Protein- and peptide-modified synthetic polymeric biomaterials
- PMID: 20091878
- PMCID: PMC4437713
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.21333
Protein- and peptide-modified synthetic polymeric biomaterials
Abstract
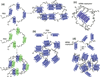
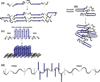
This review presents an overview on bio-hybrid approaches of integrating the structural and functional features of proteins and peptides with synthetic polymers and the resulting unique properties in such hybrids, with a focus on bioresponsive/bioactive systems with biomaterials applications. The review is divided in two broad sections. First, we describe several examples of bio-hybrids produced by combining versatile synthetic polymers with proteins/enzymes and drugs that have resulted in (1) hybrid materials based on responsive polymers, (2) responsive hydrogels based on enzyme-catalyzed reactions, protein-protein interactions and protein-drug sensing, and (3) dynamic hydrogels based on conformational changes of a protein. Next, we present hybrids produced by combining synthetic polymers with peptides, classified based on the properties of the peptide domain: (1) peptides with different conformations, such as alpha-helical, coiled-coil, and beta-sheet; (2) peptides derived from structural protein domains such as silk, elastin, titin, and collagen; and (3) peptides with other biofunctional properties such as cell-binding domains and enzyme-recognized degradation domains.
(c) 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


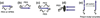
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

