Golimumab for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20091667
- PMCID: PMC10732339
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008341
Golimumab for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Golimumab is a humanized inhibitor of Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objectives: The objective of this systematic review was to compare the efficacy and safety of golimumab (alone or in combination with DMARDs or biologics) to placebo (alone or in combination with DMARDs or biologics) in randomized or quasi-randomized clinical trials in adults with RA.
Search strategy: An expert librarian searched six databases for any clinical trials of golimumab in RA, including the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), OVID MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE, Science Citation Index (Web of Science) and Current Controlled Trials databases.
Selection criteria: Studies were included if they used golimumab in adults with RA, were randomized or quasi-randomized and provided clinical outcomes.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors (JS, SN) independently reviewed all titles and abstracts, selected appropriate studies for full review and reviewed the full-text articles for the final selection of included studies. For each study, they independently abstracted study characteristics, safety and efficacy data and performed risk of bias assessment. Disagreements were resolved by consensus. For continuous measures, we calculated mean differences or standardized mean differences and for categorical measures, relative risks. 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
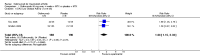
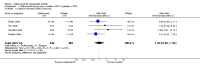
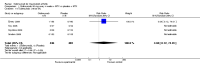
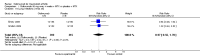
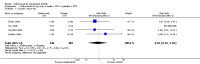
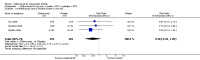
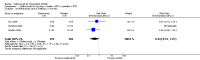
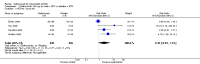
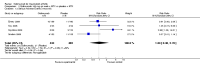
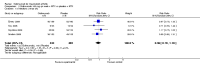
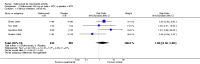
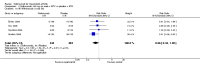
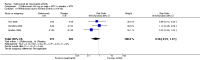
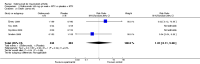
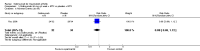
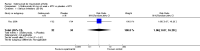
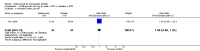
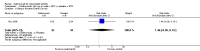
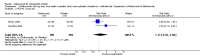
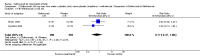
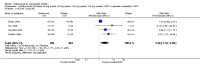
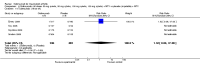
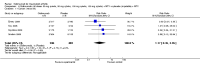
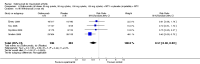
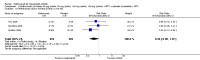
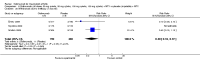
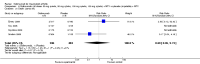
Main results: Four RCTs with 1,231 patients treated with golimumab and 483 patients treated with placebo were included. Of these, 436 were treated with the FDA-approved dose of golimumab 50 mg every four weeks. Compared to patients treated with placebo+methotrexate, patients treated with the FDA-approved dose of golimumab+methotrexate were 2.6 times more likely to reach ACR50 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3 to 4.9; P=0.005 and NNT= 5, 95% confidence interval 2 to 20), no more likely to have any adverse event (relative risk 1.1, 95% Cl 0.9 to 1.2; P=0.44), and 0.5 times as likely to have overall withdrawals (95% Cl 0.3 to 0.8; P=0.005). Golimumab-treated patients were significantly more likely to achieve remission, low disease activity and improvement in functional ability compared to placebo (all statistically significant). No significant differences were noted between golimumab and placebo regarding serious adverse events, infections, serious infections, lung infections, tuberculosis, cancer, withdrawals due to adverse events and inefficacy and deaths. No radiographic data were reported.
Authors' conclusions: With an overall high grade of evidence, at the FDA-approved dose, golimumab is significantly more efficacious than placebo in treatment of patients with active RA , when used in combination with methotrexate. The short-term safety profile, based on short-term RCTs, is reasonable with no differences in total adverse events, serious infections, cancer, tuberculosis or deaths. Long-term surveillance studies are needed for safety assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
JS‐ Speaker honoraria from Abbott; research and travel grants from Takeda, Savient, Wyeth and Amgen; consultant fees from Savient and URL pharmaceuticals
SN‐ None
GS‐ Honoraria/consultant/research grants from Centocor, Abbott, AMGEN, Johnson and Johnson
Figures

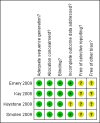
























































































References
References to studies included in this review
Emery 2009 {published data only}
-
- Emery P, Fleischmann RM, Moreland LW, Hsia EC, Strusberg I, Durez P, et al. Golimumab, a human anti‐tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, injected subcutaneously every four weeks in methotrexate‐naive patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Twenty‐four‐week results of a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of golimumab before methotrexate as first‐line therapy for early‐onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60(8):2272‐83. - PubMed
Kay 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kay J, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B, Nash P, Durez P, Hall S, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐ranging study. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:964‐75. - PubMed
Keystone 2009 {published data only}
-
- Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Klareskog L, Hsia EC, Hall ST, Miranda PC, et al. Golimumab, a human antibody to tumour necrosis factor {alpha} given by monthly subcutaneous injections, in active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy: the GO‐FORWARD Study. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:789‐96. - PMC - PubMed
Smolen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Smolen JS, Kay J, Doyle MK, Landewe R, Matteson EL, Wollenhaupt J, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (GO‐AFTER study): a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase III trial. Lancet 2009;374(9685):210‐21. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
O'Connell 2008 {published data only}
-
- O'Connell N. New data shows golimumab significantly improves signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Geriatric Medicine 2008;38:374‐375.
