Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal
- PMID: 20091529
- PMCID: PMC7065589
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub3
Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal
Abstract
Background: Withdrawal (detoxification) is necessary prior to drug-free treatment or as the end point of long-term substitution treatment.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of opioid antagonists to induce opioid withdrawal with concomitant heavy sedation or anaesthesia, in terms of withdrawal signs and symptoms, completion of treatment and adverse effects.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2009), Medline (January 1966 to 11 August 2009), Embase (January 1985 to 2009 Week 32), PsycINFO (1967 to July 2009), and reference lists of articles.
Selection criteria: Controlled studies of antagonist-induced withdrawal under heavy sedation or anaesthesia in opioid-dependent participants compared with other approaches, or a different regime of anaesthesia-based antagonist-induced withdrawal.
Data collection and analysis: One reviewer assessed studies for inclusion, undertook data extraction and assessed quality. Inclusion decisions and the overall process were confirmed by consultation between all authors.
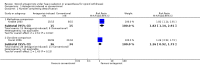
Main results: Nine studies (eight randomised controlled trials) involving 1109 participants met the inclusion criteria for the review.Antagonist-induced withdrawal is more intense but less prolonged than withdrawal managed with reducing doses of methadone, and doses of naltrexone sufficient for blockade of opioid effects can be established significantly more quickly with antagonist-induced withdrawal than withdrawal managed with clonidine and symptomatic medications. The level of sedation does not affect the intensity and duration of withdrawal, although the duration of anaesthesia may influence withdrawal severity. There is a significantly greater risk of adverse events with heavy, compared to light, sedation (RR 3.21, 95% CI 1.13 to 9.12, P = 0.03) and probably with this approach compared to other forms of detoxification.
Authors' conclusions: Heavy sedation compared to light sedation does not confer additional benefits in terms of less severe withdrawal or increased rates of commencement on naltrexone maintenance treatment. Given that the adverse events are potentially life-threatening, the value of antagonist-induced withdrawal under heavy sedation or anaesthesia is not supported. The high cost of anaesthesia-based approaches, both in monetary terms and use of scarce intensive care resources, suggest that this form of treatment should not be pursued.
Conflict of interest statement
Two of the authors of this review (LG, RA) were involved in one of the studies (McGregor 2002) included in this review.
Figures
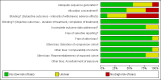
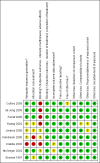
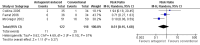



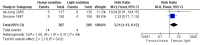




Update of
-
Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub3. PMID: 16625552 Updated.
Similar articles
-
Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub3. PMID: 16625552 Updated.
-
Opioid antagonists with minimal sedation for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 29;5(5):CD002021. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002021.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28553701 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub2. PMID: 12076432 Updated.
-
Opioid antagonists with minimal sedation for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 7;(4):CD002021. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002021.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 29;5:CD002021. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002021.pub4. PMID: 19821290 Updated.
-
Opioid antagonists under sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD002022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022. PMID: 11279746 Updated.
Cited by
-
Deaths and severe adverse events associated with anesthesia-assisted rapid opioid detoxification--New York City, 2012.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013 Sep 27;62(38):777-80. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013. PMID: 24067581 Free PMC article.
-
Harms associated with taking nalmefene for substance use and impulse control disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 29;12(8):e0183821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183821. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28850596 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological strategies for detoxification.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;77(2):302-14. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12245. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24118014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for the reduction of prescribed opioid use in chronic non-cancer pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 13;11(11):CD010323. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010323.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29130474 Free PMC article.
-
Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 21;2(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28220474 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Collins 2005 {published data only}
-
- Collins ED, Kleber HD, Whittington RA, Heitler NE. Anaesthesia‐assisted vs buprenorphine‐ or clonidine‐assisted heroin detoxification and naltrexone induction. A randomised trial. JAMA 2005;294(8):903‐13. - PubMed
-
- Collins ED, Whittington RA, Heitler NE, Kleber HD. A randomised comparison of anaesthesia‐assisted heroin detoxification with buprenorphine and clonidine assisted detoxifications. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2002;66(Supplement):35.
