Introducing change (science into the operating room): quality improvement versus experimentation
- PMID: 20092081
- PMCID: PMC4813529
Introducing change (science into the operating room): quality improvement versus experimentation
Abstract
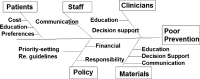
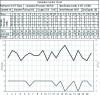
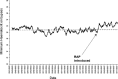
Introducing change is sometimes vital on an individual, departmental, and institutional level to improve the quality of care of patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. This review discussed the following areas: cost of poor quality, variation, knowledge, Deming's red bead experiments and his conclusions, how do you try to improve, measurement, statistics, and quality improvement verses research. Successes and failures with regard to the introduction of change, and strategies to introduce change without creating conflict are discussed with reference to the hospital in which the author works.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Implementing change in perfusion practice: quality improvement vs. experimentation?J Extra Corpor Technol. 2009 Dec;41(4):P16-20. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2009. PMID: 20092082 Free PMC article.
-
Translational research in the radiologic sciences.Radiol Technol. 2014 Jan-Feb;85(3):327-9. Radiol Technol. 2014. PMID: 24395899 No abstract available.
-
Deming's quality principles: a health care application.Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1991 Spring;36(1):111-20. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1991. PMID: 10108969
-
Surgery and Research: A Practical Approach to Managing the Research Process.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Jan;137(1):361-366. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001888. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016. PMID: 26710037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blueprint for a new American College of Surgeons: National Surgical Quality Improvement Program.J Am Coll Surg. 2008 Nov;207(5):777-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2008.07.018. Epub 2008 Sep 19. J Am Coll Surg. 2008. PMID: 18954793 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moen R, Nolan TW, Provost LP.. Quality Improvement through Planned Experimentation. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1998.
-
- Neus A, Scherf P.. Opening minds: Cultural change with the introduction of open-source collaboration methods. IBM Syst J. 2005;44:215–25.
-
- Thornton AC.. Variation Risk Management: Focusing Quality Improvements in Product Development and Production. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2003.
-
- Michael Arthur Johnson Company, California: RED BEAD Experiment. Available at: www.redbead.com. Accessed July 24, 2009.
-
- Deming WE.. Out of the Crisis, 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2000.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
