Sulindac sulfide suppresses 5-lipoxygenase at clinically relevant concentrations
- PMID: 20091083
- PMCID: PMC11115735
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0206-0
Sulindac sulfide suppresses 5-lipoxygenase at clinically relevant concentrations
Abstract
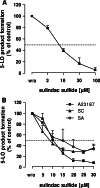
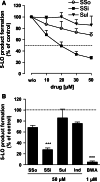
Sulindac is a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenases (COX) used to treat inflammation and pain. Additionally, non-COX targets may account for the drug's chemo-preventive efficacy against colorectal cancer and reduced gastrointestinal toxicity. Here, we demonstrate that the pharmacologically active metabolite of sulindac, sulindac sulfide (SSi), targets 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of proinflammatory leukotrienes (LTs). SSi inhibited 5-LO in ionophore A23187- and LPS/fMLP-stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (IC(50) approximately 8-10 microM). Importantly, SSi efficiently suppressed 5-LO in human whole blood at clinically relevant plasma levels (IC(50) = 18.7 microM). SSi was 5-LO-selective as no inhibition of related lipoxygenases (12-LO, 15-LO) was observed. The sulindac prodrug and the other metabolite, sulindac sulfone (SSo), failed to inhibit 5-LO. Mechanistic analysis demonstrated that SSi directly suppresses 5-LO with an IC(50) of 20 muM. Together, these findings may provide a novel molecular basis to explain the COX-independent pharmacological effects of sulindac under therapy.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Potent inhibition of human 5-lipoxygenase and microsomal prostaglandin E₂ synthase-1 by the anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory agent embelin.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;86(4):476-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.015. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23623753
-
The molecular mechanism of the inhibition by licofelone of the biosynthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;152(4):471-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707416. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17704828 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor RF-22c potently suppresses leukotriene biosynthesis in cellulo and blocks bronchoconstriction and inflammation in vivo.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jul 15;112:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 May 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27157409
-
5-lipoxygenase and FLAP.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003 Aug-Sep;69(2-3):99-109. doi: 10.1016/s0952-3278(03)00070-x. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003. PMID: 12895592 Review.
-
Inhibitors of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway in atherosclerosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(27):3116-32. doi: 10.2174/138161209789058020. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19754386 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitors of Human 5-Lipoxygenase Potently Interfere With Prostaglandin Transport.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 21;12:782584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.782584. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35126121 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen-mediated sex bias impairs efficiency of leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitors in males.J Clin Invest. 2017 Aug 1;127(8):3167-3176. doi: 10.1172/JCI92885. Epub 2017 Jul 24. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28737505 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective Potential of Sulindac Sulfide to Prevent DNA Damage Due to Ionizing Radiation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Dec 6;13:4127-4134. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S218022. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31827319 Free PMC article.
-
2-(4-(Biphenyl-4-ylamino)-6-chloropyrimidin-2-ylthio)octanoic acid (HZ52)--a novel type of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor with favourable molecular pharmacology and efficacy in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):781-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01451.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21506958 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of phospho-sulindac (OXT-328) and the effect of difluoromethylornithine.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(7):2152-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01705.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21955327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haanen C. Sulindac and its derivatives: a novel class of anticancer agents. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2001;2:677–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

