Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) versus multiple insulin injections for type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20091571
- PMCID: PMC12582037
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005103.pub2
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) versus multiple insulin injections for type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes is a metabolic disorder resulting from a defect in insulin secretion. Onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus may occur at any age and it is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood and adolescence. Since there are no interventions known to prevent onset, it is vital that effective treatment regimes are available. Glycaemic control is maintained by replacement of insulin and may be in the form of 'conventional' insulin therapy (multiple injections per day) or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII).
Objectives: To assess the effects of CSII compared to multiple insulin injections (MI) in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Search strategy: Studies were obtained from electronic searches of The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL.
Selection criteria: Studies were included if they were randomised controlled trials comparing CSII with three or more insulin injections per day (MI) in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed risk of bias and extracted characteristics of included studies. Authors contacted study investigators to obtain missing information. Generic inverse variance meta-analyses using a random-effects model were performed.
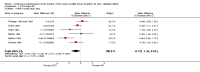
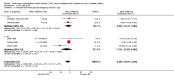
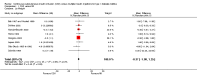
Main results: Twenty three studies randomised 976 participants with type 1 diabetes to either intervention. There was a statistically significant difference in glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) favouring CSII (weighted mean difference -0.3% (95% confidence interval -0.1 to -0.4). There were no obvious differences between the interventions for non-severe hypoglycaemia, but severe hypoglycaemia appeared to be reduced in those using CSII. Quality of life measures suggest that CSII is preferred over MI. No significant difference was found for weight. Adverse events were not well reported, no information is available on mortality, morbidity and costs.
Authors' conclusions: There is some evidence to suggest that CSII may be better than MI for glycaemic control in people with type 1 diabetes. Non-severe hypoglycaemic events do not appear to be reduced with CSII. There is insufficient evidence regarding adverse events, mortality, morbidity and costs.
Conflict of interest statement
JONATHAN SHAW: Received honoraria for lectures and for advisory boards; his department has received funding for research and for organizing educational activities from NovoNordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis and Medtronic.
Figures

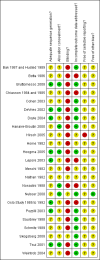
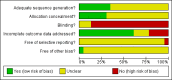


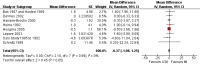

























Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bak 1987 and Husted 1989 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bak JF, Nielsen OH, Pedersen O, Beck‐Nielsen H. Multiple insulin injections using a pen injector versus insulin pump treatment in young diabetic patients. Diabetes Research 1987;6(3):155‐8. - PubMed
-
- Husted SE, Nielsen HK, Bak JF, Beck‐Nielsen H. Antithrombin III activity, von Willebrand factor antigen and platelet function in young diabetic patients treated with multiple insulin injections versus insulin pump treatment. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 1989;19(1):90‐4. - PubMed
Botta 1986 {published data only}
-
- Botta RM, Sinagra D, Angelico MC, Bompiani GD. [Comparison of intensified traditional insulin therapy and micropump therapy in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus]. Minerva Medica 1986;77(17):657‐61. - PubMed
Bruttomesso 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bruttomesso D, Crazzolara D, Maran A, Costa S, Dal Pos M, Girelli A, et al. In Type 1 diabetic patients with good glycaemic control, blood glucose variability is lower during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion than during multiple daily injections with insulin glargine. Diabetic Medicine 2008;25(3):326‐32. - PubMed
Chiasson 1984 and 1985 {published data only}
-
- Chiasson JL, Ducros F, Poliquin‐Hamet M, Lopez D, Lecavalier L, Hamet P. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (Mill‐Hill Infuser) versus multiple injections (Medi‐Jector) in the treatment of insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus and the effect of metabolic control on microangiopathy. Diabetes Care 1984;7(4):331‐7. - PubMed
Cohen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cohen D, Weintrob N, Benzaquen H, Galatzer A, Fayman G, Phillip M. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections in adolescents with type I diabetes mellitus: a randomized open crossover trial. Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism 2003;16(7):1047‐50. - PubMed
DeVries 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- DeVries JH, Snoek FJ, Kostense PJ, Masurel N, Heine RJ. A randomized trial of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and intensive injection therapy in type 1 diabetes for patients with long‐standing poor glycemic control. Diabetes Care 2002;25(11):2074‐80. - PubMed
Doyle 2004 {published data only}
-
- Doyle EA, Weinzimer SA, Steffen AT, Ahern JA, Vincent M, Tamborlane WV. A randomized, prospective trial comparing the efficacy of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with multiple daily injections using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care 2004;27(7):1554‐8. - PubMed
Hanaire‐Broutin 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hanaire‐Broutin H, Melki V, Bessieres‐Lacombe S, Tauber JP. Comparison of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple daily injection regimens using insulin lispro in type 1 diabetic patients on intensified treatment: a randomized study. The Study Group for the Development of Pump Therapy in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23(9):1232‐5. - PubMed
Hirsch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch IB, Bode BW, Garg S, Lane WS, Sussman A, Hu P, et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) of insulin aspart versus multiple daily injection of insulin aspart/insulin glargine in type 1 diabetic patients previously treated with CSII. Diabetes Care 2005;28(3):533‐8. - PubMed
Home 1982 {published data only}
-
- Home PD, Capaldo B, Burrin JM, Worth R, Alberti KG. A crossover comparison of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) against multiple insulin injections in insulin‐dependent diabetic subjects: improved control with CSII. Diabetes Care 1982;5(5):466‐71. - PubMed
Hoogma 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoogma RPLM, Hoekstra JB, Michels BP, Levi M. Comparison between multiple daily insulin injection therapy (MDI) and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy (CSII), results of the five nations study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2006;74 Suppl 2:S144‐7.
Lepore 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lepore G, Dodesini AR, Nosari I, Trevisan R. Both continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and a multiple daily insulin injection regimen with glargine as basal insulin are equally better than traditional multiple daily insulin injection treatment. Diabetes Care 2003;26(4):1321‐2. - PubMed
Meschi 1982 {published data only}
-
- Meschi F, Beccaria L, Vanini R, Szulc M, Chiumello G. Short‐term subcutaneous insulin infusion in diabetic children. Comparison with three daily insulin injections. Acta Diabetologica Latina 1982;19(4):371‐5. - PubMed
Nathan 1982 {published data only}
-
- Nathan Dm LPAJ. Intensive conventional and insulin pump therapies in adult type I diabetes. A crossover study. Annals of Internal Medicine 1982;97:31‐6. - PubMed
Nosadini 1988 {published data only}
-
- Nosadini R. Frequency of hypoglycaemic and hyperglycaemic‐ketotic episodes during conventional and subcutaneous continuous insulin infusion therapy in IDDM. Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolism 1988;1:289‐96.
