent study analyzed the mutational profile in the thyA gene following irradiation. The majority of thyA mutants resulted from transposition of one particular Insertion Sequence (IS), ISDra2, of the many different ISs in the D. radiodurans genome. ISDra2 is a member of a newly recognised class of ISs, the IS200/IS605 family of insertion sequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Criswell T, Leskov K, Miyamoto S, Luo G, Boothman DA. Transcription factors activated in mammalian cells after clinically relevant doses of ionizing radiation. Oncogene. 2003;22(37):5813–5827. - PubMed
-
- Fu Y, Pastushok L, Xiao W. DNA damage-induced gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32(6):908–926. - PubMed
-
- Zhou BB, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 2000;408(6811):433–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