de Jong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jong CAJ, Laheij RJF, Krabbe PFM. General anaesthesia does not improve outcome in opioid antagonist detoxification treatment: a randomised controlled trial. Addiction 2005;100:206‐15. - PubMed
Favrat 2006 {published data only}
-
- Favrat B, Zimmermann G, Zullino D, Krenz S, Dorogy F, Muller J, et al. Opioid antagonist detoxification under anaesthesia versus traditional clonidine detoxification combined with an additional week of psychosocial support: A randomised clinical trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence 2006;81(2):109‐16. - PubMed
Huang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Huang W‐Y, Xiao X‐S, Liu Y, Liao X‐Q, Zhou D‐W, Dai H. The comparison of effects of rapid opiate detoxification with ketamine complex and with tramadol and naltrexone under general anesthesia with propofol. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2002;6(23):3625‐6.
Jovaisa 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jovaisa T, Laurinenas G, Vosylius S, Sipylaite J, Badaras R, Ivaskevicius J. Effects of ketamine on precipitated opiate withdrawal. Medicina (Kaunas) 2006;42(8):625‐34. - PubMed
Kienbaum 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kienbaum P, Scherbaum N, Thurauf N, Michel MC, Gastpar M, Peters J. Acute detoxification of opioid‐addicted patients with naloxone during propofol or methohexital anaesthesia: a comparison of withdrawal symptoms, neuroendocrine, metabolic, and cardiovascular patterns. Critical Care Medicine 2000;28(4):969‐76. - PubMed
Krabbe 2003 {published data only}
-
- Krabbe PFM, Koning JPF, Heinen N, Laheij RJF, Cauter RMV, Jong CAJ. Rapid detoxification from opioid dependence under general anaesthesia versus standard methadone tapering: abstinence rates and withdrawal distress experience. Addiction Biology 2003;8(3):351‐8. - PubMed
-
- Laheij RJF, Krabbe PFM, Jong CAJ. Rapid heroin detoxification under general anaesthesia. JAMA 2000;283(9):1143. - PubMed
McGregor 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ali R, Thomas P, White J, McGregor C, Danz C, Gowing L, et al. Antagonist‐precipitated heroin withdrawal under anaesthetic prior to maintenance naltrexone treatment: determinants of withdrawal severity. Drug and Alcohol Review 2003;22(4):425‐31. - PubMed
-
- McGregor C, Ali R, White JM, Thomas P, Gowing L. A comparison of antagonist‐precipitated withdrawal under anaesthesia to standard inpatient withdrawal as a precursor to maintenance naltrexone treatment in heroin users: Outcomes at 6 and 12 months. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2002;68(1):5‐14. - PubMed
Seoane 1997 {published data only}
-
- Seoane A, Carrasco G, Cabré L, Puiggrós A, Hernández E, Álvarez M, et al. Efficacy and safety of two new methods of rapid intravenous detoxification in heroin addicts previously treated without success. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;171:340‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Albanese 2000 {published data only}
-
- Albanese AP, Gevirtz C, Oppenheim B, Field JM, Abels I, Eustace JC. Outcome and six month follow up of patients after ultra rapid opiate detoxification (URODSM). Journal of Addictive Diseases 2000;19(2):11‐28. - PubMed
Allhoff 1999 {published data only}
-
- Allhoff T, Renzing‐Kohler K, Kienbaum P, Sack S, Scherbaum N. Electrocardiographic abnormalities during recovery from ultra‐short opiate detoxification. Addiction Biology 1999;4(3):337‐44. - PubMed
Arnold‐Reed 2005 {published data only}
-
- Arnold‐Reed DE, Hulse GK. A comparison of rapid (opioid) detoxification with clonidine‐assisted detoxification for heroin‐dependent persons. Journal of Opioid Management 2005;1(1):17‐23. - PubMed
Bartter 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bartter T, Gooberman LL. Rapid opiate detoxification. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1996;22(4):489‐95. - PubMed
Bell 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bell JR, Young MR, Masterman SC, Morris A, Mattick RP, Bammer G. A pilot study of naltrexone‐accelerated detoxification in opioid dependence. Medical Journal of Australia 1999;171:26‐30. - PubMed
Boehle 2000 {published data only}
-
- Boehle C, Kindgen Milles D, Burtscheidt W, Tarnow J, Gaebel W. Antagonist‐induced opiate detoxification. Report on clinical experience as well as on short and intermediate range course [Antagonisteninduzierte Opiatentgiftung. Erfahrungsbericht zur klinischen Anwendung sowie zum kurz‐ und mittelfristigen Verlauf]. Nervenarzt 2000;71(9):745‐50. - PubMed
Brewer 1998a {published data only}
-
- Brewer C, Laban M, Schmulian C, Gooberman L, Kasvikis Y, Maksoud NA. Rapid opiate detoxification and naltrexone induction under general anaesthesia and assisted ventilation: experiences with 510 patients in four different centres. Acta psychiatrica belgica 1998;98:181‐9.