Nuboer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nuboer R, Borsboom GJJM, Zoethout JA, Koot HM, Bruining J. Effects of insulin pump vs. injection treatment on quality of life and impact of disease in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in a randomized, prospective comparison. Pediatric Diabetes 2008;9(4 Pt 1):291‐6. - PubMed
Oslo Study 1985 to 1992 {published data only}
-
- Brinchmann‐Hansen O, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF. Effects of intensified insulin treatment on various lesions of diabetic retinopathy. American Journal of Ophthalmology 1985;100(5):644‐53. - PubMed
-
- Brinchmann‐Hansen O, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF, Sandvik L. Oscillatory potentials, macular recovery time, and diabetic retinopathy through 3 years of intensified insulin treatment.[see comment]. Ophthalmology 1988;95(10):1358‐66. - PubMed
-
- Brinchmann‐Hansen O, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF, Sandvik L. The response of diabetic retinopathy to 41 months of multiple insulin injections, insulin pumps, and conventional insulin therapy. Archives of Ophthalmology 1988;106(9):1242‐6. - PubMed
-
- Dahl Jorgensen K. Blood glucose control and progression of diabetic neuropathy: eight years results from the Oslo study. Diabetologia 1992;35:A15.
-
- Dahl‐Jorgensen K. Near‐normoglycemia and late diabetic complications. The Oslo Study. Acta Endocrinologica Supplementum 1987;284:1‐38. - PubMed
Pozzilli 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pozzilli P, Crino A, Schiaffini R, Manfrini S, Fioriti E, Coppolino G, et al. A 2‐year pilot trial of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus intensive insulin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes (IMDIAB 8). Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2003;5(6):965‐74. - PubMed
Saurbrey 1988 {published data only}
-
- Saurbrey N, Arnold‐Larsen S, Moller‐Jensen B, Kuhl C. Comparison of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with multiple insulin injections using the NovoPen. Diabetic Medicine 1988;5(2):150‐3. - PubMed
Schmitz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Schmitz A, Christiansen JS, Christensen CK, Hermansen K, Mogensen CE. Effect of pump versus pen treatment on glycaemic control and kidney function in long‐term uncomplicated insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Danish Medical Bulletin 1989;36(2):176‐8. - PubMed
Skogsberg 2008 {published data only}
-
- Skogsberg L, Fors H, Hanas R, Chaplin JE, Lindman E, Skogsberg J. Improved treatment satisfaction but no difference in metabolic control when using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion vs. multiple daily injections in children at onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatric Diabetes 2008;9(5):472‐9. - PubMed
Tsui 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tsui E, Barnie A, Ross S, Parkes R, Zinman B. Intensive insulin therapy with insulin lispro: a randomized trial of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily insulin injection.[see comment]. Diabetes Care 2001;24(10):1722‐7. - PubMed
Weintrob 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Weintrob N, Schechter A, Benzaquen H, Shalitin S, Lilos P, Galatzer A, et al. Glycemic patterns detected by continuous subcutaneous glucose sensing in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus treated by multiple daily injections vs continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2004;158(7):677‐84. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alemzadeh 2005 {published data only}
-
- Alemzadeh R, Palma‐Sisto P, Parton EA, Holzum MK. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple dose of insulin regimen display similar patterns of blood glucose excursions in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2005;7(4):587‐96. - PubMed
Amemiya 1983 {published data only}
-
- Amemiya S, Kato K, Asayama K. The improved response in endogenous insulin due to continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin therapy in juvenile diabetes. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine 1983;141 Suppl:713‐7. - PubMed
Arias 1985 {published data only}
-
- Arias P, Kerner W, Zier H, Navascues I, Pfeiffer EF. Incidence of hypoglycemic episodes in diabetic patients under continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and intensified conventional insulin treatment: assessment by means of semiambulatory 24‐hour continuous blood glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 1985;8(2):134‐40. - PubMed
Bagdade 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bagdade JD, Helve E, Taskinen MR. Effects of continuous insulin infusion therapy on lipoprotein surface and core lipid composition in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 1991;40(5):445‐9. - PubMed
Bangstad 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bangstad HJ, Osterby R, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Berg KJ, Hartmann A, Hanssen KF. Improvement of blood glucose control in IDDM patients retards the progression of morphological changes in early diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 1994;37(5):483‐90. - PubMed
Barbosa 1981 {published data only}
-
- Barbosa J, Menth L, Eaton J, Sutherland D, Freier EF, Najarian J. Long‐term, ambulatory, subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections in brittle diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1981;4(2):269‐74. - PubMed
Barrett 1995 {published data only}
-
- Barrett DH, Davidson PC, Steed LJ, Abel GG, Loman KE, Saudek CD. Evaluation of the psychosocial impact of the MiniMed variable‐rate implantable insulin pump. Southern Medical Journal 1995;88(12):1226‐30. - PubMed
Bech 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bech P, Gudex C, Staehr Johansen K. The WHO (Ten) well‐being index: Validation in diabetes. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 1996;65(4):183‐90. - PubMed
Beck‐Nielsen 1984 {published data only}
-
- Beck‐Nielsen H, Richelsen B, Hasling C, Nielsen OH, Heding L, Sorensen NS. Improved in vivo insulin effect during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in patients with IDDM. Diabetes 1984;33(9):832‐7. - PubMed
Beck‐Nielsen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Beck‐Nielsen H, Richelsen B, Mogensen CE, Olsen T, Ehlers N, Nielsen CB, et al. Effect of insulin pump treatment for one year on renal function and retinal morphology in patients with IDDM. Diabetes Care 1985;8(6):585‐9. - PubMed
Beck‐Nielsen 1985a {published data only}
-
- Beck‐Nielsen H, Richelsen B, Sorensen NS, Nielsen OH. Insulin pump treatment: Effect on glucose homeostasis, metabolites, hormones, insulin antibodies and quality of life. Diabetes Research 1985;2(1):37‐43. - PubMed
Beck‐Nielsen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Beck‐Nielsen H, Olesen T, Mogensen CE, Richelsen B, Olsen HW, Ehlers N, et al. Effect of near normoglycemia for 5 years on progression of early diabetic retinopathy and renal involvement. Diabetes Research 1990;15(4):185‐90. - PubMed
Behme 1984 {published data only}
-
- Behme MT, Dupre J. Insulin‐binding to erythrocytes in type I diabetes mellitus: effects of continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin. Clinical & Investigative Medicine ‐ Medecine Clinique et Experimentale 1984;7(2):109‐14. - PubMed
Bell 1985 {published data only}
-
- Bell PM, Hayes JR, Hadden DR, Archer DB. The effect of plasma glucose control by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or conventional therapy on retinal morphology and urinary albumin excretion. Diabete et Metabolisme 1985;11(4):254‐61. - PubMed
Bell 1985a {published data only}
-
- Bell PM, Sawhney B, Hayes JR, Hadden DR. Effect of plasma glucose control by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on nerve conduction. Irish Journal of Medical Science 1985;154(10):378‐84. - PubMed
