Self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles: from molecules to nanostructures to biomaterials
- PMID: 20091874
- PMCID: PMC2921868
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.21328
Self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles: from molecules to nanostructures to biomaterials
Abstract
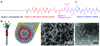
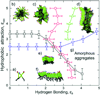
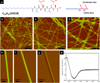
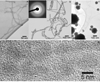
Peptide amphiphiles are a class of molecules that combine the structural features of amphiphilic surfactants with the functions of bioactive peptides and are known to assemble into a variety of nanostructures. A specific type of peptide amphiphiles are known to self-assemble into one-dimensional nanostructures under physiological conditions, predominantly nanofibers with a cylindrical geometry. The resultant nanostructures could be highly bioactive and are of great interest in many biomedical applications, including tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and drug delivery. In this context, we highlight our strategies for using molecular self-assembly as a toolbox to produce peptide amphiphile nanostructures and materials and efforts to translate this technology into applications as therapeutics. We also review our recent progress in using these materials for treating spinal cord injury, inducing angiogenesis, and for hard tissue regeneration and replacement.
(c) 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Self-Assembly of Short Amphiphilic Peptides and Their Biomedical Applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(44):3546-3562. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221124103526. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 36424793 Review.
-
Design of nanostructures based on aromatic peptide amphiphiles.Chem Soc Rev. 2014 Dec 7;43(23):8150-77. doi: 10.1039/c4cs00247d. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Chem Soc Rev. 2014. PMID: 25199102 Review.
-
T-shaped Peptide Amphiphiles Self Assemble into Nanofiber Networks.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017;5(3):215-219. doi: 10.2174/2211738505666170828095937. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28847269
-
Supramolecular Assembly of Peptide Amphiphiles.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Oct 17;50(10):2440-2448. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00297. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28876055 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled peptide amphiphile nanofibers conjugated to MRI contrast agents.Nano Lett. 2005 Jan;5(1):1-4. doi: 10.1021/nl0484898. Nano Lett. 2005. PMID: 15792402
Cited by
-
Bioactive nanofibers enable the identification of thrombospondin 2 as a key player in enamel regeneration.Biomaterials. 2015 Aug;61:216-28. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.05.035. Epub 2015 May 19. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26004236 Free PMC article.
-
Elastin-like peptide amphiphiles form nanofibers with tunable length.Biomacromolecules. 2012 Sep 10;13(9):2645-54. doi: 10.1021/bm300472y. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Biomacromolecules. 2012. PMID: 22849577 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of chirality and sequence in lysine-rich lipopeptide biosurfactants and micellar model colloid systems.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 8;15(1):6785. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51234-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39117639 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide-Protein Interactions: From Drug Design to Supramolecular Biomaterials.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1219. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051219. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Vaccines, Adjuvants, and Delivery Systems.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 30;12:627932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627932. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33859638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Palmer LC, Velichko YS, de la Cruz MO, Stupp SI. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences. 2007;365:1417–1433. - PubMed
-
- Stupp SI, Pralle MU, Tew GN, Li LM, Sayar M, Zubarev ER. Mrs Bulletin. 2000;25:42–48.
-
- Service RF. Science. 2005;309:95–95. - PubMed
-
- Hartgerink JD, Zubarev ER, Stupp SI. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science. 2001;5:355–361.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