Cucchia 1998 {published data only}
-
- Cucchia AT, Monnat M, Spagnoli J, Ferrero F, Bertschy G. Ultra‐rapid opiate detoxification using deep sedation with oral midazolam: short and long‐term results. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1998;52:243‐50. - PubMed
Dettling 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dettling M, Tretter F. Opiate withdrawal in anaesthesia (forced narcotic withdrawal, "turbo withdrawal") in narcotic dependence. Changes in withdrawal treatment‐‐wishes and reality [Der Opiatentzug in Narkose (forcierter Narkoseentzug, "Turboentzug") bei Opiatabhangigkeit. Entzugsbehandlungen im Wandel der Zeit‐‐Wunsch und Wirklichkeit]. Nervenarzt 1996;67(9):805‐10. - PubMed
E. Berenguel 2001 {published data only}
-
- Espinosa Berenguel JL, Palazon Sanchez C, Felices Abad F, Garcia Basterrechea JM, Gil Rueda B, Blanco Molina TB, et al. Study of an ultrashort opiate detoxification protocol in an intensive care unit: Preliminary results. Medicina Intensiva 2001;25(6):217‐22.
Elman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Elman I, D'Ambra MN, Krause S, Breiter H, Kane M, Morris R, et al. Ultrarapid opioid detoxification: effects on cardiopulmonary physiology, stress hormones and clinical outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2001;61(2):163‐72. - PubMed
Foster 2003 {published data only}
-
- Foster J, Brewer C, Steele T. Naltrexone implants can completely prevent early (1‐month) relapse after opiate detoxification: A pilot study of two cohorts totaling 101 patients with a note on naltrexone blood levels. Addiction Biology 2003;8(2):211‐7. - PubMed
Gold 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gold CG, Cullen DJ, Gonzales S, Houtmeyers D, Dwyer MJ. Rapid opioid detoxification during general anaesthesia: a review of 20 patients. Anesthesiology 1999;91(6):1639‐47. - PubMed
Hensel 2000a {published data only}
-
- Hensel M, Wolter S, Kox WJ. EEG controlled rapid opioid withdrawal under general anaesthesia. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;84(2):236‐8. - PubMed
Hensel 2000b {published data only}
-
- Hensel M, Kox WJ. Safety, efficacy, and long‐term results of a modified version of rapid opiate detoxification under general anaesthesia: a prospective study in methadone, heroin, codeine and morphine addicts. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2000;44(3):326‐33. - PubMed
Ivaskevicius 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ivaskevicius J, Jovaisa T, Laurinenas G, Vosylius S, Sipylaite J, Badaras R. [Safety and effectiveness of opiate antagonist detoxification under general anesthesia]. Medicina (Kaunas) 2005;41(12):1011‐8. - PubMed
Kasvikis 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kasvikis Y, Mitskidou P, Brewer C, Siafaka A, Anagnostakos A. Opiate withdrawal under general anaesthesia and naltrexone induction in 24 hours: A clinical report on 25 cases from Athens, Greece, and a short literature review. Psychiatriki 1997;7(3):191‐8.