Bending 1986 {published data only}
Berg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Berg TJ, Nourooz‐Zadeh J, Wolff SP, Tritschler HJ, Bangstad HJ, Hanssen KF. Hydroperoxides in plasma are reduced by intensified insulin treatment. A randomized controlled study of IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 1998;21(8):1295‐300. - PubMed
Bergenstal 1985 {published data only}
-
- Bergenstal RM, Dupre J, Lawson PM, Rizza RA, Rubenstein AH. Observations on C‐peptide and free insulin in the blood during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and conventional insulin therapy. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:31‐6. - PubMed
Berger 1989 {published data only}
-
- Berger M, Chantelau EA, Spraul M. [Treatment of type I diabetes mellitus with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: indications and quality control]. Verhandlungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur Innere Medizin 1989;95:135‐40. - PubMed
Bibergeil 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bibergeil H, Huttl I, Felsing W, Felsing U, Seidlein I, Herfurth S, et al. 36 months continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) in insulin dependent diabetes (IDDM)‐‐influence on early stages of retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy‐‐psychological analysis. Experimental & Clinical Endocrinology 1987;90(1):51‐61. - PubMed
Biesenbach 1988 {published data only}
-
- Biesenbach G, Grafinger P, Kaiser W, Stuby U, Zazgornik J. [Metabolic control in labile type I diabetes with conventional insulin therapy, basal bolus insulin therapy using pens and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with the pump]. Medizinische Klinik 1988;83(12):398‐401. - PubMed
Bode 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bode BW, Steed RD, Davidson PC. Reduction in severe hypoglycemia with long‐term continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type I diabetes. Diabetes Care 1996;19(4):324‐7. - PubMed
Bode 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bode B, Shelmet J, Gooch B, Hassman DR, Liang J, Smedegaard JK, et al. Patient perception and use of an insulin injector/glucose monitor combined device. Diabetes Educator 2004;30(2):301‐9. - PubMed
Bombor 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bombor H, Bruns W, Ratzmann KP, Jutzi E, Albrecht G, Michaelis D, et al. Long‐term improvement in metabolic control of unstable type I diabetes by s.c. insulin injection patterns based on the dose profiles required by bed‐side artificial beta‐cell. Experimental & Clinical Endocrinology 1984;83(2):143‐51. - PubMed
Borisova 1989 {published data only}
-
- Borisova AM, Koev D, Kirilov G. [An improvement in insulin efficacy in patients with type‐1 diabetes mellitus following treatment using an insulin infusion pump]. Vutreshni Bolesti 1989;28(1):74‐7. - PubMed
Brunetti 1984 {published data only}
-
- Brunetti P, Bueti A, Antonella MA, Calabrese G, Fabietti PG, Santeusanio F, et al. Metabolic effects of intensified insulin therapy. Experimental & Clinical Endocrinology 1984;83(2):130‐5. - PubMed
Buysschaert 1981 {published data only}
-
- Buysschaert M, Lejeune M, Lambert AE. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the treatment of juvenile‐onset diabetes. Diabete et Metabolisme 1981;7(3):189‐93. - PubMed
Buysschaert 1983 {published data only}
-
- Buysschaert M, Marchand E, Ketelslegers JM, Lambert AE. Comparison of plasma glucose and plasma free insulin during CSII and intensified conventional insulin therapy. Diabetes Care 1983;6(1):1‐5. - PubMed
Calabrese 1982 {published data only}
-
- Calabrese G, Bueti A, Santeusanio F, Giombolini A, Zega G, Angeletti G, et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion treatment in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients: a comparison with conventional optimized treatment in a long‐term study. Diabetes Care 1982;5(5):457‐65. - PubMed
Canny 1985 {published data only}
-
- Canny CL, Kohner EM, Trautman J, Puklin J, Morse P. Comparison of stereofundus photographs in patients with insulin‐dependent diabetes during conventional insulin treatment or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:50‐5. - PubMed
Carta 1986 {published data only}
-
- Carta Q, Meriggi E, Trossarelli GF, Catella G, Dal Molin V, Menato G, et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus intensive conventional insulin therapy in type I and type II diabetic pregnancy. Diabete et Metabolisme 1986;12(3):121‐9. - PubMed
Cavallo‐Perin 1983 {published data only}
-
- Cavallo‐Perin P, Pagano G, Tagliaferro V, Jarre P, Ozzello A, Lenti G. The treatment of unstable type I diabetes: conventional versus portable pump insulin administration. Acta Diabetologica Latina 1983;20(4):363‐70. - PubMed
Chisholm 1984 {published data only}
-
- Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW, Hewett MJ. Hypoglycemic episodes during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: decreased frequency but increased susceptibility. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1984;14(3):255‐9. - PubMed
Christensen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Christensen CK, Christiansen JS, Christensen T, Hermansen K, Mogensen CE. The effect of six months continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on kidney function and size in insulin‐dependent diabetics. Diabetic Medicine 1986;3(1):29‐32. - PubMed
Christensen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Christensen CK, Christiansen JS, Schmitz A, Christensen T, Hermansen K, Mogensen CE. Effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on kidney function and size in IDDM patients: a 2 year controlled study. Journal of Diabetic Complications 1987;1(3):91‐5. - PubMed
Christiansen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Christiansen JS, Ingerslev J, Bernvil SS, Christensen CK, Hermansen K, Schmitz A. Near normoglycemia for 1 year has no effect on platelet reactivity, factor VIII, and von Willebrand factor in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus: a controlled trial. Journal of Diabetic Complications 1987;1(3):100‐6. - PubMed
Ciavarella 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ciavarella A, Vannini P, Flammini M, Bacci L, Forlani G, Borgnino LC. Effect of long‐term near‐normoglycemia on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabete et Metabolisme 1985;11(1):3‐8. - PubMed
Colette 1986 {published data only}
-
- Colette C, Monnier L, Arnal J, Selam JL, Mirouze J. Effects of different insulin administration modalities on vitamin D metabolism of insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology 1986;208:501‐8. - PubMed
Colette 1989 {published data only}
-
- Colette C, Pares‐Herbute N, Monnier L, Selam JL, Thomas N, Mirouze J. Effect of different insulin administration modalities on vitamin D metabolism of insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. Hormone & Metabolic Research 1989;21(1):37‐41. - PubMed
Connis 1989 {published data only}
-
- Connis RT, Taylor TR, Gordon MJ, Mecklenburg RS, Liljenquist JE, Stephens JW, et al. Changes in cognitive and social functioning of diabetic patients following initiation of insulin infusion therapy. Experimental Aging Research 1989;15(1‐2):51‐60. - PubMed
Coustan 1986 {published data only}
-
- Coustan DR, Reece EA, Sherwin RS, Rudolf MC, Bates SE, Sockin SM, et al. A randomized clinical trial of the insulin pump vs intensive conventional therapy in diabetic pregnancies. JAMA 1986;255(5):631‐6. - PubMed
Davies 1984 {published data only}
de Beaufort 1985 {published data only}
-