Oldfield 2009 {published data only}
-
- Oldfield V, Plosker GL. Golimumab: in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Bio Drugs 2009;23:125‐35. - PubMed
Additional references
Arnett 1988
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31:315‐24. - PubMed
Barlow 1999
-
- Barlow JH, Cullen LA, Rowe IF. Comparison of knowledge and psychological well‐being between patients with a short disease duration (< or = 1 year) and patients with more established rheumatoid arthritis (> or = 10 years duration). Patient Educ Couns 1999;38(3):195‐203. - PubMed
Bhandari 2004
Blumenauer 2002
Boers 2001
-
- Boers M. Rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment of early disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2001;27(2):405‐14. - PubMed
Brennan 2008
Choy 2001
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2001;344(12):907‐16. - PubMed
Choy 2005
-
- Choy EHS, Smith C, Dore CJ, Scott DL. A meta‐analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of combining disease‐modifying anti‐rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis based on patient withdrawal. Rheumatology 2005;44(11):1414‐21. - PubMed
Chung 2006
-
- Chung CP, Thompson JL, Koch GG, Amara I, Strand V, Pincus T. Are American College of Rheumatology 50% response criteria superior to 20% criteria in distinguishing active aggressive treatment in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials reported since 1997? A meta‐analysis of discriminant capacities. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65(12):1602‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Connell 2006
-
- Connell L, McInnes IB. New cytokine targets in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2006;20(5):865‐78. - PubMed
Deeks 2008
-
- Deeks J, Higgins J, Altman D. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses, Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.0 (updated February 2008). The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from: www.cochrane‐handbook.org. 2008.
FDA 2009a
-
- FDA. SIMPONI® (Golimumab) Physician Packet Insert: Highlights of Prescribing Information. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatdfa_docs/label/2009/125289s000lbl.pdf 2009.
FDA 2009b
-
- FDA. SIMPONI® (Golimumab) Summary Review. FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatdfa_docs/nda/2009/125289s000_SumR.pdf April 4, 2009 (accessed September 20, 2009).
FDA 2009c
-
- FDA. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Blockers (marketed as Remicade, Enbrel, Humira, Cimzia, and Simponi) August 2009. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHuma... August 31, 2009.
Felson 1995
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, et al. American college of rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1995;38(6):727‐35. - PubMed
Fransen 2005
-
- Fransen J, Riel PLCM. The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2005;23(S39):S93‐9. - PubMed
Fries 1980
-
- Fries JF, Spitz PW, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1980;23:137‐45. - PubMed
Gomez‐Reino 2006
Harris 1990
-
- Harris E.D. Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 1990;322(18):1277‐89. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. . In: Higgins JP, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.0 [updated February 2008]. www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Karlsson 2008
-
- Karlsson JA, Kristensen LE, Kapetanovic MC, Gulfe A, Saxne T, Geborek P. Treatment response to a second or third TNF‐inhibitor in RA: results from the South Swedish Arthritis Treatment Group Register. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47(4):507‐13. - PubMed
Kvien 2005
-
- Kvien TK, Uhlig T. Quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 2005;34(5):333‐41. - PubMed
Larsen 1977
-
- Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiologic Diagnosis (Stockholm) 1977;18(4):481–91. - PubMed
Lethaby 2003
Lopez‐Olivo 2008
Lubeck 2004
-
- Lubeck DP. Patient‐reported outcomes and their role in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):27‐38. - PubMed
Maxwell 2008
Mertens 2009
Navarro‐Sarabia 2005
Odegard 2005
-
- Odegard S, Finset A, Kvien Tk, Mowinckel P, Uhlig T. Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis is predicted by physical and psychological health status: a 7‐year study from the Oslo RA register.. Scand J Rheumatol 2005;34(6):441‐7. - PubMed
Pappas 2009
-
- Pappas DA, Bathon JM, Hanicq D, Yasothan U, Kirkpatrick P. Golimumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009;8:695‐696. - PubMed
Pincus 1983
-
- Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA, Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1983;26:1346‐53. - PubMed
Prevoo 1995
-
- Prevoo MLL, Van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, Leeuwen MA, Putte LBA, Riel PLCM. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty‐eight‐joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1995;38:44‐8. - PubMed
Scott 2006
-
- Scott DL, Kingsley GH. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2006;355(7):704‐12. - PubMed
Scott 2009
-
- Scott DL, Cope A. New tumour necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis: are there benefits from extending choice?. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:767‐769. - PubMed
Sharp 1971
-
- Sharp JT, Lidsky MD, Collins LC, Moreland J. Methods of scoring the progression of radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of radiologic, clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1971;14(6):706–20. - PubMed
Siddiqui 2007
-
- Siddiqui MA. The efficacy and tolerability of newer biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: best current evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2007;19(3):308‐13. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1989
-
- Heijde DMFM, Riel PL, Nuver‐Zwart IH, Gribnau FW, Puttte LB. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989;1:1036‐8. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1993
-
- Heijde DM, 't Hof M, Riel PL, Putte LB. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20(3):579‐81. - PubMed
van Gestel 1996
-
- Gestel A, Riel P. American College of Rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis: comment on the article by Felson et al. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39(3):535‐7. - PubMed
Weissmann 2006
-
- Weissmann G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2006;64(1‐2):12‐5. - PubMed
Wells 1993
-
- Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, Baker PR, Groh J, Redelmeier DA. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20:557. - PubMed
Yazici 2009
-
- Yazici Y. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: we are getting there. Lancet 2009;374:178‐180. - PubMed
Yelin 2007
-
- Yelin E. Work disability in rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2007;19(2):91‐6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