Lawental 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lawental E. Ultra rapid opiate detoxification as compared to 30‐day inpatient detoxification program ‐ a retrospective follow‐up study. Journal of Substance Abuse 2000;11(2):173‐81. - PubMed
Legarda 1994 {published data only}
-
- Legarda JJ, Gossop M. A 24‐h inpatient detoxification treatment for heroin addicts: a preliminary investigation. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1994;35(2):91‐3. - PubMed
Loimer 1989 {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Schmid R, Presslich O, Lenz K. Continuous naloxone administration suppresses opiate withdrawal symptoms in human opiate addicts during detoxification treatment. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1989;23(1):81‐6. - PubMed
Loimer 1990 {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Schmid R, Lenz K, Presslich O, Grünberger J. Acute blocking of naloxone‐precipitated opiate withdrawal symptoms by methohexitone. British Journal of Psychiatry 1990;157:748‐52. - PubMed
Loimer 1991a {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Lenz K, Schmid R, Presslich O. Technique for greatly shortening the transition from methadone to naltrexone maintenance of patients addicted to opiates. American Journal of Psychiatry 1991;148(7):933‐5. - PubMed
Loimer 1991b {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Linzmayer L, Grunberger J. Comparison between observer assessment and self rating of withdrawal distress during opiate detoxification. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1991;28:265‐8. - PubMed
Loimer 1991c {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Linzmayer L, Schmid R, Grunberger J. Similar efficacy of abrupt and gradual opiate detoxification. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1991;17(3):307‐12. - PubMed
Loimer 1993 {published data only}
-
- Loimer N, Hofmann P, Chaudhry H. Ultrashort noninvasive opiate detoxification. American Journal of Psychiatry 1993;150(5):839. - PubMed
London 1999 {published data only}
-
- London M, Paul E, Gkolia I. Ultra‐rapid opiate detoxification in hospital. Psychiatric Bulletin 1999;23(9):544‐6.
Lorenzi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lorenzi P, Marsili M, Boncinelli S, Fabbri LP, Fontanari P, Zorn AM, et al. Searching for a general anaesthesia protocol for rapid detoxification from opioids. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 1999;16(10):719‐27. - PubMed
Ma 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ma H, Tang J, White PF, Wender RH, Leverone T, Quon R, et al. The effect of clonidine on gastrointestinal side effects associated with ultra‐rapid opioid detoxification. Anaesthesia and Analgesia 2003;96(5):1409‐12. - PubMed
McDonald 2000a {published data only}
-
- McDonald T. Plasma naltrexone during opioid detoxification. Journal of Addictive Diseases 2000;19(4):59‐64. - PubMed
McDonald 2001 {published data only}
-
- McDonald T, Hoffman WE, Berkowitz R. Combining median electroencephalography frequency and sympathetic activity in an index to evaluate opioid detoxification in patients. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 2001;13(2):74‐8. - PubMed
Pereira 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pereira C, Brewer C. Rapid opiate detoxification under sedation during pregnancy : a report on 14 cases with one ten‐year follow‐up. Addiction Biology 1999;4(2):239‐40.
Pfab 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pfab R, Hirtl C, Zilker T. Opiate detoxification under anaesthesia: no apparent benefit but suppression of thyroid hormones and risk of pulmonary and renal failure. Journal of Toxicology . Clinical Toxicology 1999;37(1):43‐50. - PubMed
Pinto 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pinto E, Reggers J, Delhez M, Fuchs S, Venneman I, Lamy M, Ansseau M. Ultra‐fast opiate detoxification under general anaesthesia: preliminary results of the Liege protocol. Revue Medicale de Liege 2001;56(8):572‐6. - PubMed
Presslich 1989a {published data only}
-
- Presslich O, Loimer N, Aschauer G, Fodor G, Pfersmann D, Muller K, et al. Staggered opiate withdrawal via tiapride and naloxone, as a new therapeutic approach [Fraktionierter opiatentzug mit tiaprid und naloxon, ein neuer therapieansatz]. Psychiatrische Praxis 1989;16(5):179‐81. - PubMed
Presslich 1989b {published data only}
-
- Presslich O, Loimer N, Lenz K, Schmid R. Opiate detoxification under general anaesthesia by large doses of naloxone. Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology 1989;27(4‐5):263‐70. - PubMed
Rabinowitz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rabinowitz J, Cohen H, Atias S. Outcomes of naltrexone maintenance following ultra rapid opiate detoxification versus intensive inpatient detoxification. American Journal on Addictions 2002;11(1):52‐6. - PubMed
Saunders 2002 {published data only}
-
- Saunders JB, Jones R, Dean A, Connor J, Young R, Keen L, et al. Comparison of rapid opiate detoxification and naltrexone with methadone maintenance in the treatment of opiate dependence: A randomised controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2002;66(Suppl 1):156.