- Beaufort CE, Bruining GJ, Aarsen RS, Boer NC, Grose WF. Does continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) prolong the remission phase of insulin‐dependent diabetic children? Preliminary findings of a randomized prospective study. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 1985;28 Suppl 1:53‐4. - PubMed
de Beaufort 1989 {published data only}
-
- Beaufort CE, Houtzagers CM, Bruining GJ, Aarsen RS, Boer NC, Grose WF, et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) versus conventional injection therapy in newly diagnosed diabetic children: two‐year follow‐up of a randomized, prospective trial. Diabetic Medicine 1989;6(9):766‐71. - PubMed
Dicker 1987 {published data only}
-
- Dicker D, Feldberg D, Karp M, Yeshaya A, Samuel N, Goldman JA. Preconceptional diabetes control in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus patients with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 1987;15(2):161‐7. - PubMed
DiMeglio 2004 {published data only}
-
- DiMeglio LA, Pottorff TM, Boyd SR, France L, Fineberg N, Eugster EA. A randomized, controlled study of insulin pump therapy in diabetic preschoolers. Journal of Pediatrics 2004;145(3):380‐4. - PubMed
Edelmann 1987 {published data only}
-
- Edelmann E, Walter H, Biermann E, Schleicher E, Bachmann W, Mehnert H. Sustained normoglycemia and remission phase in newly diagnosed type I diabetic subjects. Comparison between continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and conventional therapy during a one year follow‐up. Hormone & Metabolic Research 1987;19(9):419‐21. - PubMed
Feldt‐Rasmussen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Mathiesen ER, Deckert T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin‐dependent diabetes. Lancet 1986;328(8519):1300‐4. - PubMed
Feldt‐Rasmussen 1986a {published data only}
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Mathiesen ER, Hegedus L, Deckert T. Kidney function during 12 months of strict metabolic control in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 1986;314(11):665‐70. - PubMed
Feldt‐Rasmussen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Mathiesen ER, Jensen T, Lauritzen T, Deckert T. Effect of improved metabolic control on loss of kidney function in type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients: an update of the Steno studies. Diabetologia 1991;34(3):164‐70. - PubMed
Flores 1984 {published data only}
-
- Flores d'Arcais A, Morandi F, Beccaria L, Meschi F, Chiumello G. Metabolic control in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetic children. Effect of continuous subcutaneous infusion. Hormone Research 1984;19(2):65‐9. - PubMed
Garg 2004 {published data only}
-
- Garg SK, Walker AJ, Hoff HK, D'Souza AO, Gottlieb PA, Chase HP. Glycemic parameters with multiple daily injections using insulin glargine versus insulin pump.[see comment]. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2004;6(1):9‐15. - PubMed
Garmo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Garmo A, Pettersson‐Frank B, Ehrenberg A. Treatment effects and satisfaction in diabetic patients changing from multiple daily insulin injections to CSII. Practical Diabetes International 2004;21(1):7‐12.
Giocolea 1988 {published data only}
-
- Giocolea I, Hernandez I, Fombellida J, Vazquez JA. Renal function of insulin‐dependent diabetic patients, treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump. A comparison with conventional insulin therapy during a follow‐up period of one year. Anales de Medicina Interna 1988;5(4):169‐72.
Goicolea 1986 {published data only}
-
- Goicolea Opacua I, Hernandez Colau I, Vazquez Garcia JA. [Comparative study between the subcutaneous continuous insulin infusion pump and optimized conventional treatment. Effects at 6 months]. Revista Clinica Espanola 1986;179(1):3‐7. - PubMed
Goicolea 1987 {published data only}
-
- Goicolea Opacua I, Hernandez Colau I, Cortazar Galarza A, Vazquez Garcia JA. [Comparison of metabolic control between the continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump and augmented conventional treatment. Effects after 12 months]. Medicina Clinica 1987;88(16):617‐20. - PubMed
Goicolea 1988 {published data only}
-
- Goicolea Opacua I, Martinez Castillo A, Santamaria Pelarda E, Sola Sarabia C, Vazquez Garcia JA. [Metabolic control using a subcutaneous insulin infusion pump: effects 2 years after treatment]. Revista Clinica Espanola 1988;182(4):200‐2. - PubMed
Goicolea 1989 {published data only}
-
- Goicolea I, Santamaria E, Pardo C, Vazquez JA, Martin A, Castresana I. [Course of diabetic retinopathy and metabolic control with subcutaneous insulin infusion pump: 18‐month study]. Anales de Medicina Interna 1989;6(2):71‐3. - PubMed
Greene 1983 {published data only}
Grimm 1987 {published data only}
-
- Grimm JJ, Haardt MJ, Thibult N, Goicolea I, Tchobroutsky G, Slama G. Lifestyle, metabolic control and social implications of pump therapy in 54 routine type I diabetic patients. Diabete et Metabolisme 1987;13(1):3‐11. - PubMed
Guerci 1998 {published data only}
-
- Guerci B, Meyer L, Delbachian I, Kolopp M, Ziegler O, Drouin P. Blood glucose control on Sunday in IDDM patients: intensified conventional insulin therapy versus continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1998;40(3):175‐80. - PubMed
Gulan 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gulan M, Perlman K, Sole M, Albisser AM, Zinman B. Counterregulatory hormone responses preserved after long‐term intravenous insulin infusion compared to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes 1988;37(5):526‐31. - PubMed
Haakens 1989 {published data only}
-
- Haakens K, Hanssen KF, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Vaaler S, Torjesen P, Try K. Early morning glycaemia and the metabolic consequences of delaying breakfast/morning insulin. A comparison of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple injection therapy with human isophane or human ultralente insulin at bedtime in insulin‐dependent diabetics. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1989;49(7):653‐9. - PubMed
Haakens 1990 {published data only}
-
- Haakens K, Hanssen KF, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Vaaler S, Aagenaes O, Mosand R. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII), multiple injection (MI) and conventional insulin therapy (CT) in self‐selecting insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. A comparison of metabolic control, acute complications and patient preferences. Journal of Internal Medicine 1990;228(5):457‐64. - PubMed
Hall 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hall K, Johansson BL, Povoa G, Thalme B. Serum levels of insulin‐like growth factor (IGF) I, II and IGF binding protein in diabetic adolescents treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Journal of Internal Medicine 1989;225(4):273‐8. - PubMed
Haug 1987 {published data only}
-
- Haug PJ, Kelly TM, Cannon RB, Edwards CQ. A self‐controlled study of the effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on diabetic neuropathy. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1987;82(1‐3):123‐32. - PubMed
Heber 1977 {published data only}
-
- Heber D, Molitch ME, Sperling MA. Low‐dose continuous insulin therapy for diabetic ketoacidosis. Prospective comparison with "conventional" insulin therapy. Archives of Internal Medicine 1977;137(10):1377‐80. - PubMed
Helve 1987 {published data only}
-
- Helve E. High density lipoprotein subfractions during continuous insulin infusion therapy. Atherosclerosis 1987;64(2‐3):173‐80. - PubMed
Helve 1987a {published data only}
-
- Helve E, Koivisto VA, Lehtonen A. A crossover comparison of continuous insulin infusion and conventional injection treatment of type I diabetes. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1987;221(4):385‐93. - PubMed
Helve 1987b {published data only}
-
- Helve E, Laatikainen L, Merenmies L, Koivisto VA. Continuous insulin infusion therapy and retinopathy in patients with type I diabetes. Acta Endocrinologica 1987;115(3):313‐9. - PubMed
