Therapeutic efficacy of Cintredekin Besudotox (IL13-PE38QQR) in murine lung fibrosis is unaffected by immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
- PMID: 20090941
- PMCID: PMC2806906
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008721
Therapeutic efficacy of Cintredekin Besudotox (IL13-PE38QQR) in murine lung fibrosis is unaffected by immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
Abstract
Background: We have previously explored a therapeutic strategy for specifically targeting the profibrotic activity of IL-13 during experimental pulmonary fibrosis using a fusion protein comprised of human IL-13 and a mutated form of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (IL13-PE) and observed that the intranasal delivery of IL13-PE reduced bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through its elimination of IL-13-responsive cells in the lung. The aim of the present study was to determine whether the presence of an immune response to P. aeruginosa and/or its exotoxin A (PE) would diminish the anti-fibrotic properties of IL13-PE.
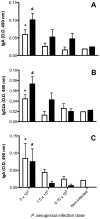
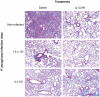
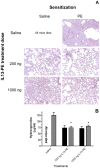
Methodology/principal findings: Fourteen days after P. aeruginosa infection, C57BL/6 mice were injected with bleomycin via the intratracheal route. Other groups of mice received 4 doses of saline or IL13-PE by either intranasal or intraperitoneal application, and were challenged i.t. with bleomycin 28 days later. At day 21 after bleomycin, all mice received either saline vehicle or IL13-PE by the intranasal route and histopatological analyses of whole lung samples were performed at day 28 after bleomycin. Intrapulmonary P. aeruginosa infection promoted a neutralizing IgG2A and IgA antibody response in BALF and serum. Surprisingly, histological analysis showed that a prior P. aeruginosa infection attenuated the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, which was modestly further attenuated by the intranasal administration of IL13-PE. Although prior intranasal administration of IL13-PE failed to elicit an antibody response, the systemic administration of IL13-PE induced a strong neutralizing antibody response. However, the prior systemic sensitization of mice with IL13-PE did not inhibit the anti-fibrotic effect of IL13-PE in fibrotic mice.
Conclusions: Thus, IL13-PE therapy in pulmonary fibrosis works regardless of the presence of a humoral immune response to Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Interestingly, a prior infection with P. aeruginosa markedly attenuated the pulmonary fibrotic response suggesting that the immune elicitation by this pathogen exerts anti-fibrotic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of an immunotoxin to folate receptor beta on bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Aug;161(2):348-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04182.x. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20550546 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to taming a toxin--recombinant immunotoxins constructed from Pseudomonas exotoxin A for the treatment of cancer.FEBS J. 2011 Dec;278(23):4683-700. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08182.x. Epub 2011 Jun 2. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21585657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of IL-4- and IL-13-responsive cells in pulmonary fibrosis.Immunol Res. 2004;30(3):339-49. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:3:339. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15531774 Review.
-
Cintredekin besudotox in treatment of malignant glioma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008 Jun;8(6):805-12. doi: 10.1517/14712598.8.6.805. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18476792 Review.
-
Interleukin-13 fusion cytotoxin as a potent targeted agent for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma xenograft.Blood. 2000 Jun 1;95(11):3506-13. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10828036
Cited by
-
Rationally designed chemokine-based toxin targeting the viral G protein-coupled receptor US28 potently inhibits cytomegalovirus infection in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 7;112(27):8427-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1509392112. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26080445 Free PMC article.
-
IL-13 induces YY1 through the AKT pathway in lung fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0119039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119039. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775215 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis through the Induction of Profibrotic CD8+ T Cells.J Immunol. 2015 Dec 1;195(11):5251-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500777. Epub 2015 Oct 30. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26519529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King TE, Jr, Tooze JA, Schwarz MI, Brown KR, Cherniack RM. Predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: scoring system and survival model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1171–1181. - PubMed
-
- Hancock A, Armstrong L, Gama R, Millar A. Production of interleukin 13 by alveolar macrophages from normal and fibrotic lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;18:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Lukacs NW, Hogaboam C, Chensue SW, Blease K, Kunkel SL. Type 1/type 2 cytokine paradigm and the progression of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2001;120:5S–8S. - PubMed
-
- Wallace WA, Howie SE. Immunoreactive interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma expression by type II alveolar epithelial cells in interstitial lung disease. J Pathol. 1999;187:475–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