Scherbaum 1998 {published data only}
-
- Scherbaum N, Klein S, Kaube H, Kienbaum P, Peters J, Gastpar M. Alternative strategies of opiate detoxification: evaluation of the so‐called ultra‐rapid detoxification. Pharmacopsychiatry 1998;31(6):205‐9. - PubMed
Teplin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Teplin D, Raz B, Daiter J, Varenbut M, Zachos CT, Whang P, et al. Measurement of symptom withdrawal severity in a 24‐hour period after the anesthesia‐assisted rapid opiate detoxification procedure. American Journal of Drug & Alcohol Abuse 2005;31(2):327‐35. - PubMed
Tornay 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tornay CB, Favrat B, Monnat M, Daeppen JB, Schnyder C, Bertschy G, et al. Ultra‐rapid opiate detoxification using deep sedation and prior oral buprenorphine preparation: long‐term results. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2003;69(3):283‐8. - PubMed
Tretter 1998 {published data only}
-
- Tretter F, Burkhardt D, Bussello‐Spieth B, Reiss J, Walcher S, Büchele W. Clinical experience with antagonist‐induced opiate withdrawal under anaesthesia. Addiction 1998;93(2):269‐75. - PubMed
Zemtsovski 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zemtsovski MI, Kipriianov VS, Tros'ko OU, Brazhnikov AV, Strashnov VI. [Complications of accelerated opioid detoxification]. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 2005;3:11‐5. - PubMed
Zimmermann 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zimmermann G, Favrat B, Muller J, Zullino D, Krenz S, Deyras E, et al. [Ultrafast opiate detoxification under general anesthesia: the St. Loup Hospital experience]. Revue Medicale de la Suisse Romande 2003;123(2):97‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
Amato 2005
Amato 2008
Bearn 1999
-
- Bearn J, Gossop M, Strang J. Rapid opiate detoxification treatments. Drug and Alcohol Review 1999;18(1):75‐81.
Blake 1999
-
- Blake S. Addict robbed of her new life. The Sunday Telegraph (Australia) 1999, issue 6 May.
Brewer 1997
-
- Brewer C. Ultra‐rapid, antagonist‐precipitated opiate detoxification under general anaesthetic or sedation. Addiction Biology 1997;2(3):291‐302. - PubMed
Brewer 1998b
-
- Brewer C, Gastfriend DR. Rapid opioid detoxification. JAMA 1998;279(23):1872. - PubMed
Broers 2000
-
- Broers B, Giner F, Dumont P, Mino A. Inpatient opiate detoxification in Geneva: follow‐up at 1 and 6 months. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2000;58(1):85‐92. - PubMed
Bulthuis 2000
-
- Bulthuis D, Diaz JE. Ultrarapid opiate detoxification. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2000;35(1):100‐1. - PubMed
Chanmugam 2000
-
- Chanmugam AS, Hengeller M, Ezenkwele U. Development of rhabdomyolysis after rapid opioid detoxification with subcutaneous naltrexone maintenance therapy. Academic Emergency Medicine 2000;7(3):303‐5. - PubMed
Cochrane Handbook 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.0. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, [updated February 2008].
Day 2005
Dyer 1998
Farrell 1994
-
- Farrell M. Opiate withdrawal. Addiction 1994;89(11):1471‐5. - PubMed
Gevirtz 1999
-
- Gevirtz C, Subhedar DV, Choi CS. Catecholamine surge in opioid‐addicted patients undergoing detoxification under general anaesthesia. Anesthesiology 1999;90(1):334‐5. - PubMed
Gooberman 1998
-
- Gooberman LL, Bradway DW. Depot naltrexone vs oral naltrexone post‐detoxification. Journal of Addictive Diseases 1998;17(2):150.