Hermansen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hermansen K, Moller A, Christensen CK, Christiansen JS, Schmitz O, Orskov H, et al. Diurnal plasma profiles of metabolite and hormone concentration in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients during conventional insulin treatment and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. A controlled study. Acta Endocrinologica 1987;114(3):433‐9. - PubMed
Hermansen 1988 {published data only}
-
- Hermansen K, Schmitz O, Boye N, Christensen CK, Christiansen JS, Alberti KG, et al. Glucagon responses to intravenous arginine and oral glucose in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients during six months conventional or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 1988;37(7):640‐4. - PubMed
Hoogma 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hoogma RP, Spijker AJ, Doorn‐Scheele M, Doorn TT, Michels RP, Doorn RG, et al. Quality of life and metabolic control in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 treated by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or multiple daily insulin injections.[see comment]. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 2004;62(10):383‐7. - PubMed
Hung 1984 {published data only}
-
- Hung J, Menth L, Thompson MJ, Saner B, Rao KV, Barbosa J. The Minnesota Diabetes Complications Clinical Trial cognitive functions under long‐term maximized and standard metabolic controls. Diabete et Metabolisme 1984;10(1):48‐51. - PubMed
Jakobsen 1988 {published data only}
-
- Jakobsen J, Christiansen JS, Kristoffersen I, Christensen CK, Hermansen K, Schmitz A, et al. Autonomic and somatosensory nerve function after 2 years of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type I diabetes. Diabetes 1988;37(4):452‐5. - PubMed
Jensen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Jensen BM, Kuhl C, Molsted‐Pedersen L. Preconceptional treatment with insulin infusion pumps in insulin‐dependent diabetic women with particular reference to prevention of congenital malformations. Acta Endocrinologica, Supplement 1986;112(277):81‐5. - PubMed
Kamoi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kamoi K, Miyakoshi M, Maruyama R. A quality‐of‐life assessment of intensive insulin therapy using insulin lispro switched from short‐acting insulin and measured by an ITR‐QOL questionnaire: a prospective comparison of multiple daily insulin injections and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2004;64(1):19‐25. - PubMed
Kelly 1984 {published data only}
-
- Kelly TM, Sanborn GE, Haug PJ, Edwards CQ. Effect of insulin infusion pump use on diabetic retinopathy. Archives of Ophthalmology 1984;102(8):1156‐9. - PubMed
Knight 1986 {published data only}
-
- Knight G, Boulton AJM, Drury J, Ward JD. Long term glycaemic control by alternative regimens in a feasibility study of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Research 1986;3(7):355‐8. - PubMed
Kobayashi 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kobayashi T, Sawano S, Itoh T, Kosaka K. Plasma immunoreactive somatostatin response to arginine after glycemic control with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type I diabetics. Diabetes Care 1987;10(3):286‐92. - PubMed
Koivisto 1983 {published data only}
-
- Koivisto VA, Tronier B. Postprandial blood glucose response to exercise in type I diabetes: comparison between pump and injection therapy. Diabetes Care 1983;6(5):436‐40. - PubMed
Kordonouri 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kordonouri O, Hartmann R, Lauterborn R, Barnekow C, Hoeffe J, Deiss D. Age‐specific advantages of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion as compared with multiple daily injections in pediatric patients: one‐year follow‐up comparison by matched‐pair analysis. Diabetes Care 2006;29(1):133‐4. - PubMed
Kritz 1983 {published data only}
-
- Kritz H, Hagmuller G, Lovett R, Irsigler K. Implanted constant basal rate insulin infusion devices for Type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1983;25(2):78‐81. - PubMed
Kroc 1984 {published data only}
-
- Kroc. Blood glucose control and the evolution of diabetic retinopathy and albuminuria. A preliminary multicenter trial. The Kroc Collaborative Study Group. The New England journal of medicine 1984;311:365‐72. - PubMed
Kroc 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kroc. Diabetic retinopathy after two years of intensified insulin treatment. Follow‐up of the Kroc Collaborative Study. The Kroc Collaborative Study Group. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association 1988;260:37‐41. - PubMed
Kuno 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kuno T, Tasaki H, Miyazaki S. Continuous subcutaneous insulin injection for self‐care of young patients with insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1996;38(5):464‐9. - PubMed
Laatikainen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Laatikainen L, Teramo K, Hieta‐Heikurainen H, Koivisto V, Pelkonen R. A controlled study of the influence of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion treatment on diabetic retinopathy during pregnancy. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1987;221(4):367‐76. - PubMed
Lager 1983 {published data only}
Lager 1986 {published data only}
-
- Lager I, Attvall S, Blohme G, Smith U. Altered recognition of hypoglycaemic symptoms in type I diabetes during intensified control with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetic Medicine 1986;3(4):322‐5. - PubMed
Lapolla 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lapolla A, Dalfra MG, Masin M, Bruttomesso D, Piva I, Crepaldi C, et al. Analysis of outcome of pregnancy in type 1 diabetics treated with insulin pump or conventional insulin therapy. Acta Diabetologica 2003;40(3):143‐9. - PubMed
Lauritzen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Lauritzen T, Frost‐Larsen K, Larsen HW, Deckert T. Two‐year experience with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in relation to retinopathy and neuropathy. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:74‐9. - PubMed
Lawson 1984 {published data only}
-
- Lawson P, Trayner I, Rosenstock J, Kohner E. The effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on serum lipids. Diabete et Metabolisme 1984;10(4):239‐44. - PubMed
Lawson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Lawson P, Home PD, Bergenstal R. Observations on blood lipid and intermediary metabolite concentrations during conventional insulin treatment or CSII. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:27‐30. - PubMed
Leblanc 1986 {published data only}
-
- Leblanc H, Obadia G, Passa P. [Reduction of hypoglycemia in 10 diabetic patients treated with continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin]. Presse Medicale 1986;15(10):463‐6. - PubMed
Lecavalier 1987 {published data only}
-
- Lecavalier L, Havrankova J, Hamet P, Chiasson J‐L. Effects of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple injections on insulin receptors in insulin‐dependent diabetics. Diabetes Care 1987;10(3):300‐5. - PubMed
Lepore 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lepore G, Dodesini AR, Nosari I, Trevisan R. Effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion vs multiple daily insulin injection with glargine as basal insulin: an open parallel long‐term study. Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2004;17(2):84‐9. - PubMed
Levy 1984 {published data only}
-
- Levy I, Bergua M, Esmatjes E, Halperin I, Figuerola D. [Unstable type I diabetes mellitus: comparative study between intensive conventional treatment and continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin]. Medicina Clinica 1984;83(13):525‐8. - PubMed