Gossop 1988
-
- Gossop M. Clonidine and the treatment of the opiate withdrawal syndrome. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1988;21(3):253‐9. - PubMed
Gossop 1989
-
- Gossop M, Green L, Phillips G, Bradley B. Lapse, relapse and survival among opiate addicts after treatment. A prospective follow‐up study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:348‐53. - PubMed
Gossop 1990
-
- Gossop M. The development of a short opiate withdrawal scale (SOWS). Addictive Behaviours 1990;15(5):487‐90. - PubMed
Gowing 2009
Gowing 2009a
Gowing 2009b
Hall 1998
-
- Hall W, Darke S. Trends in opiate overdose deaths in Australia 1979‐1995. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1998;52:71‐7. - PubMed
Handelsman 1987
-
- Handelsman L, Cochrane KJ, Aronson MJ, Ness RA, Rubinstein KJ, Kanof PD. Two new rating scales for opiate withdrawal. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1987;13(3):293‐308. - PubMed
Hoffman 1998
-
- Hoffman WE, Berkowitz R, McDonald T, Hass F. Ultra‐rapid opioid detoxification increases spontaneous ventilation. Journal of Clinical Anaesthesia 1998;10(5):372‐6. - PubMed
Jaffe 1997
-
- Jaffe JH, Knapp CM, Ciraulo DA. Opiates: Clinical Aspects. In: Lowinson JH, Ruiz P, Millman RB, Langrod JG editor(s). Substance Abuse: A comprehensive textbook. 3rd Edition. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1997.
Kienbaum 1998
-
- Kienbaum P, Thurauf N, Michel MC, Scherbaum N, Gastpar M, Peters J. Profound increase in epinephrine concentration in plasma and cardiovascular stimulation after mu‐opioid receptor blockade in opioid‐addicted patients during barbiturate‐induced anaesthesia for acute detoxification. Anesthesiology 1998;88(5):1154‐61. - PubMed
Kleber 1982
-
- Kleber HD, Riordan CE. The treatment of narcotic withdrawal: a historical review. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1982;43(6):30‐4. - PubMed
Lipton 1983
-
- Lipton D, Maranda M. Detoxification from heroin dependency: An overview of method and effectiveness. Advances in Alcohol and Substance Abuse 1983;2(1):31‐55.
Mark 2001
-
- Mark TL, Woody GE, Juday T, Kleber HD. The economic costs of heroin addiction in the United States. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2001;61(2):195‐206. - PubMed
Mattick 1996
-
- Mattick RP, Hall W. Are detoxification programmes effective?. Lancet 1996;347:97‐100. - PubMed
Mayor 1997
McDonald 2000
-
- McDonald T. Plasma naltrexone during opioid detoxification. Journal of Addictive Diseases 2000;19(4):59‐64. - PubMed
NIH 1997
-
- NIH Consensus Development Statement. Effective Medical Treatment of Heroin Addiction. National Institutes of Health. National Institutes of Health, 1997, November 17‐19.
Peachey 1988
-
- Peachey JE, Lei H. Assessment of opioid dependence with naloxone. British Journal of Addiction 1988;83:193‐201. - PubMed
Phillips 1986
-
- Phillips GT, Gossop M, Bradley B. The influence of psychological factors on the opiate withdrawal syndrome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;149:235‐8. - PubMed
Preston 1985
-
- Preston KL, Bigelow GE. Pharmacological advances in addiction treatment. International Journal of the Addictions 1985;20(6&7):845‐67. - PubMed
Satel 1993
-
- Satel SL, Kosten TR, Schuckit MA, Fischman MW. Should protracted withdrawal from drugs be included in DSM‐IV?. American Journal of Psychiatry 1993;150(5):695‐704. - PubMed
Simon 1997
-
- Simon DL. Rapid opioid detoxification using opioid antagonists: history, theory and the state of the art. Journal of Addictive Diseases 1997;16(1):103‐22. - PubMed
Stephenson 1997
-
- Stephenson J. Opiate detoxification under anaesthetic. JAMA 1997;278(16):1319. - PubMed
Vaillant 1988
-
- Vaillant GE. What can long‐term follow‐up teach us about relapse and prevention of relapse in addiction?. British Journal of Addiction 1988;83(10):1147‐57. - PubMed
Wang 1974
-
- Wang RI, Wiesen RL, Lamid S, Roh BL. Rating the presence and severity of opiate dependence. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1974;16:653‐8. - PubMed
White 1999
-
- White JM, Irvine RJ. Mechanisms of fatal opioid overdose. Addiction 1999;94(7):961‐72. - PubMed
Whittington 2000
-
- Whittington A, Collins ED, Kleber HD. Rapid opioid detoxification during general anaesthesia: is death not a significant outcome?. Anesthesiology 2000;93(5):1363‐4. - PubMed
World Drug Report 2007
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2007. Available from www.unodc.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