Levy‐Marchal 1983 {published data only}
-
- Levy‐Marchal C, Albisser AM, Zinman B. Overnight metabolic control with pulsed intermittent versus continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Care 1983;6(4):356‐60. - PubMed
Levy‐Marchal 1988 {published data only}
-
- Levy‐Marchal C, Czernichow P. Feasibility of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in young diabetic patients. Diabete et Metabolisme 1988;14(2):108‐13. - PubMed
Litton 2002 {published data only}
-
- Litton J, Rice A, Friedman N, Oden J, Lee MM, Freemark M. Insulin pump therapy in toddlers and preschool children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(4):490‐5. - PubMed
Ludvigsson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ludvigsson J, Hanas R. Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring improved metabolic control in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: a controlled crossover study. Pediatrics 2003;111(5 Pt 1):933‐8. - PubMed
Lunetta 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lunetta M, Mauro M, Moli R, Nicoletti F. Effect of octreotide on blood glucose and counterregulatory hormones in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients: the role of dose and route of administration. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1996;51(2):139‐44. - PubMed
Mancuso 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mancuso S, Caruso A, Lanzone A. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) in pregnant diabetic women. Acta Endocrinologica, Supplement 1986;112(277):112‐6. - PubMed
Marshall 1987 {published data only}
-
- Marshall SM, Home PD, Taylor R, Alberti KG. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus injection therapy: a randomized cross‐over trial under usual diabetic clinic conditions. Diabetic Medicine 1987;4(6):521‐5. - PubMed
Marshall 1988 {published data only}
-
- Marshall SM, Taylor R, Home PD, Alberti KG. Intermediary metabolism, insulin sensitivity and insulin receptor status under comparable long‐term therapy with insulin injections and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Acta Endocrinologica 1988;117(4):417‐27. - PubMed
McDonald 1982 {published data only}
-
- McDonald JW, Dupre J, Rodger NW, Champion MC, Webb CD, Ali M. Comparison of platelet thromboxane synthesis in diabetic patients on conventional insulin therapy and continuous insulin infusions. Thrombosis Research 1982;28(6):705‐12. - PubMed
Mecklenburg 1982 {published data only}
-
- Mecklenburg RS, Benson JW Jr, Becker NM, Brazel PL, Fredlund PN, Metz RJ, et al. Clinical use of the insulin infusion pump in 100 patients with type I diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;307(9):513‐8. - PubMed
Minkina‐Pedras 2005 {published data only}
-
- Minkina‐Pedras M, Jarosz‐Chobot P, Malecka‐Tendera E, Deja G. [Assessment of metabolic control and safety of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in prepubertal children with type 1 diabetes mellitus]. Endokrynologia, Diabetologia i Choroby Przemiany Materii Wieku Rozwojowego 2005;11(3):171‐6. - PubMed
Moberg 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moberg EA, Lins PE, Adamson UK. Variability of blood glucose levels in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus on intensified insulin regimens. Diabete et Metabolisme 1994;20(6):546‐52. - PubMed
Moller 1986 {published data only}
-
- Moller A, Rasmussen L, Ledet T, Christiansen JS, Christensen CK, Mogensen CE, et al. Lipoprotein changes during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1986;46(5):471‐5. - PubMed
Monnier 1987 {published data only}
-
- Monnier LH, Rodier M, Gancel A. Plasma lipid fatty acids and platelet function during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in type I diabetes. Diabete et Metabolisme 1987;13(3):210‐6. - PubMed
Muller 1999 {published data only}
-
- Muller UA, Femerling M, Reinauer KM, Risse A, Voss M, Jorgens V, et al. Intensified treatment and education of type 1 diabetes as clinical routine. A nationwide quality‐circle experience in Germany. ASD (the Working Group on Structured Diabetes Therapy of the German Diabetes Association). Diabetes Care 1999;22 Suppl 2:B29‐34. - PubMed
Nathan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Nathan DM, Dunn FL, Bruch J, McKitrick C, Larkin M, Haggan C, et al. Postprandial insulin profiles with implantable pump therapy may explain decreased frequency of severe hypoglycemia, compared with intensive subcutaneous regimens, in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus patients. American Journal of Medicine 1996;100(4):412‐7. - PubMed
Ng 1986 {published data only}
-
- Ng Tang Fui S, Pickup JC, Bending JJ, Collins AC, Keen H, Dalton N. Hypoglycemia and counterregulation in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients: a comparison of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and conventional insulin injection therapy. Diabetes Care 1986;9(3):221‐7. - PubMed
Nijs 1991 {published data only}
-
- Nijs HG, Radder JK, Poorthuis BJ, Krans HM. Glucose disposal and intermediary metabolism during one year of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1991;12(1):1‐9. - PubMed
Olsen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Olsen T, Ehlers N, Nielsen CB, Beck‐Nielsen H. Diabetic retinopathy after one year of improved metabolic control obtained by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). Acta Ophthalmologica 1985;63(3):315‐9. - PubMed
Olsen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Olsen T, Richelsen B, Ehlers N, Beck‐Nielsen H. Diabetic retinopathy after 3 years' treatment with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). Acta Ophthalmologica 1987;65(2):185‐9. - PubMed
Pickup 1979 {published data only}
-
- Pickup JC, Keen H, Parsons JA, Alberti KG. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion:good blood glucose control for up to 4 days. Diabetologia 1979;16(6):385‐9. - PubMed
Pickup 1979a {published data only}
-
- Pickup JC, Keen H, Parsons JA, Alberti KG, Rowe AS. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: improved blood‐glucose and intermediary‐metabolite control in diabetics. Lancet 1979;1(8129):1255‐7. - PubMed
Pickup 1984 {published data only}
-
- Pickup JC, Collins AC, Keen H. Urinary insulin excretion rate: an index of free insulinaemia in insulin‐dependent diabetics. Diabetic Medicine 1984;1(4):291‐4. - PubMed
Pickup 1985 {published data only}
-
- Pickup JC, Sherwin RS, Tamborlane WV, Rizza RA, Service FJ. Conference on insulin pump therapy in diabetes. Multicenter study of effect on microvascular disease. The pump life. Patient responses and clinical and technological problems. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:37‐41. - PubMed
Pickup 1989 {published data only}
-
- Pickup JC, Collins AC, Walker JD, Viberti GC, Pasic J. Patterns of hyperinsulinaemia in type 1 diabetic patients with and without nephropathy. Diabetic Medicine 1989;6(8):685‐91. - PubMed
Pietri 1980 {published data only}
-
- Pietri A, Dunn FL, Raskin P. The effect of improved diabetic control on plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels: a comparison of conventional therapy and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes 1980;29(12):1001‐5. - PubMed
Pietri 1983 {published data only}
-
- Pietri AO, Dunn FL, Grundy SM, Raskin P. The effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on very‐low‐density lipoprotein triglyceride metabolism in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1983;32(1):75‐81. - PubMed
Reeves 1982 {published data only}
-
- Reeves ML, Seigler DE, Ryan EA, Skyler JS. Glycemic control in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Comparison of outpatient intensified conventional therapy with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. American Journal of Medicine 1982;72(4):673‐80. - PubMed
Regal 1988 {published data only}
-
- Regal H, Koivisto VA, Maury CP, Irsigler K. No sign of amyloidosis in pump‐treated diabetics. Diabetes Research 1988;8(4):195‐9. - PubMed
Rizza 1980 {published data only}
-
- Rizza RA, Gerich JE, Haymond MW, Westland RE, Hall LD, Clemens AH, et al. Control of blood sugar in insulin‐dependent diabetes: comparison of an artificial endocrine pancreas, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, and intensified conventional insulin therapy. New England Journal of Medicine 1980;303(23):1313‐8. - PubMed
Rodger 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rodger NW, Dupre J, Canny CLB. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in adults: Glycemic advantage is predicted by venous plasma C‐peptide concentrations. Diabetes Care 1985;8(5):447‐55. - PubMed
Rodger 1988 {published data only}
-
- Rodger NW, Behme MT, Dupre J, Chamberlain MJ. Metabolic effects of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: evidence that a rise and fall of portal vein insulin concentration with each major meal facilitates post‐absorptive glycemic control. Clinical & Investigative Medicine ‐ Medecine Clinique et Experimentale 1988;11(3):167‐86. - PubMed
Saibene 1981 {published data only}
-
- Saibene V, Melandri M, Brembilla L, Spotti D, Pozza G. Comparison between multi‐injection and continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy in insulin‐dependent diabetic inpatients. Acta Diabetologica Latina 1981;18(1):45‐50. - PubMed
Schaepelynck‐Belicar 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schaepelynck‐Belicar P, Vague P, Simonin G, Lassmann‐Vague V. Improved metabolic control in diabetic adolescents using the continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS). Diabetes & Metabolism 2003;29(6):608‐12. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1982 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Belmonte M. Multiple daily self‐glucose monitoring: its essential role in long‐term glucose control in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients treated with pump and multiple subcutaneous injections. Diabetes Care 1982;5(5):479‐84. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1982a {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Belmonte MM. Comparison between continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple injections of insulin. A one‐year prospective study. Diabetes 1982;31(3):255‐64. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1983 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Desrosiers M, Moffatt M, Belmonte MM. Feasibility of strict diabetes control in insulin‐dependent diabetic adolescents. Journal of Pediatrics 1983;103(4):522‐7. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1984 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Parikh S, Marliss EB, Desrosiers MM. Metabolic response to fasting exercise in adolescent insulin‐dependent diabetic subjects treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and intensive conventional therapy. Diabetes Care 1984;7(3):255‐60. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1984a {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin AD, Desrosiers M, Aleyassine H, Belmonte MM. Intensified insulin therapy in the type I diabetic adolescent: a controlled trial. Diabetes Care 1984;7(2):107‐13. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1985 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Parikh S. Accommodating planned exercise in type I diabetic patients on intensive treatment. Diabetes Care 1985;8(4):337‐42. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1987 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin A, Suissa S. Predicting nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82(6):1127‐32. - PubMed
Schmitz 1987 {published data only}
-
- Schmitz O, Sorensen SS, Alberti KG, Orskov H, Hansen HE. Metabolic control in newly kidney transplanted insulin‐dependent diabetics: improvement by insulin pump treatment (CSII). Journal of Diabetic Complications 1987;1(3):81‐6. - PubMed
Schottenfeld‐Naor 1985 {published data only}
-
- Schottenfeld‐Naor Y, Galatzer A, Karp M, Josefsberg Z, Laron Z. Comparison of metabolic and psychological parameters during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and intensified conventional insulin treatment in type I diabetic patients. Israel Journal of Medical Sciences 1985;21(10):822‐8. - PubMed
Scuffham 2003 {published data only}
-
- Scuffham P, Carr L. The cost‐effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion compared with multiple daily injections for the management of diabetes.[see comment]. Diabetic Medicine 2003;20(7):586‐93. - PubMed
Service 1985 {published data only}
-
- Service FJ, Rizza RA, Daube JR, O'Brien PC, Dyck PJ. Near normoglycaemia improved nerve conduction and vibration sensation in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 1985;28(10):722‐7. - PubMed
Siebenhofer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Siebenhofer A, Plank J, Berghold A, Horvath K, Sawicki PT, Beck P, et al. Meta‐analysis of short‐acting insulin analogues in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus injection therapy. Diabetologia 2004;47(11):1895‐905. - PubMed
Simonson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Simonson DC, Tamborlane WV, Sherwin RS, Smith JD, DeFronzo RA. Improved insulin sensitivity in patients with type I diabetes mellitus after CSII. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:80‐6. - PubMed
Skare 1986 {published data only}
-
- Skare S, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Kriz V, Hanssen KF. Plasma somatostatin and plasma glucagon in long‐term IDDM without residual B‐cell function. No effect of different long‐term metabolic control. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1986;46(7):635‐8. - PubMed
Skyler 1982 {published data only}
-
- Skyler JS, Seigler DE, Reeves ML. A comparison of insulin regimens in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1982;5 Suppl 1:11‐8. - PubMed
Sleightholm 1986 {published data only}
-
- Sleightholm MA, Gallimore R, Tennent GA. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion does not provoke significant acute‐phase response. Diabetes Care 1986;9(1):50‐2. - PubMed
Slijper 1990 {published data only}
-
- Slijper FME, Beaufort CE, Bruining GJ, Visser JJ, Aarsen RSR, Kicken DAM, et al. Psychological impact of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy in non‐selected newly diagnosed insulin dependent (type 1) diabetic children: Evaluation after two years of therapy. Diabete et Metabolisme 1990;16(4):273‐7. - PubMed
Steno 1982 {published data only}
-
- Steno. Effect of 6 months of strict metabolic control on eye and kidney function in insulin‐dependent diabetics with background retinopathy. Steno study group. Lancet 1982;1(8264):121‐4. - PubMed
Sulli 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sulli N, Shashaj B. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus: decreased HbA1c with low risk of hypoglycemia. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology 2003;16(3):393‐9. - PubMed
Tamborlane 1979 {published data only}
-
- Tamborlane WV, Sherwin RS, Genel M, Felig P. Reduction to normal of plasma glucose in juvenile diabetes by subcutaneous administration of insulin with a portable infusion pump. New England Journal of Medicine 1979;300(11):573‐8. - PubMed
Tamborlane 1979a {published data only}
-
- Tamborlane WV, Sherwin RS, Genel M, Felig P. Restoration of normal lipid and aminoacid metabolism in diabetic patients treated with a portable insulin‐infusion pump. Lancet 1979;1(8129):1258‐61. - PubMed
Tamborlane 1981 {published data only}
-
- Tamborlane WV, Hintz RL, Bergman M, Genel M, Felig P, Sherwin RS. Insulin‐infusion‐pump treatment of diabetes: influence of improved metabolic control on plasma somatomedin levels. New England Journal of Medicine 1981;305(6):303‐7. - PubMed
Tamborlane 1982 {published data only}
-
- Tamborlane WV, Puklin JE, Bergman M, Verdonk C, Rudolf MC, Felig P, et al. Long‐term improvement of metabolic control with the insulin pump does not reverse diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetes Care 1982;5 Suppl 1:58‐64. - PubMed
Testa 1985 {published data only}
-
- Testa MA, Puklin JE, Sherwin RS, Simonson DC. Clinical predictors of retinopathy and its progression in patients with type I diabetes during CSII or conventional insulin treatment. Diabetes 1985;34 Suppl 3:61‐8. - PubMed
Thuesen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Thuesen L, Christiansen JS, Sorensen KE, Falstie‐Jensen N, Christensen CK, Hermansen K, et al. Exercise capacity and cardiac function in type 1 diabetic patients treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. A controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1986;46(8):779‐84. - PubMed
Tilvis 1986 {published data only}
-
- Tilvis RS, Helve E, Miettinen TA. Improvement of diabetic control by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy changes fatty acid composition of serum lipids and erythrocytes in type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 1986;29(10):690‐4. - PubMed
Toni 2004 {published data only}
-
- Toni S, Reali MF, Fasulo A, Festini P, Medici A, Martinucci ME. The use of insulin pumps improves the metabolic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes.[comment][erratum appears in Arch Dis Child. 2004 Oct;89(10):985 Note: Festini, F [corrected to Festini, P]]. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2004;89(8):796‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Turk 1996 {published data only}
-
- Turk Z, Flego I, Kerum G. Platelet aggregation in type 1 diabetes without microvascular disease during continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Hormone & Metabolic Research 1996;28(2):95‐100. - PubMed
van Ballegooie 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ballegooie E, Jong PE, Donker AJ, Sluiter WJ. The effect of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on renal function in type I diabetic patients with and without proteinuria. Proceedings of the European Dialysis & Transplant Association ‐ European Renal Association 1985;21:722‐4. - PubMed
Viberti 1981 {published data only}
-
- Viberti G, Pickup JC, Bilous RW, Keen H, Mackintosh D. Correction of exercise‐induced microalbuminuria in insulin‐dependent diabetics after 3 weeks of subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes 1981;30(10):818‐23. - PubMed
Viberti 1984 {published data only}
-
- Viberti GC, Home PD, Bilous RW, Alberti KG, Dalton N, Keen H, et al. Metabolic effects of physical exercise in insulin‐dependent diabetics controlled by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or conventional injection therapy. Acta Endocrinologica 1984;105(4):515‐20. - PubMed
Warmolts 1987 {published data only}
-
- Warmolts JR, Mendell JR, O'Dorisio TM, Cataland S. Comparison of the effects of continuous subcutaneous infusion and split‐mixed injection of insulin on nerve function in type I diabetes mellitus. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1987;82(1‐3):161‐9. - PubMed
Weinzimer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Weinzimer SA, Ahern JH, Doyle EA, Vincent MR, Dziura J, Steffen AT, et al. Persistence of benefits of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in very young children with type 1 diabetes: a follow‐up report. Pediatrics 2004;114(6):1601‐5. - PubMed
Willi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Willi SM, Planton J, Egede L, Schwarz S. Benefits of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in children with type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;143(6):796‐801. - PubMed
Wilson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wilson DM, Buckingham BA, Kunselman EL, Sullivan MM, Paguntalan HU, Gitelman SE. A two‐center randomized controlled feasibility trial of insulin pump therapy in young children with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28(1):15‐9. - PubMed
Wredling 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wredling R, Hannerz L, Johansson U. Variability of blood glucose levels in patients treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: a pilot study. Practical Diabetes International 1997;14(1):5‐8.
Yki‐Jarvinen 1984 {published data only}
-
- Yki‐Jarvinen H, Koivisto VA. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy decreases insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1984;58(4):659‐66. - PubMed
Ziegler 1988 {published data only}
-
- Ziegler D, Wiefels K, Dannehl K, Gries FA. Effects of one year of near‐normoglycemia on peripheral nerve function in type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients. Klinische Wochenschrift 1988;66(9):388‐96. - PubMed
Additional references
ADA 1997
-
- American Diabetes Association. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 1997;20(7):1183‐97. - PubMed
APEG 2004
-
- Australian Paediatric Endocrine Group. Clinical Practise Guidelines: Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents. www.chw.edu.au/prof/services/endocrinology/apeg www.chw.edu.au/prof/services/endocrinology/apeg http://www.chw.edu.au/prof/services/endocrinology/apeg/ 2004.
Couper 2002
-
- Couper JJ. Children with type 1 diabetes: where are we at?. The Medical Journal of Australia 2002;177(5):228‐9. - PubMed
Dabelea 2009
-
- Dabelea D. The accelerating epidemic of childhood diabetes. The Lancet 2009;373(9680):1999‐2000. - PubMed
DPT 2002
-
- Diabetes Prevention Trial‐Type 1 Diabetes Study Group. Effects of insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;346(22):1685‐91. - PubMed
ENDIT 2003
-
- The European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT) Group. Intervening before the onset of Type 1 diabetes: baseline data from the European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT). Diabetologia 2003;46(3):339‐46. - PubMed
Guinn 1988
-
- Guinn TS, Bailey GJ, Mecklenberg RS. Factors related to discontinuation of continuous subcutaneous insulin‐infusion therapy. Diabetes Care 1988;11(1):46‐51. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. WileyBlackwell, 2008.
HTA 2004
-
- Colquitt JL, Green C, Sidhu MK, Hartwell D, Waugh N. Clinical and cost‐effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes. Health Technology Assessment 2004; Vol. 8, issue number 43. - PubMed
Karvonen 2000
-
- Karvonen M, Viik‐Kajander M, Moltchanova E, Libman I, LaPorte R, Tuomilehto J. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide. Diabetes Mondiale (DiaMond) Project Group. Diabetes Care 2000;23(10):1516‐26. - PubMed
Liberati 2009
NDDG 1979
-
- National Diabetes Data Group. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 1979;28(12):1039‐57. - PubMed
NICE 2008
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. London (UK): National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE); Technology appraisal guidance no. 151 2008 July.
Pickup 1980a
-
- Pickup JC. A new approach to improved metabolic control in diabetics: Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. American Heart Journal 1980;100(4):417‐20. - PubMed
Pickup 2002
Sterne 2001
Sutton 1990
-
- Sutton L, Plant AJ, Lyle DM. Services and cost of hospitalization for children and adolescents with insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus in New South Wales. The Medical Journal of Australia 1990;152(3):130‐6. - PubMed
WHO 1980
-
- World Health Organisation. WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus: second report. World Health Organization Technical Report Series 1980;646:1‐80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

